Abstract
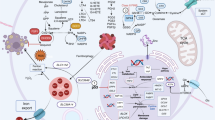
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a prevalent form of gastrointestinal malignancy with challenges in chemotherapy resistance and side effects. Effective and low toxic drugs for CRC treatment are urgently needed. Ferroptosis is a novel mode of cell death, which has garnered attention for its therapeutic potential against cancer. Baicalein (5, 6, 7-trihydroxyflavone) is the primary flavone extracted from the dried roots of Scutellaria baicalensis that exhibits anticancer effects against several malignancies including CRC. In this study, we investigated whether baicalein induced ferroptosis in CRC cells. We showed that baicalein (1–64 μM) dose-dependently inhibited the viability of human CRC lines HCT116 and DLD1. Co-treatment with the ferroptosis inhibitor liproxstatin-1 (1 μM) significantly mitigated baicalein-induced CRC cell death, whereas autophagy inhibitor chloroquine (25 μM), necroptosis inhibitor necrostatin-1 (10 μM), or pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (10 μM) did not rescue baicalein-induced CRC cell death. RNA-seq analysis confirmed that the inhibitory effect of baicalein on CRC cells is associated with ferroptosis induction. We revealed that baicalein (7.5–30 μM) dose-dependently decreased the expression levels of GPX4, key regulator of ferroptosis, in HCT116 and DLD1 cells by blocking janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/STAT3 signaling pathway via direct interaction with JAK2, ultimately leading to ferroptosis in CRC cells. In a CRC xenograft mouse model, administration of baicalein (10, 20 mg/kg, i.g., every two days for two weeks) dose-dependently inhibited the tumor growth with significant ferroptosis induced by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3/GPX4 axis in tumor tissue. This study demonstrates that ferroptosis contributes to baicalein-induced anti-CRC activity through blockade of the JAK2/STAT3/GPX4 signaling pathway, which provides evidence for the therapeutic application of baicalein against CRC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
García-Alfonso P, Torres G, García G, Gallego I, Ortega L, Sandoval C, et al. FOLFOXIRI plus biologics in advanced colorectal cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19:411–22.
Haraldsdottir S, Einarsdottir HM, Smaradottir A, Gunnlaugsson A, Halfdanarson TR. Colorectal cancer - review. Laeknabladid. 2014;100:75–82.
Biller LH, Schrag D. Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a review. JAMA. 2021;325:669–85.
Brody H. Colorectal cancer. Nature. 2015;521:S1.
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149:1060–72.
Dixon SJ, Stockwell BR. The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10:9–17.
Wei R, Zhao Y, Wang J, Yang X, Li S, Wang Y, et al. Tagitinin C induces ferroptosis through PERK-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17:2703–17.
Sui X, Zhang R, Liu S, Duan T, Zhai L, Zhang M, et al. RSL3 drives ferroptosis through GPX4 inactivation and ROS production in colorectal cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1371.
Xia Y, Liu S, Li C, Ai Z, Shen W, Ren W, et al. Discovery of a novel ferroptosis inducer-talaroconvolutin A-killing colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:988.
Miao Q, Deng WQ, Lyu WY, Sun ZT, Fan SR, Qi M, et al. Erianin inhibits the growth and metastasis through autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in KRAS(G13D) colorectal cancer. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023;204:301–12.
Chen P, Li X, Zhang R, Liu S, Xiang Y, Zhang M, et al. Combinative treatment of β-elemene and cetuximab is sensitive to KRAS mutant colorectal cancer cells by inducing ferroptosis and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Theranostics. 2020;10:5107–19.
Yu Z, Tong S, Wang C, Wu Z, Ye Y, Wang S, et al. PPy@Fe3O4 nanoparticles inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of CRC via suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway and promoting ferroptosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:1001994.
Yang C, Zhang Y, Lin S, Liu Y, Li W. Suppressing the KIF20A/NUAK1/Nrf2/GPX4 signaling pathway induces ferroptosis and enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer to oxaliplatin. Aging. 2021;13:13515–34.
Zeng K, Li W, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. Inhibition of CDK1 overcomes oxaliplatin resistance by regulating ACSL4-mediated ferroptosis in colorectal cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10:e2301088.
Lv Y, Tang W, Xu Y, Chang W, Zhang Z, Lin Q, et al. Apolipoprotein L3 enhances CD8+ T cell antitumor immunity of colorectal cancer by promoting LDHA-mediated ferroptosis. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19:1284–98.
Fan F, Liu P, Bao R, Chen J, Zhou M, Mo Z, et al. A dual PI3K/HDAC inhibitor induces immunogenic ferroptosis to potentiate cancer immune checkpoint therapy. Cancer Res. 2021;81:6233–45.
Lei G, Zhuang L, Gan B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22:381–96.
Yan H, Talty R, Johnson CH. Targeting ferroptosis to treat colorectal cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2023;33:185–8.
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171:273–85.
Li-Weber M. New therapeutic aspects of flavones: the anticancer properties of Scutellaria and its main active constituents Wogonin, Baicalein and Baicalin. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009;35:57–68.
Lin CC, Shieh DE. The anti-inflammatory activity of Scutellaria rivularis extracts and its active components, baicalin, baicalein and wogonin. Am J Chin Med. 1996;24:31–6.
Ye F, Xui L, Yi J, Zhang W, Zhang DY. Anticancer activity of Scutellaria baicalensis and its potential mechanism. J Alter Complement Med. 2002;8:567–72.
Tuli HS, Aggarwal V, Kaur J, Aggarwal D, Parashar G, Parashar NC, et al. Baicalein: a metabolite with promising antineoplastic activity. Life Sci. 2020;259:118183.
Chen M, Zhong K, Tan J, Meng M, Liu CM, Chen B, et al. Baicalein is a novel TLR4-targeting therapeutics agent that inhibits TLR4/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11:e564.
Kim SJ, Kim HJ, Kim HR, Lee SH, Cho SD, Choi CS, et al. Antitumor actions of baicalein and wogonin in HT-29 human colorectal cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6:1443–9.
Rui X, Yan XI, Zhang K. Baicalein inhibits the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of the AKT signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2016;11:685–8.
Kim DH, Hossain MA, Kang YJ, Jang JY, Lee YJ, Im E, et al. Baicalein, an active component of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells and prevents AOM/DSS-induced colon cancer in mice. Int J Oncol. 2013;43:1652–8.
Su MQ, Zhou YR, Rao X, Yang H, Zhuang XH, Ke XJ, et al. Baicalein induces the apoptosis of HCT116 human colon cancer cells via the upregulation of DEPP/Gadd45a and activation of MAPKs. Int J Oncol. 2018;53:750–60.
Zhang Z, Guo M, Shen M, Kong D, Zhang F, Shao J, et al. The BRD7-P53-SLC25A28 axis regulates ferroptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101619.
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:369–79.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:798–809.
Wang K, Zhang T, Lei Y, Li X, Jiang J, Lan J, et al. Identification of ANXA2 (annexin A2) as a specific bleomycin target to induce pulmonary fibrosis by impeding TFEB-mediated autophagic flux. Autophagy. 2018;14:269–82.
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM, Wallace MB. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2019;394:1467–80.
Yu T, Guo F, Yu Y, Sun T, Ma D, Han J, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by modulating autophagy. Cell. 2017;170:548–63.e16.
Qian P, Linbo L, Xiaomei Z, Hui P. Circ_0002770, acting as a competitive endogenous RNA, promotes proliferation and invasion by targeting miR-331-3p in melanoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:264.
Conrad M, Lorenz SM, Proneth B. Targeting ferroptosis: new hope for as-yet-incurable diseases. Trends Mol Med. 2021;27:113–22.
Atanasov AG, Waltenberger B, Pferschy-Wenzig EM, Linder T, Wawrosch C, Uhrin P, et al. Discovery and resupply of pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2015;33:1582–614.
Aung TN, Qu Z, Kortschak RD, Adelson DL. Understanding the effectiveness of natural compound mixtures in cancer through their molecular mode of action. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:656.
Choi EO, Park C, Hwang HJ, Hong SH, Kim GY, Cho EJ, et al. Baicalein induces apoptosis via ROS-dependent activation of caspases in human bladder cancer 5637 cells. Int J Oncol. 2016;49:1009–18.
Ye F, Wang H, Zhang L, Zou Y, Han H, Huang J. Baicalein induces human osteosarcoma cell line MG-63 apoptosis via ROS-induced BNIP3 expression. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:4731–40.
Kim HJ, Park C, Han MH, Hong SH, Kim GY, Hong SH, et al. Baicalein induces caspase-dependent apoptosis associated with the generation of ROS and the activation of AMPK in human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Drug Dev Res. 2016;77:73–86.
Li B, Lu M, Jiang XX, Pan MX, Mao JW, Chen M. Inhibiting reactive oxygen species-dependent autophagy enhanced baicalein-induced apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Nat Med. 2017;71:433–41.
Lee JH, Li YC, Ip SW, Hsu SC, Chang NW, Tang NY, et al. The role of Ca2+ in baicalein-induced apoptosis in human breast MDA-MB-231 cancer cells through mitochondria- and caspase-3-dependent pathway. Anticancer Res. 2008;28:1701–11.
Liu ZH, Yang CX, Zhang L, Yang CY, Xu XQ. Baicalein, as a prooxidant, triggers mitochondrial apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells through mobilization of intracellular copper and reactive oxygen species generation. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:10749–61.
Lin YT, Yang JS, Lin HJ, Tan TW, Tang NY, Chaing JH, et al. Baicalein induces apoptosis in SCC-4 human tongue cancer cells via a Ca2+-dependent mitochondrial pathway. vivo. 2007;21:1053–8.
Wang J, Yu Y, Hashimoto F, Sakata Y, Fujii M, Hou DX. Baicalein induces apoptosis through ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction pathway in HL-60 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2004;14:627–32.
Chuang TC, Shao WS, Hsu SC, Lee SL, Kao MC, Wang V. Baicalein induces G2/M cell cycle arrest associated with ROS generation and CHK2 activation in highly invasive human ovarian cancer cells. Molecules. 2023;28:1039.
Zhang B, Chen X, Ru F, Gan Y, Li B, Xia W, et al. Liproxstatin-1 attenuates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting renal tubular epithelial cells ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:843.
Zilka O, Shah R, Li B, Friedmann Angeli JP, Griesser M, Conrad M, et al. On the mechanism of cytoprotection by ferrostatin-1 and liproxstatin-1 and the role of lipid peroxidation in ferroptotic cell death. ACS Cent Sci. 2017;3:232–43.
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156:317–31.
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:1180–91.
Zhao Y, Wang C, Yang T, Wang H, Zhao S, Sun N, et al. Chlorogenic acid alleviates chronic stress-induced duodenal ferroptosis via the inhibition of the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70:4353–61.
Zhao X, Chen F. Propofol induces the ferroptosis of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating STAT3 expression. Oncol Lett. 2021;22:767.
Huang Q, Li J, Ma M, Lv M, Hu R, Sun J, et al. High‑throughput screening identification of a small‑molecule compound that induces ferroptosis and attenuates the invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting the STAT3/GPX4 axis. Int J Oncol. 2023;62:42.
Li Y, Zhang Y, Qiu Q, Wang L, Mao H, Hu J, et al. Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation promotes GPX4-dependent ferroptosis through the JAK2/STAT3/P53 axis in renal cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2353115.
Susmitha GD, Miyazato K, Ogura K, Yokoyama S, Hayakawa Y. Anti-metastatic effects of baicalein by targeting STAT3 activity in breast cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020;43:1899–905.
Ke M, Zhang Z, Xu B, Zhao S, Ding Y, Wu X, et al. Baicalein and baicalin promote antitumor immunity by suppressing PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105824.
Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Lee JY, Kim DH, Kang MS, Park W. Anti-inflammatory effect of baicalein on polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid-induced RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages. Viruses. 2018;10:224.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82173236, 81973341), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2024A1515013108), the program of Guangdong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases (2020B1111170004), Medical Joint Fund of Jinan University (YXJC2022002), Guangzhou High-level Key Clinical Specialty Construction Project (No.9), the Project of Key Medical Discipline in Guangzhou (2021–2023), Guangzhou Science and Technology Planning Project (202206080008), and 2023 Guangzhou digestive disease high-quality integrated treatment system construction project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JQL, QQ, and JC guided and designed the study; JQL performed all experiments. LLZ, CH, and QMZ provided the main technical support. SJL, JXS, XFZ, ZSL and BD contributed to the data collection and data analysis. JQL, QQ and BD wrote and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, Jq., Zhao, Ll., Hong, C. et al. Baicalein triggers ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells via blocking the JAK2/STAT3/GPX4 axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01258-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01258-z