Abstract
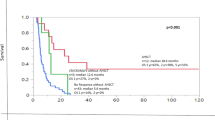
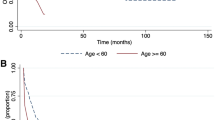
The rarity of mixed-phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) has resulted in diffuse literature consisting of small case series, thus precluding a consensus treatment approach. We conducted a meta-analysis and systematic review to investigate the association of treatment type (acute lymphoblastic leukemia [ALL], acute myeloid leukemia [AML], or “hybrid” regimens), disease response, and survival. We searched seven databases from inception through June 2017 without age or language restriction. Included studies reported sufficient treatment detail for de novo MPAL classified according to the well-established European Group for Immunological Characterization of Acute Leukemias (EGIL) or World Health Organization (WHO2008) criteria. Meta-analyses and multivariable analyses of a patient-level compiled case series were performed for the endpoints of complete remission (CR) and overall survival (OS). We identified 97 reports from 33 countries meeting criteria, resulting in 1,499 unique patients with data, of whom 1,351 had sufficient detail for quantitative analysis of the study endpoints. Using either definition of MPAL, meta-analyses revealed that AML induction was less likely to achieve a CR as compared to ALL regimens, (WHO2008 odds ratio [OR] = 0.33, 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 0.18–0.58; EGIL, OR = 0.18, 95% CI 0.08–0.40). Multivariable analysis of the patient-level data supported poorer efficacy for AML induction (versus ALL: OR = 0.45 95% CI 0.27–0.77). Meta-analyses similarly found better OS for those beginning with ALL versus AML therapy (WHO2008 OR = 0.45, 95% CI 0.26–0.77; EGIL, OR = 0.43, 95% CI 0.24–0.78), but multivariable analysis of patient-level data showed only those starting with hybrid therapy fared worse (hazard ratio [HR] = 2.11, 95% CI 1.30–3.43). MPAL definition did not impact trends within each endpoint and were similarly predictive of outcome. Using either definition of MPAL, ALL-therapy is associated with higher initial remission rates for MPAL and is at least equivalent to more intensive AML therapy for long-term survival. Prospective trials are needed to establish a uniform approach to this heterogeneous disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinberg OK, Arber DA. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: historical overview and a new definition. Leukemia. 2010;24(11):1844–51.
Bene MC, Castoldi G, Knapp W, Ludwig WD, Matutes E, Orfao A, et al. Proposals for the immunological classification of acute leukemias. European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL). Leukemia. 1995;9(10):1783–6.
Matutes E, Morilla R, Farahat N, Carbonell F, Swansbury J, Dyer M, et al. Definition of acute biphenotypic leukemia. Haematologica. 1997;82(1):64–6.
Swerdlow SH, Campo, E, Harris, NL, Jaffe, ES, Pileri, SA, Stein, H, et al. World Health Organization classification of tumors of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon: IARC press; 2008.
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114(5):937–51.
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127(20):2391–405.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7(3):177–88.
Aasha B, Sharma S, Rai P, Chauhan R, Chandra J. A girl with mixed phenotype acute leukemia: B/T subtype-a rare variant. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2013;29(4):331.
Abdulwahab AS, AlJurf MD, Elkum NM, Almohareb FI, Owaidah TM. Clinical presentation, treatment response and survival in adult acute biphenotypic leukemia: single centre experience. Blood. 2007;110(11):150B–150B.
Alhuraiji A, Shad A, Owaidah T, Alzahrani H, Al Mhareb F, Chaudhri N et al. Efficacy and safety of VCEP-M for induction treatment of mixed phenotypic acute leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(15_suppl):e18504.
Al-Qurashi FH, Owaidah T, Iqbal MA, Aljurf M. Trisomy 4 as the sole karyotypic abnormality in a case of acute biphenotypic leukemia with T-lineage markers in minimally differentiated acute myelocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2004;150(1):66–9.
Al-Seraihy AS, Owaidah TM, Ayas M, El-Solh H, Al-Mahr M, Al-Ahmari A, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of children with biphenotypic acute leukemia. Haematologica. 2009;94(12):1682–90.
Alvarado Y, Welch MA, Swords R, Bruzzi J, Schlette E, Giles FJ. Nelarabine activity in acute biphenotypic leukemia. Leuk Res. 2007;31(11):1600–3.
Atfy M, Al Azizi NMA, Elnaggar AM. Incidence of Philadelphia-chromosome in acute myelogenous leukemia and biphenotypic acute leukemia patients: and its role in their outcome. Leuk Res. 2011;35(10):1339–44.
Bachir F, Zerrouk J, Howard SC, Graoui O, Lahjouji A, Hessissen L, et al. Outcomes in patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemia in Morocco. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2013;36(6):e392–7.
Bhamidipati PK, Jabbour E, Konoplev S, Estrov Z, Cortes J, Daver N. Epstein-Barr Virus induced CD30-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in a patient with mixed-phenotypic leukemia treated with Clofarabine. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013;13(3):342–6.
Bhatia P, Binota J, Varma N, Marwaha RK, Varma S. A study on the expression of BCR-ABL transcript in mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) cases using the reverse transcriptase polymerase reaction assay (RT-PCR) and its correlation with hematological remission status post induction. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2011;27(4):196.
Bhella SD, Musani R, Porwit A, Tierens A, Gupta V, Schimmer AD, et al. Outcomes of mixed phenotype leukemia, not otherwise specified (NOS), in adults: a single centre retrospective review from 2000 to 2014. Blood. 2015;126(23):4865.
Bleahu ID, Vladasel R, Gheorghe A. A special case of acute leukemia in childhood. J Med Life. 2012;4(3):297–301.
Bogunovic M, Kraguljac-Kurtovic N, Bogdanovic A, Perunicic M, Djordjevic V, Lazarevic V, et al. Mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) according to the who 2008 classification-report of 17 cases. Haematologica. 2011;96:240–1.
Butcher BW, Wilson KS, Kroft SH, Collins RH Jr, Bhushan V. Acute leukemia with B-lymphoid and myeloid differentiation associated with an inv(5)(q13q33) in an adult patient. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2005;157(1):62–66.
Colovic M, Colovic N, Jankovic G, Kurtovic NK, Vidovic A, Djordjevic V. et al. Mixed phenotype acute leukemia of T/myeloid type with a prominent cellular heterogeneity and unique karyotypic aberration 45,XY, dic(11;17). Int J Lab Hematol. 2012;34(3):290–4.
de Leeuw DC, van den Ancker W, Westers TM, Loonen AH, Bhola SL, Ossenkoppele GJ, et al. Challenging diagnosis in a patient with clear lymphoid immunohistochemical features and myeloid morphology: mixed phenotype acute leukemia with erythrophagocytosis. Leuk Res. 2011;35(5):693–6.
Deffis-Court M, Alvarado-Ibarra M, Ruiz-Arguelles GJ, Rosas-Lopez A, Barrera-Lumbreras G, Aguayo-Gonzalez A, et al. Diagnosing and treating mixed phenotype acute leukemia: a multicenter 10-year experience in Mexico. Ann Hematol. 2014;93(4):595–601.
Derwich K, Sedek L, Meyer C, Pieczonka A, Dawidowska M, Gaworczyk A, et al. Infant acute bilineal leukemia. Leuk Res. 2009;33(7):1005–8.
Duployez N, Debarri H, Fouquet G. Mixed phenotype acute leukaemia with Burkitt-like cells and positive peroxidase cytochemistry. Br J Haematol. 2013;163(2):148.
Ferla V, Vincenti D, Fracchiolla NS, Cro L, Cortelezzi A. A rare case of mixed phenotype acute leukemia, T/myeloid, nos: Diagnosis, therapy and clinical outcome. Haematologica. 2013;98:208.
Gaipa G, Leani V, Maglia O, Benetello A, Cantu-Rajnoldi A, Bugarin C, et al. Four pediatric acute biphenotypic leukemia cases: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Cytom Part A. 2006;69A(5):451–451.
Gao H, Liu Y, Zhang R, Xie J, Shi H, Wu M et al. Pediatric mixed phenotype acute leukemia-41 cases report. Blood. 2012; 120(21):4811.
Gerr H, Zimmermann M, Schrappe M, Dworzak M, Ludwig WD, Bradtke J, et al. Acute leukaemias of ambiguous lineage in children: characterization, prognosis and therapy recommendations. Br J Haematol. 2010;149(1):84–92.
Getta BM, Zheng J, Tallman MS, Park JH, Stein EM, Roshal M et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant with ablative conditioning is associated with favorable outcomes in patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemia clinical allogeneic transplantation. Blood 2016;128(22):3487.
Gozzetti A, Calabrese S, Raspadori D, Crupi R, Tassi M, Bocchia M, et al. Concomitant t(4;11) and t(1;19) in a patient with biphenotypic acute leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007;177(1):81–2.
Guariglia R, Guastafierro S, Annunziata S, Tirelli A. Development of a transient monoclonal gammopathy after chemotherapy in a patient with biphenotypic acute leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43(2):441–3.
Gujral S, Polampalli S, Badrinath Y, Kumar A, Subramanian PG, Raje G, et al. Clinico-hematological profile in biphenotypic acute leukemia. Indian J Cancer. 2009;46(2):160–8.
He G, Zhou L, Wu D, Xue Y, Zhu M, Liang J, et al. Clinical research of biphenotypic acute leukemia with t(8;21)(q22; q22). Chin-Ger J Clin Oncol. 2007;6(4):389–92.
He G, Wu D, Sun A, Xue Y, Jin Z, Qiu H, et al. B-Lymphoid and myeloid lineages biphenotypic acute leukemia with t(8;21)(q22; q22). Int J Hematol. 2008;87(2):132–6.
Heesch S, Neumann M, Schwartz S, Bartram I, Schlee C, Burmeister T, et al. Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage in adults: molecular and clinical characterization. Ann Hematol. 2013;92(6):747–58.
Kaćanski N, Konstantinidis N, Kolarović J, Slavković B, Vujić D. Biphenotypic acute leukaemia: case reports of two paediatric patients. Med Pregl. 2010;63(11-12):867–9.
Kalashetty M, Dalal BI, Roland KJ, Abou Mourad Y, Barnett MJ, Broady R, et al. Improved survival in adults with mixed-phenotype acute leukemia following stem cell transplantation (SCT): a single centre experience. Blood. 2013;122(21):5540.
Kawajiri C, Tanaka H, Hashimoto S, Takeda Y, Sakai S, Takagi T, et al. Successful treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive mixed phenotype acute leukemia by appropriate alternation of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors according to BCR-ABL1 mutation status. Int J Hematol. 2014;99(4):513–8.
Khodadoust MS, Luo B, Medeiros BC, Johnson RC, Ewalt MD, Schalkwyk AS, et al. Clinical activity of ponatinib in a patient with FGFR1-rearranged mixed-phenotype acute leukemia. Leukemia. 2016;30(4):947–50.
Killick S, Matutes E, Powles RL, Hamblin M, Swansbury J, Treleaven JG, et al. Outcome of biphenotypic acute leukemia. Haematologica. 1999;84(8):699–706.
Kim HN, Hur M, Kim H, Ji M, Moon HW, Yun YM, et al. First case of biphenotypic/bilineal (B/myeloid, B/monocytic) mixed phenotype acute leukemia with t(9;22) (q34; q11.2);BCR-ABL1. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016;46(4):435–8.
Kohla SA, Sabbagh AA, Omri HE, Ibrahim FA, Otazu IB, Alhajri H, et al. Mixed phenotype acute leukemia with two immunophenotypically distinct B and T blasts populations, double Ph (+) chromosome and complex karyotype: report of an unusual case. Clin Med Insights Blood Disord. 2015;8:25–31.
Krishnan AY, Chang KL, Fung HC, O’Donnell M, Bhatia R, Spielberger R, et al. Impact of allogeneic stem cell transplantation (ASCT) on outcome of biphenotypic acute leukemia (BAL). Blood. 2004;104(11):370B
Lee JH, Min YH, Chung CW, Kim BK, Yoon HJ, Jo DY, et al. Prognostic implications of the immunophenotype in biphenotypic acute leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49(4):700–9.
Lee JY, Lee SM, Lee JY, Kim KH, Choi MY, Lee WS. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia treated with decitabine. Korean J Intern Med. 2016;31(2):406–8.
Lee S, Jung CW, Song SY, Park JO, Kim K, Kim WS, et al. The effect of ffigh dose cytarabine and idarubicin as an induction therapy in biphenotypic acute leukemia. Blood. 2002;100(11):264B
Lim F, Wong GC. Biphenotypic acute leukaemia: treatment with all-type regime may offer a better outcome. Haematolgica. 2010;95:273–273.
Liu QF, Fan ZP, Wu MQ, Sun J, Wu XL, Xu D, et al. Allo-HSCT for acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage in adults: the comparison between standard conditioning and intensified conditioning regimens. Ann Hematol. 2013;92(5):679–87.
Lopes GS, Leitao JP, Kaufman J, Duarte FB, Matos DM. T-cell/myeloid mixed-phenotype acute leukemia with monocytic differentiation and isolated 17p deletion. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter. 2014;36(4):293–6.
Lou ZJ, Zhang CC, Tirado CA, Slone T, Zheng J, Zaremba CM, et al. Infantile mixed phenotype acute leukemia (bilineal and biphenotypic) with t(10;11)(p12; q23);MLL-MLLT10. Leuk Res. 2010;34(8):1107–9.
Lu J, Ashwani N, Zhang M, He H, Wang Y, Zhao W, et al. Children diagnosed as mixed-phenotype acute leukemia didn’t benefit from the CCLG-2008 protocol, retrospective analysis from single center. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2014;31(1):32–37.
Manola KN, Georgakakos VN, Marinakis T, Stavropoulou C, Paterakis G, Anagnostopoulos NI, et al. Translocation (X;12)(p11; p13) as a sole abnormality in biphenotypic acute leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007;173(2):159–63.
Marques-Salles Tde J, Barros JE, Soares-Ventura EM, Cartaxo Muniz MT, Santos N, Ferreira da Silva E, et al. Unusual childhood biphenotypic acute leukemia with a yet unreported t(3;13)(p25.1; q13). Leuk Res. 2010;34(8):e206–207.
Matsumoto Y, Taki T, Fujimoto Y, Taniguchi K, Shimizu D, Shimura K, et al. Monosomies 7p and 12p and FLT3 internal tandem duplication: possible markers for diagnosis of T/myeloid biphenotypic acute leukemia and its clonal evolution. Int J Hematol. 2009;89(3):352–8.
Matutes E, Pickl WF, Van’t Veer M, Morilla R, Swansbury J, Strobl H, et al. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: clinical and laboratory features and outcome in 100 patients defined according to the WHO 2008 classification. Blood. 2011;117(11):3163–71.
Mejstrikova E, Volejnikova J, Fronkova E, Zdrahalova K, Kalina T, Sterba J, et al. Prognosis of children with mixed phenotype acute leukemia treated on the basis of consistent immunophenotypic criteria. Haematologica. 2010;95(6):928–35.
Mejstrikova E, Slamova L, Fronkova E, Volejnikova J, Muzikova K, Domansky J et al. Acute bilineal leukemia is a very rare entity in childhood. Blood 2011;118(21):4871.
Mikulic M, Batinic D, Sucic M, Davidovic-Mrsic S, Dubravcic K, Nemet D, et al. Biological features and outcome of biphenotypic acute leukemia: a case series. Hematol Oncol stem Cell Ther. 2008;1(4):225–30.
Miyazawa Y, Irisawa H, Matsushima T, Mitsui T, Uchiumi H, Saitoh T, et al. Der(2)t(2; 11)(p21; q23), a variant form of t(2; 11), in biphenotypic acute leukemia with T lymphoid lineage and myeloid lineage differentiation. Kitakanto Med J. 2012;62(3):287–90.
Moraveji S, Torabi A, Nahleh Z, Farrag S, Gaur S. Acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage with trisomy 4 as the sole cytogenetic abnormality: a case report and literature review. Leuk Res Rep. 2014;3(2):33–5.
Moreira C, Domingues N, Moreira I, Oliveira I, Martins A, Viterbo L, et al. Adult mixed-phenotype acute leukemia according to the who 2008 classification-a single center experience. Haematologica. 2013;98:267.
Mori J, Ishiyama K, Yamaguchi T, Tanaka J, Uchida N, Kobayashi T, et al. Outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with biphenotypic acute leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2016;95(2):295–300.
Munker R, Brazauskas R, Wang HL, de Lima M, Khoury HJ, Gale RP, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(6):1024–9.
Naghashpour M, Lancet J, Moscinski L, Zhang L. Mixed phenotype acute leukemia with t(11;19)(q23; p13.3)/ MLL-MLLT1(ENL), B/T-lymphoid type: a first case report. Am J Hematol. 2010;85(6):451–4.
Nishiuchi T, Ohnishi H, Kamada R, Kikuchi F, Shintani T, Waki F, et al. Acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage, biphenotype, without CD34, TdT or TCR-rearrangement. Intern Med. 2009;48(16):1437–41.
Oka S, Yokote T, Akioka T, Hara S, Kobayashi K, Hirata Y, et al. Trisomy 21 as the sole acquired karyotypic abnormality in biphenotypic acute leukemia. Int J Hematol. 2007;85(3):270–2.
Oliveira JL, Kumar R, Khan SP, Law ME, Erickson-Johnson M, Oliveira AM, et al. Successful treatment of a child with T/myeloid acute bilineal leukemia associated with TLX3/BCL11B fusion and 9q deletion. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2011;56(3):467–9.
Orgel E, Oberley M, Li S, Malvar J, O’Gorman M. Predictive value of minimal residual disease in WHO2016-defined mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL). Blood. 2016;128(22):178.
Otsubo K, Yabe M, Yabe H, Fukumura A, Morimoto T, Kato M, et al. Successful acute lymphoblastic leukemia-type therapy in two children with mixed-phenotype acute leukemia. Pediatr Int: Off J Jpn Pediatr Soc. 2016;58(10):1072–6.
Park JA, Ghim TT, Bae K, Im HJ, Jang SS, Park CJ, et al. Stem cell transplant in the treatment of childhood biphenotypic acute leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009;53(3):444–52.
Park JA, Lee JM, Lee KS, Kim JY, Lim JY, Park ES, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for pediatric mixed phenotype acute leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:S596–7.
Patel B, Saygin C, Przychodzen BP, Hirsch CM, Clemente MJ, Hamilton BK, et al. Molecular and immunophenotypic characteristics of adult acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage. Blood 2016;128(22).
Rahman K, George S, Tewari A, Mehta A. Mixed phenotypic acute leukemia with two immunophenotypically distinct blast populations: report of an unusual case. Cytom B Clin Cytom. 2013;84(3):198–201.
Ratei R, Schabath R, Karawajew L, Zimmermann M, Moricke A, Schrappe M, et al. Lineage classification of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia according to the EGIL recommendations: results of the ALL-BFM 2000 trial. Klin Padiatr. 2013;225(Suppl 1):S34–9.
Rubio MT, Dhedin N, Boucheix C, Bourhis JH, Reman O, Boiron JM, et al. Adult T-biphenotypic acute leukaemia: clinical and biological features and outcome. Br J Haematol. 2003;123(5):842–9.
Rubnitz JE, Onciu M, Pounds S, Shurtleff S, Cao X, Raimondi SC, et al. Acute mixed lineage leukemia in children: the experience of St Jude Children’s Research Hospital. Blood. 2009;113(21):5083–9.
Saito M, Izumiyama K, Mori A, Irie T, Tanaka M, Morioka M, et al. Biphenotypic acute leukemia with t(15;17) lacking promyelocytic-retinoid acid receptor α rearrangement. Hematol Rep. 2013;5(4):50–52.
Saitoh T, Matsushima T, Iriuchishima H, Yamane A, Irisawa H, Handa H, et al. Presentation of extramedullary Philadelphia chromosome-positive biphenotypic acute leukemia as testicular mass: response to imatinib-combined chemotherapy. Leuk Lymphoma. 2006;47(12):2667–9.
Scolnik MP, Aranguren PN, Cuello MT, Palacios MF, Sanjurjo J, Giunta M, et al. Biphenotypic acute leukemia with t(15;17). Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46(4):607–10.
Serefhanoglu S, Buyukasik Y, Goker H, Sayinalp N, Ozcebe OI. Biphenotypic acute leukemia treated with acute myeloid leukemia regimens: a case series. J Natl Med Assoc. 2009;101(3):270–2.
Shao-Yan H, Jing L, Zhenghua J, Yaxiang H, Yiping H. The clinical features and laboratory findings of mixedphenotype acute leukemia in 15 children-retrospective analysis from single center during 2008-12. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013;60:75.
Sharma P, Lall M, Jain P, Saraf A, Sachdeva A, Bhargava M. A bi-lineal acuteleukemia (T/Myeloid, NOS) with complex cytogenetic abnormalities. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2014;29(2):119–22.
Shimizu H, Saitoh T, Machida S, Kako S, Doki N, Mori T, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemia: results of a matched-pair analysis. Eur J Haematol. 2015;95(5):455–60.
Shimizu H, Yokohama A, Hatsumi N, Takada S, Handa H, Sakura T, et al. Philadelphia chromosome-positive mixed phenotype acute leukemia in the imatinib era. Eur J Haematol. 2014;93(4):297–301.
Steiner M, Attarbaschi A, Dworzak M, Strobl H, Pickl W, Kornmüller R, et al. Cytochemically myeloperoxidase positive childhood acute leukemia with lymphoblastic morphology treated as lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2010;32(1):e4–7.
Takata H, Ikebe T, Sasaki H, Miyazaki Y, Ohtsuka E, Saburi Y, et al. Two elderly patients with Philadelphia chromosome positive mixed phenotype acute Leukemia who were successfully treated with Dasatinib and Prednisolone. Intern Med. 2016;55(9):1177–81.
Tarsitano M, Leszl A, Parasole R, Cavaliere ML, Menna G, Di Meglio A, et al. Trisomy 7 and deletion of the 9p21 locus as novel acquired abnormalities in a case of pediatric biphenotypic acute leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2012;34(3):e126–e129.
Tassano E, Tavella E, Micalizzi C, Scuderi F, Cuoco C, Morerio C. Monosomal complex karyotype in pediatric mixed phenotype acute leukemia. Cancer Genet. 2011;204(9):507–11.
Tian H, Xu Y, Liu L, Yan L, Jin Z, Tang X, et al. Comparison of outcomes in mixed phenotype acute leukemia patients treated with chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation versus chemotherapy alone. Leuk Res. 2016;45:40–46.
Tiribelli M, Damiani D, Masolini P, Candoni A, Calistri E, Fanin R. Biological and clinical features of T-biphenotypic acute leukaemia: report from a single centre. Br J Haematol. 2004;125(6):814–5.
Udayakumar AM, Pathare AV, Alkindi S, Raeburn JA. Biphenotypic leukemia with interstitial del(9)(q22q32) as a sole abnormality. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007;178(2):170–2.
Vardhan R, Kotwal J, Ganguli P, Ahmed R, Sharma A, Singh J. Mixed phenotypic acute leukemia presenting as mediastinal mass-2 cases. Indian J Hematol & Blood Transfus: Off J Indian Soc Hematol Blood Transfus. 2016;32(Suppl 1):72–77.
Wang Y, Gu M, Mi YC, Qiu LG, Bian SG, Wang JX. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of mixed phenotype acute leukemia with Philadelphia chromosome positive and/or bcr-abl positive in adult. Int J Hematol. 2011;94(6):552–5.
Xu XQ, Wang JM, Lu SQ, Chen L, Yang JM, Zhang WP, et al. Clinical and biological characteristics of adult biphenotypic acute leukemia in comparison with that of acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case series of a Chinese population. Haematologica. 2009;94(7):919–27.
Yan LZ, Ping NN, Zhu MQ, Sun AN, Xue YQ, Ruan CG, et al. Clinical, immunophenotypic, cytogenetic, and molecular genetic features in 117 adult patients with mixed-phenotype acute leukemia defined by WHO-2008 classification. Haematol Hematol J. 2012;97(11):1708–12.
Zhang YM, Wu DP, Sun AN, Qiu HY, He GS, Jin ZM, et al. Clinical characteristics, biological profile, and outcome of biphenotypic acute leukemia: a case series. Acta Haematol. 2011;125(4):210–8.
Zucchini A, Fattori PP, Lanza F, Ferrari L, Bagli L, Imola M, et al. Biphenotypic acute leukemia: a case report. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2004;18(3-4):387–91.
Costa ES, Thiago LS, Otazu IB, Ornellas MH, Land MG, Orfao A. An uncommon case of childhood biphenotypic precursor-B/T acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;50(4):941–2.
Darwish A, Samra M, Alsharkawy N, Gaber O. Adult biphenotypic acute leukemia: The Egyptian National Cancer Institute experience. Haematologica. 2016;101:680–1.
Pawar RN, Banerjee S, Bramha S, Krishnan S, Bhattacharya A, Saha V, et al. Mixed-phenotypic acute leukemia series from tertiary care center. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2017;60(1):43–49.
Pomerantz A, Rodriguez-Rodriguez S, Demichelis-Gomez R, Barrera-Lumbreras G, Barrales-Benitez O, Lopez-Karpovitch X, et al. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: suboptimal treatment when the 2008/2016 WHO classification is used. Blood Res. 2016;51(4):233–41.
Dai H, Zhang W, Li X, Han Q, Guo Y, Zhang Y, et al. Tolerance and efficacy of autologous or donor-derived T cells expressing CD19 chimeric antigen receptors in adult B-ALL with extramedullary leukemia. Oncoimmunology. 2015;4(11):e1027469.
Yao L, Cen J, Pan J, Liu D, Wang Y, Chen Z, et al. TAF15–ZNF384 fusion gene in childhood mixed phenotype acute leukemia. Cancer Genet. 2017;211:1–4.
Shi R, Munker R. Survival of patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemias: a large population-based study. Leuk Res. 2015;39(6):606–16.
Guru Murthy GS, Dhakal I, Lee JY, Mehta P. Acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage in elderly patients—analysis of survival using surveillance epidemiology and end results-medicare database. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017;17(2):100–7.
Hrusak O, Haas VD, Luks A, Janotova I, Mejstrikova E, Bleckmann K et al. Acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage: a comprehensive survival analysis enables designing new treatment strategies. Blood. 2016;128(22):584.
Wolach O, Stone RM. How I treat mixed-phenotype acute leukemia. Blood. 2015;125(16):2477–85.
Munker R, Wang HL, Brazauskas R, Saber W, Weisdorf DJ. Allogeneic transplant for acute biphenotypic leukemia: characteristics and outcome in the CIBMTR database. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(2):S83
Author Contributions:
E.O. conceived the study; E.O., M.M., and L.K. designed the study; L.K. designed the search strategy and conducted the search; E.O., M.M. reviewed literature and extracted data; R.S. conducted the statistical analyses; E.O., M.M, M.O. and R.S. interpreted the analyses; M.M. wrote the first draft of the paper; all authors reviewed, edited, and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest:
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maruffi, M., Sposto, R., Oberley, M.J. et al. Therapy for children and adults with mixed phenotype acute leukemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Leukemia 32, 1515–1528 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-018-0058-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-018-0058-4
This article is cited by
-
Unmanipulated haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for mixed phenotype acute leukemia: a single center study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
First report of familial mixed phenotype acute leukemia: shared clinical characteristics, Philadelphia translocation, and germline variants
International Journal of Hematology (2024)
-
Successful treatment of a B/T MPAL patient by chemo-free treatment with venetoclax, azacitidine, and blinatumomab
Annals of Hematology (2024)
-
Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis in the course of mixed phenotype acute leukaemia treated with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia-like therapy—a case report
Thrombosis Journal (2023)
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing distinctly characterizes the wide heterogeneity in pediatric mixed phenotype acute leukemia
Genome Medicine (2023)