Abstract
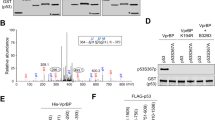
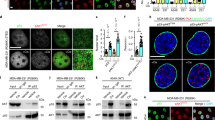
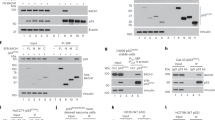
p73 is a member of the p53 tumor suppressor family, which mediates genotoxic stress response by triggering cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Similar to p53, p73 is maintained at very low levels, but it gets rapidly induced upon genotoxic stress. Mounting evidences demonstrate that p73 is primarily regulated posttranslationally. However, the molecular mechanisms which determine its stability and activity discerningly under normal and stress conditions are still not well understood. Here, we employed a proteomics approach to identify differential interactors of p73 under normal and genotoxic stress conditions. We report here that TRIM28, an E3 ligase, interacts with p73 and targets it for proteasomal degradation under normal conditions. Genotoxic stress-induced phosphorylation of p73 at tyrosine 99 residue by c-abl kinase leads to abrogation of this interaction thereby promoting p73 stabilization. Furthermore, the phosphorylated form of p73 specifically interacts with MED15, which serves as a transcriptional coactivator and leads to activation of proarrest, proapoptotic and anti-metastatic genes. RNAi-mediated abrogation of TRIM28 expression facilitates p73-mediated tumor suppression in mouse tumor models, whereas disruption of MED15 expression abrogates p73 tumor suppressor and anti-metastatic functions. These findings provide new insights into the pivotal role of Tyr99 phosphorylation in determining p73 levels and functions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan JC, Valent A et al. Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell 1997; 90: 809–819.
Jost CA, Marin MC, Kaelin WG Jr . p73 is a simian [correction of human] p53-related protein that can induce apoptosis. Nature 1997; 389: 191–194.
Zhu J, Jiang J, Zhou W, Chen X . The potential tumor suppressor p73 differentially regulates cellular p53 target genes. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 5061–5065.
Melino G, De Laurenzi V, Vousden KH . p73: Friend or foe in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 605–615.
Irwin MS, Kondo K, Marin MC, Cheng LS, Hahn WC, Kaelin WG Jr . Chemosensitivity linked to p73 function. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 403–410.
Oberst A, Rossi M, Salomoni P, Pandolfi PP, Oren M, Melino G et al. Regulation of the p73 protein stability and degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 331: 707–712.
Ozaki T, Nakagawara A . p73, a sophisticated p53 family member in the cancer world. Cancer Sci 2005; 96: 729–737.
Agami R, Blandino G, Oren M, Shaul Y . Interaction of c-Abl and p73alpha and their collaboration to induce apoptosis. Nature 1999; 399: 809–813.
Gong JG, Costanzo A, Yang HQ, Melino G, Kaelin WG Jr, Levrero M et al. The tyrosine kinase c-Abl regulates p73 in apoptotic response to cisplatin-induced DNA damage. Nature 1999; 399: 806–809.
Yuan ZM, Shioya H, Ishiko T, Sun X, Gu J, Huang YY et al. p73 is regulated by tyrosine kinase c-Abl in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Nature 1999; 399: 814–817.
Sanchez-Prieto R, Sanchez-Arevalo VJ, Servitja JM, Gutkind JS . Regulation of p73 by c-Abl through the p38 MAP kinase pathway. Oncogene 2002; 21: 974–979.
Rossi M, De Laurenzi V, Munarriz E, Green DR, Liu YC, Vousden KH et al. The ubiquitin-protein ligase Itch regulates p73 stability. EMBO J 2005; 24: 836–848.
Peschiaroli A, Scialpi F, Bernassola F, Pagano M, Melino G . The F-box protein FBXO45 promotes the proteasome-dependent degradation of p73. Oncogene 2009; 28: 3157–3166.
Strano S, Monti O, Pediconi N, Baccarini A, Fontemaggi G, Lapi E et al. The transcriptional coactivator Yes-associated protein drives p73 gene-target specificity in response to DNA Damage. Mol Cell 2005; 18: 447–459.
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, Jin B, Duraisingham S, Crook T, Lu X . ASPP1 and ASPP2: common activators of p53 family members. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 1341–1350.
Meroni G, Diez-Roux G . TRIM/RBCC, a novel class of 'single protein RING finger' E3 ubiquitin ligases. Bioessays 2005; 27: 1147–1157.
Wang C, Ivanov A, Chen L, Fredericks WJ, Seto E, Rauscher FJ 3rd et al. MDM2 interaction with nuclear corepressor KAP1 contributes to p53 inactivation. EMBO J 2005; 24: 3279–3290.
Noon AT, Shibata A, Rief N, Lobrich M, Stewart GS, Jeggo PA et al. 53BP1-dependent robust localized KAP-1 phosphorylation is essential for heterochromatic DNA double-strand break repair. Nat Cell Biol 2010; 12: 177–184.
Liang Q, Deng H, Li X, Wu X, Tang Q, Chang TH et al. Tripartite motif-containing protein 28 is a small ubiquitin-related modifier E3 ligase and negative regulator of IFN regulatory factor 7. J Immunol 2011; 187: 4754–4763.
Beer DG, Kardia SL, Huang CC, Giordano TJ, Levin AM, Misek DE et al. Gene-expression profiles predict survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Med 2002; 8: 816–824.
Yokoe T, Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, Tanaka K, Ohi M, Inoue Y et al. KAP1 is associated with peritoneal carcinomatosis in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2010; 17: 821–828.
Naar AM, Beaurang PA, Zhou S, Abraham S, Solomon W, Tjian R . Composite co-activator ARC mediates chromatin-directed transcriptional activation. Nature 1999; 398: 828–832.
Kato Y, Habas R, Katsuyama Y, Naar AM, He X . A component of the ARC/Mediator complex required for TGF beta/Nodal signalling. Nature 2002; 418: 641–646.
Yang F, Vought BW, Satterlee JS, Walker AK, Jim Sun ZY, Watts JL et al. An ARC/Mediator subunit required for SREBP control of cholesterol and lipid homeostasis. Nature 2006; 442: 700–704.
Wezensky SJ, Hanks TS, Wilkison MJ, Ammons MC, Siemsen DW, Gauss KA . Modulation of PLAGL2 transactivation by positive cofactor 2 (PC2), a component of the ARC/Mediator complex. Gene 2010; 452: 22–34.
Jing C, El-Ghany MA, Beesley C, Foster CS, Rudland PS, Smith P et al. Tazarotene-induced gene 1 (TIG1) expression in prostate carcinomas and its relationship to tumorigenicity. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 94: 482–490.
Zhang J, Liu L, Pfeifer GP . Methylation of the retinoid response gene TIG1 in prostate cancer correlates with methylation of the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Oncogene 2004; 23: 2241–2249.
Takai N, Kawamata N, Walsh CS, Gery S, Desmond JC, Whittaker S et al. Discovery of epigenetically masked tumor suppressor genes in endometrial cancer. Mol Cancer Res 2005; 3: 261–269.
Lapi E, Iovino A, Fontemaggi G, Soliera AR, Iacovelli S, Sacchi A et al. S100A2 gene is a direct transcriptional target of p53 homologues during keratinocyte differentiation. Oncogene 2006; 25: 3628–3637.
Suzuki F, Oridate N, Homma A, Nakamaru Y, Nagahashi T, Yagi K et al. S100A2 expression as a predictive marker for late cervical metastasis in stage I and II invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Oncol Rep 2005; 14: 1493–1498.
Zhang X, Hunt JL, Shin DM, Chen ZG . Down-regulation of S100A2 in lymph node metastases of head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2007; 29: 236–243.
Beitzinger M, Hofmann L, Oswald C, Beinoraviciute-Kellner R, Sauer M, Griesmann H et al. p73 poses a barrier to malignant transformation by limiting anchorage-independent growth. EMBO J 2008; 27: 792–803.
Jiang WG, Martin TA, Lewis-Russell JM, Douglas-Jones A, Ye L, Mansel RE . Eplin-alpha expression in human breast cancer, the impact on cellular migration and clinical outcome. Mol Cancer 2008; 7: 71.
Steder M, Alla V, Meier C, Spitschak A, Pahnke J, Furst K et al. DNp73 exerts function in metastasis initiation by disconnecting the inhibitory role of EPLIN on IGF1R-AKT/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Cell 2013; 24: 512–527.
Zhang S, Wang X, Osunkoya AO, Iqbal S, Wang Y, Chen Z et al. EPLIN downregulation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells and correlates with clinical lymph node metastasis. Oncogene 2011; 30: 4941–4952.
Sasaki Y, Koyama R, Maruyama R, Hirano T, Tamura M, Sugisaka J et al. CLCA2, a target of the p53 family, negatively regulates cancer cell migration and invasion. Cancer Biol Ther 2012; 13: 1512–1521.
Tanikawa C, Nakagawa H, Furukawa Y, Nakamura Y, Matsuda K . CLCA2 as a p53-inducible senescence mediator. Neoplasia 2012; 14: 141–149.
Melino G, Gallagher E, Aqeilan RI, Knight R, Peschiaroli A, Rossi M et al. Itch: a HECT-type E3 ligase regulating immunity, skin and cancer. Cell Death Differ 2008; 15: 1103–1112.
Allton K, Jain AK, Herz HM, Tsai WW, Jung SY, Qin J et al. Trim24 targets endogenous p53 for degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 11612–11616.
Rachez C, Freedman LP . Mediator complexes and transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2001; 13: 274–280.
Levy D, Adamovich Y, Reuven N, Shaul Y . Yap1 phosphorylation by c-Abl is a critical step in selective activation of proapoptotic genes in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell 2008; 29: 350–361.
Levy D, Adamovich Y, Reuven N, Shaul Y . The Yes-associated protein 1 stabilizes p73 by preventing Itch-mediated ubiquitination of p73. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 743–751.
Dotsch V, Bernassola F, Coutandin D, Candi E, Melino G . p63 and p73, the ancestors of p53. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010; 2: a004887.
Das S, Somasundaram K . Therapeutic potential of an adenovirus expressing p73 beta, a p53 homologue, against human papilloma virus positive cervical cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther 2006; 5: 210–217.
Jones RG, Plas DR, Kubek S, Buzzai M, Mu J, Xu Y et al. AMP-activated protein kinase induces a p53-dependent metabolic checkpoint. Mol Cell 2005; 18: 283–293.
Schreiber E, Matthias P, Muller MM, Schaffner W . Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res 1989; 17: 6419.
Groisman R, Polanowska J, Kuraoka I, Sawada J, Saijo M, Drapkin R et al. The ubiquitin ligase activity in the DDB2 and CSA complexes is differentially regulated by the COP9 signalosome in response to DNA damage. Cell 2003; 113: 357–367.
Han JA, Kim JI, Ongusaha PP, Hwang DH, Ballou LR, Mahale A et al. P53-mediated induction of Cox-2 counteracts p53- or genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO J 2002; 21: 5635–5644.
Ziv Y, Bielopolski D, Galanty Y, Lukas C, Taya Y, Schultz DC et al. Chromatin relaxation in response to DNA double-strand breaks is modulated by a novel ATM- and KAP-1 dependent pathway. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 870–876.
Ishikawa H, Tachikawa H, Miura Y, Takahashi N . TRIM11 binds to and destabilizes a key component of the activator-mediated cofactor complex (ARC105) through the ubiquitin-proteasome system. FEBS Lett 2006; 580: 4784–4792.
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 2509–2514.
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the Molecular Oncology Lab for helpful discussions. This work was supported by a grant from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (BT/PR7200/BRB/10/1155/2012). We also acknowledge the financial support received from NII Core Fund. YKS was supported by a fellowship from the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satija, Y., Das, S. Tyr99 phosphorylation determines the regulatory milieu of tumor suppressor p73. Oncogene 35, 513–527 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.111
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.111
This article is cited by
-
HDAC5 modulates SATB1 transcriptional activity to promote lung adenocarcinoma
British Journal of Cancer (2023)
-
The p53 family member p73 in the regulation of cell stress response
Biology Direct (2021)
-
p73 – NAV3 axis plays a critical role in suppression of colon cancer metastasis
Oncogenesis (2020)