Abstract
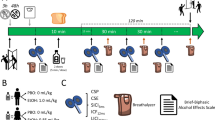
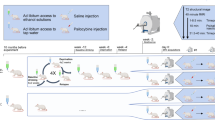
The GABAB receptor (GABABR) agonist baclofen has been used to treat alcohol and several other substance use disorders (AUD/SUD), yet its underlying neural mechanism remains unclear. The present study aimed to investigate cortical GABABR dynamics following chronic alcohol exposure. Ex vivo brain slice recordings from mice chronically exposed to alcohol revealed a reduction in GABABR-mediated currents, as well as a decrease of GABAB1/2R and G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channel 2 (GIRK2) activities in the motor cortex. Moreover, our data indicated that these alterations could be attributed to dephosphorylation at the site of serine 783 (ser-783) in GABAB2 subunit, which regulates the surface expression of GABABR. Furthermore, a human study using paired-pulse-transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) analysis further demonstrated a reduced cortical inhibition mediated by GABABR in patients with AUD. Our findings provide the first evidence that chronic alcohol exposure is associated with significantly impaired cortical GABABR function. The ability to promote GABABR signaling may account for the therapeutic efficacy of baclofen in AUD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Kranzler HR, Soyka M. Diagnosis and pharmacotherapy of alcohol use disorder: a review. JAMA. 2018;320:815–24.
Agabio R, Colombo G. GABAB receptor ligands for the treatment of alcohol use disorder: preclinical and clinical evidence. Front Neurosci. 2014;8:140.
Addolorato G, Leggio L, Abenavoli L, Agabio R, Caputo F, Capristo E, et al. Baclofen in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome: a comparative study vs diazepam. Am J Med. 2006;119:276 e213–78.
Rose AK, Jones A. Baclofen: its effectiveness in reducing harmful drinking, craving, and negative mood. A meta-analysis. Addiction. 2018;113:1396–406.
Pierce M, Sutterland A, Beraha EM, Morley K, van den Brink W. Efficacy, tolerability, and safety of low-dose and high-dose baclofen in the treatment of alcohol dependence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018;28:795–806.
Spanagel R. Aberrant choice behavior in alcoholism. Science. 2018;360:1298–9.
Padgett CL, Slesinger PA. GABAB receptor coupling to G-proteins and ion channels. Adv Pharmacol. 2010;58:123–47.
Chalifoux JR, Carter AG. GABAB receptor modulation of synaptic function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011;21:339–44.
Padgett CL, Lalive AL, Tan KR, Terunuma M, Munoz MB, Pangalos MN, et al. Methamphetamine-evoked depression of GABA(B) receptor signaling in GABA neurons of the VTA. Neuron. 2012;73:978–89.
Pitman KA, Puil E, Borgland SL. GABA(B) modulation of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens core. Eur J Neurosci. 2014;40:3472–80.
Claus ED, Ewing SW, Filbey FM, Sabbineni A, Hutchison KE. Identifying neurobiological phenotypes associated with alcohol use disorder severity. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:2086–96.
Claus ED, Feldstein Ewing SW, Filbey FM, Hutchison KE. Behavioral control in alcohol use disorders: relationships with severity. J Stud Alcohol drugs. 2013;74:141–51.
Dalley JW, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW. Impulsivity, compulsivity, and top-down cognitive control. Neuron. 2011;69:680–94.
MacKillop J, Weafer J, Gray JC, Oshri A, Palmer A, de Wit H. The latent structure of impulsivity: impulsive choice, impulsive action, and impulsive personality traits. Psychopharmacology. 2016;233:3361–70.
Smith JL, Mattick RP, Jamadar SD, Iredale JM. Deficits in behavioural inhibition in substance abuse and addiction: a meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;145:1–33.
Ersche KD, Turton AJ, Chamberlain SR, Muller U, Bullmore ET, Robbins TW. Cognitive dysfunction and anxious-impulsive personality traits are endophenotypes for drug dependence. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169:926–36.
Ahmadi A, Pearlson GD, Meda SA, Dager A, Potenza MN, Rosen R, et al. Influence of alcohol use on neural response to Go/No-Go task in college drinkers. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38:2197–208.
Caprioli D, Sawiak SJ, Merlo E, Theobald DE, Spoelder M, Jupp B, et al. Gamma aminobutyric acidergic and neuronal structural markers in the nucleus accumbens core underlie trait-like impulsive behavior. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;75:115–23.
Belin D, Mar AC, Dalley JW, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ. High impulsivity predicts the switch to compulsive cocaine-taking. Science. 2008;320:1352–5.
Voon V, Irvine MA, Derbyshire K, Worbe Y, Lange I, Abbott S, et al. Measuring “waiting” impulsivity in substance addictions and binge eating disorder in a novel analogue of rodent serial reaction time task. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;75:148–55.
He JL, Fuelscher I, Coxon J, Chowdhury N, Teo WP, Barhoun P, et al. Individual differences in intracortical inhibition predict motor-inhibitory performance. Exp Brain Res. 2019;237:2715–27.
Franklin K, Paxinos G. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Compact: The Coronal Plates and Diagrams 5th ed. (2019).
Rotaru DC, Yoshino H, Lewis DA, Ermentrout GB, Gonzalez-Burgos G. Glutamate receptor subtypes mediating synaptic activation of prefrontal cortex neurons: relevance for schizophrenia. J Neurosci. 2011;31:142–56.
Jesse S, Brathen G, Ferrara M, Keindl M, Ben-Menachem E, Tanasescu R, et al. Alcohol withdrawal syndrome: mechanisms, manifestations, and management. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;135:4–16.
Nardone R, Bergmann J, Kronbichler M, Caleri F, Lochner P, Tezzon F, et al. Altered motor cortex excitability to magnetic stimulation in alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Alcohol, Clin Exp Res. 2010;34:628–32.
Chung HJ, Qian X, Ehlers M, Jan YN, Jan LY. Neuronal activity regulates phosphorylation-dependent surface delivery of G protein-activated inwardly rectifying potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:629–34.
Terunuma M, Vargas KJ, Wilkins ME, Ramirez OA, Jaureguiberry-Bravo M, Pangalos MN, et al. Prolonged activation of NMDA receptors promotes dephosphorylation and alters postendocytic sorting of GABAB receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:13918–23.
Wang J, Cheng Y, Wang X, Roltsch Hellard E, Ma T, Gil H, et al. Alcohol elicits functional and structural plasticity selectively in dopamine D1 receptor-expressing neurons of the dorsomedial striatum. J Neurosci. 2015;35:11634–43.
Fontaine CJ, Patten AR, Sickmann HM, Helfer JL, Christie BR. Effects of pre-natal alcohol exposure on hippocampal synaptic plasticity: sex, age and methodological considerations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;64:12–34.
Moonat S, Sakharkar AJ, Zhang H, Tang L, Pandey SC. Aberrant histone deacetylase2-mediated histone modifications and synaptic plasticity in the amygdala predisposes to anxiety and alcoholism. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;73:763–73.
McCool BA. Ethanol modulation of synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology. 2011;61:1097–108.
Addolorato G, Leggio L, Ferrulli A, Cardone S, Vonghia L, Mirijello A, et al. Effectiveness and safety of baclofen for maintenance of alcohol abstinence in alcohol-dependent patients with liver cirrhosis: randomised, double-blind controlled study. Lancet. 2007;370:1915–22.
Morley KC, Baillie A, Fraser I, Furneaux-Bate A, Dore G, Roberts M, et al. Baclofen in the treatment of alcohol dependence with or without liver disease: multisite, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Br J Psychiatry. 2018;212:362–9.
Mirijello A, Caputo F, Vassallo G, Rolland B, Tarli C, Gasbarrini A, et al. GABAB agonists for the treatment of alcohol use disorder. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21:3367–72.
McDonnell MN, Orekhov Y, Ziemann U. The role of GABA(B) receptors in intracortical inhibition in the human motor cortex. Exp Brain Res. 2006;173:86–93.
Premoli I, Rivolta D, Espenhahn S, Castellanos N, Belardinelli P, Ziemann U, et al. Characterization of GABAB-receptor mediated neurotransmission in the human cortex by paired-pulse TMS-EEG. Neuroimage. 2014;103:152–62.
Tran VT, Snyder SH, Major LF, Hawley RJ. GABA receptors are increased in brains of alcoholics. Ann Neurol. 1981;9:289–92.
Laukkanen V, Storvik M, Hakkinen M, Akamine Y, Tupala E, Virkkunen M, et al. Decreased GABA(A) benzodiazepine binding site densities in postmortem brains of cloninger type 1 and 2 alcoholics. Alcohol. 2013;47:103–8.
Mitsuyama H, Little KY, Sieghart W, Devaud LL, Morrow AL. GABA(A) receptor alpha1, alpha4, and beta3 subunit mRNA and protein expression in the frontal cortex of human alcoholics. Alcohol, Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:815–22.
Korpi ER, Uusi-Oukari M, Wegelius K, Casanova M, Zito M, Kleinman JE. Cerebellar and frontal cortical benzodiazepine receptors in human alcoholics and chronically alcohol-drinking rats. Biol Psychiatry. 1992;31:774–86.
Dodd PR, Buckley ST, Eckert AL, Foley PF, Innes DJ. Genes and gene expression in the brains of human alcoholics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1074:104–15.
Enoch MA, Zhou Z, Kimura M, Mash DC, Yuan Q, Goldman D. GABAergic gene expression in postmortem hippocampus from alcoholics and cocaine addicts; corresponding findings in alcohol-naive P and NP rats. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e29369.
Lee C, Mayfield RD, Harris RA. Altered gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 1 splicing in alcoholics. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;75:765–73.
Naim-Feil J, Bradshaw JL, Rogasch NC, Daskalakis ZJ, Sheppard DM, Lubman DI, et al. Cortical inhibition within motor and frontal regions in alcohol dependence post-detoxification: A pilot TMS-EEG study. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2016;17:547–56.
Moran MD, Wilson AA, Elmore CS, Parkes J, Ng A, Sadovski O, et al. Development of new carbon-11 labelled radiotracers for imaging GABAA- and GABAB-benzodiazepine receptors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012;20:4482–8.
Tang YL, Xiang XJ, Wang XY, Cubells JF, Babor TF, Hao W. Alcohol and alcohol-related harm in China: policy changes needed. Bull World Health Organ. 2013;91:270–6.
Grant BF, Chou SP, Saha TD, Pickering RP, Kerridge BT, Ruan WJ, et al. Prevalence of 12-month alcohol use, high-risk drinking, and DSM-IV alcohol use disorder in the United States, 2001-2002 to 2012-2013: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:911–23.
Ait-Daoud N, Blevins D, Khanna S, Sharma S, Holstege CP, Amin P. Women and addiction: an update. Med Clin North Am. 2019;103:699–711.
Erol A, Karpyak VM. Sex and gender-related differences in alcohol use and its consequences: Contemporary knowledge and future research considerations. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015;156:1–13.
Becker JB, Koob GF. Sex differences in animal models: focus on addiction. Pharm Rev. 2016;68:242–63.
Hilderbrand ER, Lasek AW. Studying sex differences in animal models of addiction: an emphasis on alcohol-related behaviors. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018;9:1907–16.
Marco EM, Ballesta JA, Irala C, Hernandez MD, Serrano ME, Mela V, et al. Sex-dependent influence of chronic mild stress (CMS) on voluntary alcohol consumption; study of neurobiological consequences. Pharm Biochem Behav. 2017;152:68–80.
Heilig M, Augier E, Pfarr S, Sommer WH. Developing neuroscience-based treatments for alcohol addiction: a matter of choice? Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9:255.
Agabio R, Sinclair JM, Addolorato G, Aubin HJ, Beraha EM, Caputo F, et al. Baclofen for the treatment of alcohol use disorder: the Cagliari Statement. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018;5:957–60.
Augier E, Dulman RS, Damadzic R, Pilling A, Hamilton JP, Heilig M. The GABAB positive allosteric modulator ADX71441 attenuates alcohol self-administration and relapse to alcohol seeking in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017;42:1789–99.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ke Zhang and Zhuang Peng for help during data collection and management.
Funding
The study was supported by NSFC grants (81822017, 81901349, 31771215), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (18QA1403700, 18JC1420304, 18140901700), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission—Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant Support (20181715), Hundred-talent Fund from Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health (2018BR21), Medicine and Engineering Interdisciplinary Research Fund of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (ZH2018ZDA30, ZH2018QNA39), and innovative research team of high-level local universities in Shanghai. VV is supported by the Medical Research Council MR/P008747/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S-YP, ZS, D-SZ, and T-FY designed the study; S-YP, ZS, D-SZ, X-YW, X-XL, X-LL, W-DW, and G-NL performed the study; S-YP, ZS, D-SZ, X-YW, B-XP, VV, AAG, MH, M-LW, and T-FY analyzed the results and wrote the paper together; and all authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
AAG receives consulting fees from Alkermes, Lundbeck, Takeda, Roche, Lyra, Concert. The rest authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, SY., Shi, Z., Zhou, DS. et al. Reduced motor cortex GABABR function following chronic alcohol exposure. Mol Psychiatry 26, 383–395 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-01009-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-01009-6
This article is cited by
-
Partial recovery of the left DLPFC-right insula circuit with reduced craving in abstinent heroin users: a longitudinal study
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2022)
-
Physical exercise rescues cocaine-evoked synaptic deficits in motor cortex
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)