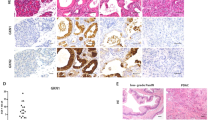
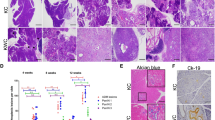
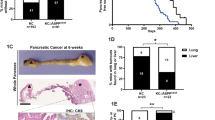
Abstract
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), a tumor-suppressor gene critically involved in familial adenomatous polyposis, is integral in Wnt/β-catenin signaling and is implicated in the development of sporadic tumors of the distal gastrointestinal tract including pancreatic cancer (PC). Here we report for the first time that functional APC is required for the growth and maintenance of pancreatic islets and maturation. Subsequently, a non-Kras mutation-induced premalignancy mouse model was developed; in this model, APC haploinsufficiency coupled with p53 deletion resulted in the development of a distinct type of pancreatic premalignant precursors, mucinous cystic neoplasms (MCNs), exhibiting pathomechanisms identical to those observed in human MCNs, including accumulation of cystic fluid secreted by neoplastic and ovarian-like stromal cells, with 100% penetrance and the presence of hepatic and gastric metastases in >30% of the mice. The major clinical implications of this study suggest targeting the Wnt signaling pathway as a novel strategy for managing MCN.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL . Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2004; 363: 1049–1057.
Maitra A, Hruban RH . Pancreatic cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 2008; 3: 157–188.
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH, Goggins M . Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2011; 378: 607–620.
Bardeesy N, DePinho RA . Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 897–909.
Hezel AF, Kimmelman AC, Stanger BZ, Bardeesy N, Depinho RA . Genetics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 1218–1249.
Horii A, Nakatsuru S, Miyoshi Y, Ichii S, Nagase H, Ando H et al. Frequent somatic mutations of the APC gene in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 6696–6698.
Maitra A, Fukushima N, Takaori K, Hruban RH . Precursors to invasive pancreatic cancer. Adv Anat Pathol 2005; 12: 81–91.
Farrell JJ, Fernandez-del Castillo C . Pancreatic cystic neoplasms: management and unanswered questions. Gastroenterology 2013; 144: 1303–1315.
Al-Haddad M, Schmidt MC, Sandrasegaran K, Dewitt J . Diagnosis and treatment of cystic pancreatic tumors. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 9: 635–648.
Ichii S, Horii A, Nakatsuru S, Furuyama J, Utsunomiya J, Nakamura Y . Inactivation of both APC alleles in an early stage of colon adenomas in a patient with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Hum Mol Genet 1992; 1: 387–390.
Bonk T, Humeny A, Sutter C, Gebert J, von Knebel Doeberitz M, Becker CM . Molecular diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP): genotyping of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) alleles by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Clin Biochem 2002; 35: 87–92.
Le Borgne J, Bouvier S, Fiche M, Smaili M, Heymann MF, Lehur PA et al. [Cystic and papillary tumor of the pancreas: diagnostic and developmental uncertainties. Apropos of a case]. Chirurgie 1997; 122: 31–34.
Beroud C, Soussi T . APC gene: database of germline and somatic mutations in human tumors and cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res 1996; 24: 121–124.
Polakis P . The adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor. Biochimica et Biophysica acta 1997; 1332: F127–F147.
Groden J, Thliveris A, Samowitz W, Carlson M, Gelbert L, Albertsen H et al. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell 1991; 66: 589–600.
Abraham SC, Klimstra DS, Wilentz RE, Yeo CJ, Conlon K, Brennan M et al. Solid-pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas are genetically distinct from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and almost always harbor beta-catenin mutations. Am J Pathol 2002; 160: 1361–1369.
Abraham SC, Wu TT, Klimstra DS, Finn LS, Lee JH, Yeo CJ et al. Distinctive molecular genetic alterations in sporadic and familial adenomatous polyposis-associated pancreatoblastomas: frequent alterations in the APC/beta-catenin pathway and chromosome 11p. Am J Pathol 2001; 159: 1619–1627.
Guo M, Jia Y, Yu Z, House MG, Esteller M, Brock MV et al. Epigenetic changes associated with neoplasms of the exocrine and endocrine pancreas. Discov Med 2014; 17: 67–73.
Pujal J, Capella G, Real FX . The Wnt pathway is active in a small subset of pancreas cancer cell lines. Biochimica et Biophysica acta 2006; 1762: 73–79.
Sato H, Suzuki H, Toyota M, Nojima M, Maruyama R, Sasaki S et al. Frequent epigenetic inactivation of DICKKOPF family genes in human gastrointestinal tumors. Carcinogenesis 2007; 28: 2459–2466.
Pasca di Magliano M, Biankin AV, Heiser PW, Cano DA, Gutierrez PJ, Deramaudt T et al. Common activation of canonical Wnt signaling in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PloS One 2007; 2: e1155.
Su LK, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW . Association of the APC tumor suppressor protein with catenins. Science 1993; 262: 1734–1737.
Rubinfeld B, Albert I, Porfiri E, Fiol C, Munemitsu S, Polakis P . Binding of GSK3beta to the APC-beta-catenin complex and regulation of complex assembly. Science 1996; 272: 1023–1026.
Toivonen S, Lundin K, Balboa D, Ustinov J, Tamminen K, Palgi J et al. Activin A and Wnt-dependent specification of human definitive endoderm cells. Exp Cell Res 2013; 319: 2535–2544.
Dessimoz J, Grapin-Botton A . Pancreas development and cancer: Wnt/beta-catenin at issue. Cell Cycle 2006; 5: 7–10.
Kaplan KB, Burds AA, Swedlow JR, Bekir SS, Sorger PK, Nathke IS . A role for the adenomatous polyposis coli protein in chromosome segregation. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 429–432.
Zumbrunn J, Kinoshita K, Hyman AA, Nathke IS . Binding of the adenomatous polyposis coli protein to microtubules increases microtubule stability and is regulated by GSK3 beta phosphorylation. Curr Biol 2001; 11: 44–49.
Fodde R, Kuipers J, Rosenberg C, Smits R, Kielman M, Gaspar C et al. Mutations in the APC tumour suppressor gene cause chromosomal instability. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 433–438.
Kuraguchi M, Wang XP, Bronson RT, Rothenberg R, Ohene-Baah NY, Lund JJ et al. Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) is required for normal development of skin and thymus. PLoS Genet 2006; 2: e146.
Hung KE, Maricevich MA, Richard LG, Chen WY, Richardson MP, Kunin A et al. Development of a mouse model for sporadic and metastatic colon tumors and its use in assessing drug treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 1565–1570.
Lang J, Maeda Y, Bannerman P, Xu J, Horiuchi M, Pleasure D et al. Adenomatous polyposis coli regulates oligodendroglial development. J Neurosci 2013; 33: 3113–3130.
Fazeli A, Steen RG, Dickinson SL, Bautista D, Dietrich WF, Bronson RT et al. Effects of p53 mutations on apoptosis in mouse intestinal and human colonic adenomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 10199–10204.
Narayan S, Jaiswal AS . Activation of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene expression by the DNA-alkylating agent N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine requires p53. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 30619–30622.
Pellegata NS, Sessa F, Renault B, Bonato M, Leone BE, Solcia E et al. K-ras and p53 gene mutations in pancreatic cancer: ductal and nonductal tumors progress through different genetic lesions. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 1556–1560.
Bardeesy N, Aguirre AJ, Chu GC, Cheng KH, Lopez LV, Hezel AF et al. Both p16(Ink4a) and the p19(Arf)-p53 pathway constrain progression of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 5947–5952.
Murakami Y, Uemura K, Ohge H, Hayashidani Y, Sudo T, Sueda T . Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas differentiated by ovarian-type stroma. Surgery 2006; 140: 448–453.
Stein U, Arlt F, Walther W, Smith J, Waldman T, Harris ED et al. The metastasis-associated gene S100A4 is a novel target of beta-catenin/T-cell factor signaling in colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2006; 131: 1486–1500.
Jiang H, Wang P, Wang Q, Wang B, Mu J, Zhuang X et al. Quantitatively controlling expression of miR-17~92 determines colon tumor progression in a mouse tumor model. Am J Pathol 2014; 184: 1355–1368.
Emmrich S, Rasche M, Schoning J, Reimer C, Keihani S, Maroz A et al. miR-99a/100~125b tricistrons regulate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell homeostasis by shifting the balance between TGFbeta and Wnt signaling. Genes Dev 2014; 28: 858–874.
Reilein A, Nelson WJ . APC is a component of an organizing template for cortical microtubule networks. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7: 463–473.
Sotillo R, Hernando E, Diaz-Rodriguez E, Teruya-Feldstein J, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW et al. Mad2 overexpression promotes aneuploidy and tumorigenesis in mice. Cancer Cell 2007; 11: 9–23.
Janssen A, van der Burg M, Szuhai K, Kops GJ, Medema RH . Chromosome segregation errors as a cause of DNA damage and structural chromosome aberrations. Science 2011; 333: 1895–1898.
Zhu M, Settele F, Kotak S, Sanchez-Pulido L, Ehret L, Ponting CP et al. MISP is a novel Plk1 substrate required for proper spindle orientation and mitotic progression. J Cell Biol 2013; 200: 773–787.
Voloshanenko O, Erdmann G, Dubash TD, Augustin I, Metzig M, Moffa G et al. Wnt secretion is required to maintain high levels of Wnt activity in colon cancer cells. Nat Commun 2013; 4: 2610.
Strom A, Bonal C, Ashery-Padan R, Hashimoto N, Campos ML, Trumpp A et al. Unique mechanisms of growth regulation and tumor suppression upon Apc inactivation in the pancreas. Development 2007; 134: 2719–2725.
Morris JPt, Cano DA, Sekine S, Wang SC, Hebrok M . Beta-catenin blocks Kras-dependent reprogramming of acini into pancreatic cancer precursor lesions in mice. J Clin Invest 2010; 120: 508–520.
Heiser PW, Lau J, Taketo MM, Herrera PL, Hebrok M . Stabilization of beta-catenin impacts pancreas growth. Development 2006; 133: 2023–2032.
Sano M, Driscoll DR, De Jesus-Monge WE, Klimstra DS, Lewis BC . Activated wnt signaling in stroma contributes to development of pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasms. Gastroenterology 2014; 146: 257–267.
Shimada M, Andoh A, Hata K, Tasaki K, Araki Y, Fujiyama Y et al. IL-6 secretion by human pancreatic periacinar myofibroblasts in response to inflammatory mediators. J Immunol 2002; 168: 861–868.
Li A, King J, Moro A, Sugi MD, Dawson DW, Kaplan J et al. Overexpression of CXCL5 is associated with poor survival in patients with pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol 2011; 178: 1340–1349.
Monti P, Leone BE, Marchesi F, Balzano G, Zerbi A, Scaltrini F et al. The CC chemokine MCP-1/CCL2 in pancreatic cancer progression: regulation of expression and potential mechanisms of antimalignant activity. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 7451–7461.
Ischenko I, Zhi J, Moll UM, Nemajerova A, Petrenko O . Direct reprogramming by oncogenic Ras and Myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 3937–3942.
Mimeault M, Batra SK . Recent progress on normal and malignant pancreatic stem/progenitor cell research: therapeutic implications for the treatment of type 1 or 2 diabetes mellitus and aggressive pancreatic cancer. Gut 2008; 57: 1456–1468.
Tang LH, Aydin H, Brennan MF, Klimstra DS . Clinically aggressive solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas: a report of two cases with components of undifferentiated carcinoma and a comparative clinicopathologic analysis of 34 conventional cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2005; 29: 512–519.
Sekine H, Chen N, Sato K, Saiki Y, Yoshino Y, Umetsu Y et al. S100A4, frequently overexpressed in various human cancers, accelerates cell motility in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012; 429: 214–219.
Tsukamoto N, Egawa S, Akada M, Abe K, Saiki Y, Kaneko N et al. The expression of S100A4 in human pancreatic cancer is associated with invasion. Pancreas 2013; 42: 1027–1033.
Kuijper S, Beverdam A, Kroon C, Brouwer A, Candille S, Barsh G et al. Genetics of shoulder girdle formation: roles of Tbx15 and aristaless-like genes. Development 2005; 132: 1601–1610.
Qin J, Liu X, Laffin B, Chen X, Choy G, Jeter CR et al. The PSA(-/lo) prostate cancer cell population harbors self-renewing long-term tumor-propagating cells that resist castration. Cell Stem Cell 2012; 10: 556–569.
Mavila N, James D, Utley S, Cu N, Coblens O, Mak K et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor-mediated activation of AKT-beta-catenin-CBP pathway regulates survival and proliferation of murine hepatoblasts and hepatic tumor initiating stem cells. PloS One 2012; 7: e50401.
Niu J, Chang Z, Peng B, Xia Q, Lu W, Huang P et al. Keratinocyte growth factor/fibroblast growth factor-7-regulated cell migration and invasion through activation of NF-kappaB transcription factors. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 6001–6011.
Ueno K, Hirata H, Majid S, Tabatabai ZL, Hinoda Y, Dahiya R . IGFBP-4 activates the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and induces M-CAM expression in human renal cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2011; 129: 2360–2369.
Milde-Langosch K, Karn T, Schmidt M, zu Eulenburg C, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Wirtz RM et al. Prognostic relevance of glycosylation-associated genes in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2014; 145: 295–305.
Jonkers J, Meuwissen R, van der Gulden H, Peterse H, van der Valk M, Berns A . Synergistic tumor suppressor activity of BRCA2 and p53 in a conditional mouse model for breast cancer. Nat Genet 2001; 29: 418–425.
Jackson EL, Willis N, Mercer K, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Montoya R et al. Analysis of lung tumor initiation and progression using conditional expression of oncogenic K-ras. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 3243–3248.
Bardeesy N, Cheng KH, Berger JH, Chu GC, Pahler J, Olson P et al. Smad4 is dispensable for normal pancreas development yet critical in progression and tumor biology of pancreas cancer. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 3130–3146.
Su HT, Weng CC, Hsiao PJ, Chen LH, Kuo TL, Chen YW et al. Stem cell marker nestin is critical for TGF-beta1-mediated tumor progression in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Res 2013; 11: 768–779.
Chiu CY, Kuo KK, Kuo TL, Lee KT, Cheng KH . The activation of MEK/ERK signaling pathway by bone morphogenetic protein 4 to increase hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Mol Cancer Res 2012; 10: 415–427.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank Dr Sheau-Fang Yang, at Kaohsiung Medical University for helping us to confirm the histologic features and pathology of MCN mice. This work was supported by grants NSC 101-2314-B-110-001-MY2, 101-2628- B-110-001-MY2 (to KH Cheng) and MOST 103-2314-B-037-062 (to DC Wu and KH Cheng) from the National Science Council, Taiwan ROC, and grants KMU-TP103G00 and KMU-TP103G01 (to DC Wu and KH Cheng) from Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
Accession codes
Microarray data are available in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) with accession number GSE 61894.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, TL., Weng, CC., Kuo, KK. et al. APC haploinsufficiency coupled with p53 loss sufficiently induces mucinous cystic neoplasms and invasive pancreatic carcinoma in mice. Oncogene 35, 2223–2234 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.284
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.284
This article is cited by
-
Loss of the transcriptional repressor TGIF1 results in enhanced Kras-driven development of pancreatic cancer
Molecular Cancer (2019)
-
Wnt pathway is involved in 5-FU drug resistance of colorectal cancer cells
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2018)