Abstract
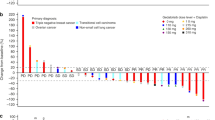
The therapeutic efficacy of gemcitabine, a new nucleoside analogue, was assessed in a variety of well-established human soft tissue sarcoma and ovarian cancer xenografts grown s.c. in nude mice. Tumour lines selected had different histological subtypes, growth rates and sensitivities to conventional cytostatic agents. The three different doses and schedules designed on the basis of a mean weight loss between 5% and 15% were i.p. injections of daily 3.5 mg kg-1 x 4, every 3 days 120 mg kg-1 x 4, and weekly 240 mg kg-1 x 2, which ultimately resulted in 19%, 10% and 4% toxic deaths, respectively. The weekly schedule induced > or = 50% growth inhibition in 2/4 soft tissue sarcoma and 4/6 ovarian cancer lines, while in three ovarian cancer lines > or = 75% growth inhibition was obtained. The anti-tumour effects of gemcitabine appeared to be similar or even better than previous data with conventional drugs tested in the same tumour lines. In comparison with the every 3 days schedule, the weekly and the daily schedule were less effective in 5/7 and 3/3 tumour lines (P < 0.001), respectively. In another experiment in three human tumour lines selected for their differential sensitivity to gemcitabine, weekly injections of 240 mg kg-1 x 6 did not result in a significant increase in the percentages of growth inhibition when compared to lower doses of 120 mg kg-1 or 60 mg kg-1 in the same schedule. However, the 240 mg kg-1 weekly x 6 schedule showed superior effects in 2/3 tumour lines in comparison with the same dose given every 2 weeks x 3 (P < 0.05). The preclinical activity of gemcitabine suggests that the drug can induce responses in soft tissue sarcoma and ovarian cancer patients. Our results further indicate that clinical trials of gemcitabine in solid tumour types should be designed on the basis of a schedule rather than a dose dependence.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boven, E., Schipper, H., Erkelens, C. et al. The influence of the schedule and the dose of gemcitabine on the anti-tumour efficacy in experimental human cancer. Br J Cancer 68, 52–56 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1993.285
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1993.285
This article is cited by
-
Evaluation of low-dose fractionated radiation therapy as a chemopotentiator of gemcitabine in advanced pancreatic cancer: results from an international multi-institutional phase II trial
Journal of Radiation Oncology (2015)
-
Metronomic gemcitabine suppresses tumour growth, improves perfusion, and reduces hypoxia in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
British Journal of Cancer (2010)
-
Gemcitabine based combination regimens for treatment of refractory advanced breast cancer
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research (2008)
-
A phase I study of bi-weekly administration of 24-h gemcitabine followed by 24-h irinotecan in patients with solid tumors
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2007)
-
Adjuvant gemcitabine and concurrent radiation for patients with resected pancreatic cancer: a phase II study
British Journal of Cancer (2006)