Abstract
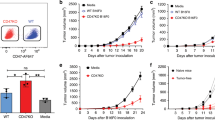
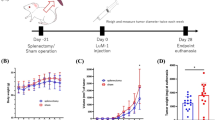
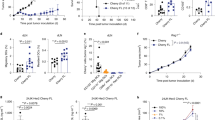
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) is a novel cytokine that can induce proliferation of activated T cells and maturation of natural killer (NK) cells. We therefore examined whether expression of the IL-21 gene in tumor cells could generate antitumor responses. Murine colon carcinoma Colon 26 cells that were transduced with the mouse IL-21 gene (Colon 26/IL-21) were rejected in syngeneic mice and the mice subsequently acquired protective immunity. The growth of Colon 26/IL-21 tumors developed in nude mice was retarded compared with that of parent tumors, and this growth suppression was not observed in nude mice that were treated with anti-asialo GM1 antibody. Spleen cells from the mice that had rejected Colon 26/IL-21 cells showed cytotoxic activity to Colon 26 but not to irrelevant tumor cells, and produced larger amounts of interferon-γ upon stimulation with irradiated Colon 26 cells. Spleen cells from Colon 26/IL-21-tumor- but not parent-tumor-bearing mice had lytic activity to YAC-1 cells. These data suggest that expression of IL-21 in tumors induces T- and NK-cell-dependent antitumor effects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tagawa M . Cytokine therapy for cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2000;6:681–699.
Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A . Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;283:787–793.
Parrish-Novok J, Dillon SR, Nelson A, et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature. 2000;408:57–63.
Ozaki K, Kikly K, Michalovich D, et al. Cloning of a type I cytokine receptor most related to the IL-2 receptor β chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:11439–11444.
Kasaian MT, Whitters MJ, Carter LL, et al. IL-21 limits NK cell responses and promotes antigen-specific T cell activation: a mediator of the transition from innate to adaptive immunity. Immunity. 2002;16:559–569.
Corbett TH, Griswold Jr DP, Roberts BJ, et al. Tumor induction relationships in development of transplantable cancers of the colon in mice for chemotherapy assays, with a note on carcinogen structure. Cancer Res. 1975;35:2434–2439.
Ebina T, Murata K . Antitumor effect of PSK at a distant site: tumor-specific immunity and combination with other chemotherapeutic agents. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992;83:775–782.
Miller AD, Rosman GJ . Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. BioTechniques. 1989;7:980–990.
Farrell HE, Vally H, Lynch DM, et al. Inhibition of natural killer cells by a cytomegalovirus MHC class I homologue in vivo. Nature. 1997;386:510–514.
Yoshida Y, Tasaki K, Miyauchi M, et al. Impaired tumorigenicity of human pancreatic cancer cells retrovirally transduced with interleukin-12 or interleukin-15 gene. Cancer Gene Ther. 2000;7:324–331.
Voßhenrich CAJ, Di Santo JP . Cytokines: IL-21 joins the γc-dependent network? Curr Biol. 2001;11:R175–R177.
Asao H, Okuyama C, Kumaki S, et al. Cutting edge: the common γ-chain is an indispensable subunit of the IL-21 receptor complex. J Immunol. 2001;167:1–5.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) and the Uehara Memorial Foundation. Y-Q Wang was supported by a JSPS fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ugai, Si., Shimozato, O., Kawamura, K. et al. Expression of the interleukin-21 gene in murine colon carcinoma cells generates systemic immunity in the inoculated hosts. Cancer Gene Ther 10, 187–192 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700552
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700552
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Engineered murine IL-21-secreting leukemia cells induce granzyme B+ T cells and CD4+CD44+CD62L− effector memory cells while suppressing regulatory T cells, leading to long-term survival
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2023)
-
Bioengineered Colorectal Cancer Drugs: Orally Delivered Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2015)
-
IL-21 gene polymorphism is associated with the prognosis of breast cancer in Chinese populations
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2013)
-
Immune activation in advanced cancer patients treated with recombinant IL-21: multianalyte profiling of serum proteins
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2009)
-
Interleukin 21: combination strategies for cancer therapy
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2008)