Abstract
Background/Objectives
To measure the endothelial cell density (ECD) of the in toto pre-stripped endothelial Descemet membrane lamellae (EDML) and to describe the impact of pre- and intraoperative endothelial cell loss (ECL) on postoperative midterm clinical outcome.
Subjects/Methods
The ECD of 56 Corneoscleral Donor Discs (CDD) was first measured with an inverted specular microscope (t0pre). The measurement was then repeated non-invasively after the preparation of the EDML (t0post). DMEK was performed the next day using these grafts. Follow-up examinations took place 6 weeks, 6 months and 1 year postoperatively where the ECD was assessed. In addition, the impact of ECL 1 (during preparation) and ECL 2 (during surgery) on the ECD, visual acuity (VA) and pachymetry at 6 months and 1 year was investigated.
Results
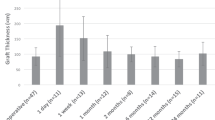
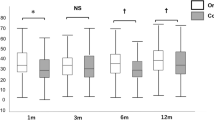
The average ECD (in cells/mm²) at time points t0pre, t0post, 6 weeks, 6 months & 1 year was 2584 ± 200, 2355 ± 207, 1366 ± 345, 1091 ± 564 and 939 ± 352. The average logMAR VA and pachymetry (in µm) was 0.50 ± 0.27 and 597 ± 63, 0.23 ± 0.17 and 535 ± 54, 0.16 ± 0.12 and 535 ± 54, 0.06 ± 0.08 and 512 ± 37, respectively The ECL 1 (9% on average) had no significant impact on the main outcome measures after 6 months and 1 year (p > 0.11). The ECL 2 correlated significantly with the ECD and the pachymetry at 1 year postop (p < 0.02).
Conclusion
Our results indicate that the non-invasive ECD measurement of the prestripped EDML roll before its transplantation is feasible. Despite significantly decreasing ECD up to 6 months postoperatively, visual acuity further improved and thickness further decreased up to 1 year postoperatively.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 18 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $14.39 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Melles GRJ, Ong TS, Ververs B, van der Wees J. Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK). Cornea. 2006;25:987–90.
Borgardts KC, Spaniol K, Bachmann B, Hellmich M, Geerling G, Maier P, et al. Outcomes after descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) in a German multicenter study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60:2224.
Flockerzi E, Maier P, Böhringer D, Reinshagen H. Trends in corneal transplantation from 2001 to 2016 in Germany: a report of the DOG-section cornea and its keratoplasty registry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2018;188:91–8.
Basak SK, Basak S, Pradhan VR. Outcomes of descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) using Surgeon’s prepared donor DM-Roll in consecutive 100 Indian eyes. Open Ophthalmol. 2018;12:134–42.
Birbal RS, Dhubhghaill SN, Bourgonje VJA, Hanko J, Ham L, Jager MJ, et al. Five-year graft survival and clinical outcomes of 500 consecutive cases after descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. Cornea. 2020;39:290–7.
Vasiliauskaite I, Oellerich S, Ham L, Dapena I, Baydoun L, van Dijk K, et al. Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty: ten-year graft survival and clinical outcomes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2020;217:114–20.
Parekh M, Ruzza A, Romano V, Favaro E, Baruzzo M, Salvalaio G, et al. Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty learning curve for graft preparation in an eye bank using 645 donor corneas. Cornea. 2018;37:767–71.
Altaan SL, Gupta A, Sidney LE, Elalfy MS, Agarwal A, Dua HS. Endothelial cell loss following tissue harvesting by pneumodissection for endothelial keratoplasty: an ex vivo study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015;99:710–3.
Jardine GJ, Holiman JD, Stoeger CG, Chamberlain WD. Imaging and quantification of endothelial cell loss in eye bank prepared DMEK grafts using trainable segmentation software. Curr Eye Res. 2014;39:894–901.
Schallhorn JM, Holiman JD, Stoeger CG, Chamberlain W. Quantification and patterns of endothelial cell loss due to eye bank preparation and injector method in descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty tissues. Cornea. 2016;35:377–82.
Tran KD, Dye PK, Odell K, Galloway J, Stoeger CG, Straiko MD, et al. Evaluation and quality assessment of prestripped, preloaded descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty grafts. Cornea. 2017;36:484–90.
Mayko ZM, Benetz BA, Menegay H, Donovan CP, Stoeger CG, Terry MA, et al. Donor endothelial cell density measurements do not change immediately after DMEK preparation. Cornea. 2016;35:1556–61.
Menzel-Severing J, Walter P, Plum WJ, Kruse FE, Salla S. Assessment of corneal endothelium during continued organ culture of pre-stripped human donor tissue for DMEK surgery. Curr Eye Res. 2018;43:1439–44.
Muraine M, Gueudry J, He Z, Piselli S, Lefevre S, Toubeau D. Novel technique for the preparation of corneal grafts for descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013;156:851–9.
Safi T, Seitz B, Berg K, Schulz K, Langenbucher A, Daas L. Reproducibility of non-invasive endothelial cell loss assessment of the pre-stripped DMEK roll after preparation and storage. Am J Ophthalmol. 2020;221:17–26.
Seitz B, Daas L, Flockerzi E, Suffo S. Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty DMEK - Donor and recipient step by step. Ophthalmologe. 2020;117:811–28.
Seitz B, Daas L, Bischoff-Jung M, Szentmáry N, Suffo S, El-Husseiny M, et al. Anatomy-based DMEK Wetlab in Homburg/Saar: Novel aspects of donor preparation and host maneuvers to teach descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. Clin Anat. 2017;31:16–27.
Bachmann BO, Laaser K, Cursiefen C, Kruse FE. A method to confirm correct orientation of descemet membrane during descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010;149:922–925.e2.
Birbal RS, Sikder S, Lie JT, Groeneveld-van Beek EA, Oellerich S, Melles GRJ. Donor tissue preparation for descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty: an updated review. Cornea. 2018;37:128–35.
Basak SK, Basak S, Gajendragadkar N, Ghatak M. Overall clinical outcomes of Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty in 600 consecutive eyes: a large retrospective case series. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:1044–53.
Pipparelli A, Thuret G, Toubeau D, He Z, Piselli S, Lefèvre S, et al. Pan-corneal endothelial viability assessment: application to endothelial grafts predissected by eye banks. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:6018–25.
Rickmann A, Boden KE, Wahl S, Jung S, Boden KT, Szurman P, et al. Significant differences between specular microscopy and corneal bank endothelial cell counts - a pilot study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019;97:e1077–e1081.
Inoda S, Hayashi T, Takahashi H, Oyakawa I, Yokogawa H, Kobayashi A, et al. Factors associated with endothelial cell density loss post Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty for bullous keratopathy in Asia. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0234202.
Miron A, Spinozzi D, Bruinsma M, Lie JT, Birbal RS, Baydoun L, et al. Asymmetrical endothelial cell migration from in vitro Quarter-Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty grafts. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018;96:828–33.
Böhm MS, Wylegala A, Leon P, Tone SO, Ciolino JB, Jurkunas UV. One-year clinical outcomes of preloaded descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty versus non- preloaded descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. Cornea. 2021;40:311–9.
Jirsová K. Light and specular microscopy of the cornea. Springer. 2017;4:59–74. 5:75-99
Krabcova I, Studeny P, Jirsova K. Endothelial cell density before and after the preparation of corneal lamellae for Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty with a stromal rim. Cornea. 2011;30:1436–41.
Downes K, Tran KD, Stoeger CG, Chamberlain W. Cumulative endothelial cell loss in descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty grafts from preparation through insertion with glass injectors. Cornea. 2018;37:698–704.
Hammer T, Sennewald J, Viestenz A, editors. DMEK optimiert – aktuelle Aspekte und klinische Resultate. Düsseldorf: German Medical Science GMS Publishing House, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3205/19sag25
Jbara D, Achiron A, Antman G, Buhbut O, Hecht I, Tuuminen R, et al. Agreement of corneal endothelial cell analysis between Konan-Noncon Robo SP-6000 and Tomey EM-3000 specular microscopes in healthy subjects. Eye Contact Lens. 2020;47:191–5.
Huang J, Maram J, Tepelus TC, Modak C, Marion K, Sadda SVR, et al. Comparison of manual & automated analysis methods for corneal endothelial cell density measurements by specular microscopy. J Optom. 2017;11:182–91.
Aljundi W, Abdin A, Suffo S, Seitz B, Daas L. Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) in previously vitrectomized eyes: complications and clinical outcomes. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2021;238:1101–7.
Kwon RO, Price MO, Price FW, Ambrósio R Jr, Belin MW. Pentacam characterization of corneas with Fuchs dystrophy treated with Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. J Refract Surg. 2010;26:972–9.
Peraza-Nieves J, Baydoun L, Dapena I, Ilyas A, Frank LE, Luceri S, et al. Two-year clinical outcome of 500 consecutive cases undergoing descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. Cornea. 2017;36:655–60.
Brockmann T, Pilger D, Brockmann C, Maier AKB, Bertelmann E, Torun N. Predictive factors for clinical outcomes after primary descemet’s membrane endothelial keratoplasty for Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy. Curr Eye Res. 2019;44:147–53.
Chamberlain W, Lin C, Austin A, Schubach N, Clover J, McLeod S, Porco T, Lietman T, Rose-Nussbaumer J. Descemet Endothelial Thickness Comparison Trial: A Randomized Trial Comparing Ultrathin Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty with Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Ophthalmology, 2019;126:19–26.
Hayashi T, Schrittenlocher S, Siebelmann S, Hung Le VN, Matthaei M, Franklin J, et al. Risk factors for endothelial cell loss after Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK). Sci Rep. 2020;10:11086.
Shahnazaryan D, Sese AH, Hollick EJ. Endothelial cell loss after descemet’s membrane endothelial keratoplasty for Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy: DMEK compared to triple DMEK. Am J Ophthalmol. 2020;218:1–6.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Klaus Faber Center for Corneal Diseases, LIONS Eye Bank Saar-Lor-Lux, Trier/Westpfalz for their help in preserving and measuring the donor corneas.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KB was responsible for writing the manuscript, conducting the search, screening potentially eligible studies, extracting and analysing data, interpreting results and updating reference lists. TS was responsible for the preclinical trial (published earlier), research and feedback. BS and LD provided their professional support and feedback to the corresponding author.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Berg, K., Safi, T., Seitz, B. et al. Non-invasive endothelial cell density measurement of in toto pre-stripped DMEK-roll – impact of pre- and intraoperative endothelial cell loss on postoperative midterm clinical outcome. Eye 37, 2956–2962 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-023-02450-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-023-02450-x