Abstract
Dysregulation of β-catenin turnover due to mutations of its regulatory proteins including adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) and p53 is implicated in the pathogenesis of cancer. Thus, intensive effort is being made to search for alternative approaches to reduce abnormally activated β-catenin in cancer cells. Nur77, an orphan member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, has a role in the growth and apoptosis of cancer cells. Here, we reported that Nur77 could inhibit transcriptional activity of β-catenin by inducing β-catenin degradation via proteasomal degradation pathway that is glycogen synthase kinase 3β and Siah-1 independent. Nur77 induction of β-catenin degradation required both the N-terminal region of Nur77, which was involved in Nur77 ubiquitination, and the C-terminal region, which was responsible for β-catenin binding. Nur77/ΔDBD, a Nur77 mutant lacking its DNA-binding domain, resided in the cytoplasm, interacted with β-catenin, and induced β-catenin degradation, demonstrating that Nur77-mediated β-catenin degradation was independent of its DNA binding and transactivation, and might occur in the cytoplasm. In addition, we reported our identification of two digitalis-like compounds (DLCs), H-9 and ATE-i2-b4, which potently induced Nur77 expression and β-catenin degradation in SW620 colon cancer cells expressing mutant APC protein in vitro and in animals. DLC-induced Nur77 protein was mainly found in the cytoplasm, and inhibition of Nur77 nuclear export by the CRM1-dependent nuclear export inhibitor leptomycin B or Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor prevented the effect of DLC on inducing β-catenin degradation. Together, our results demonstrate that β-catenin can be degraded by cytoplasmic Nur77 through their interaction and identify H-9 and ATE-i2-b4 as potent activators of the Nur77-mediated pathway for β-catenin degradation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camacho CP, Latini FR, Oler G, Hojaij FC, Maciel RM, Riggins GJ et al. (2009). Down-regulation of NR4A1 in follicular thyroid carcinomas is restored following lithium treatment. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 70: 475–483.
Cao X, Liu W, Lin F, Li H, Kolluri SK, Lin B et al. (2004). Retinoid X receptor regulates Nur77/TR3-dependent apoptosis by modulating its nuclear export and mitochondrial targeting. Mol Cell Biol 24: 9705–9725.
Chao LC, Bensinger SJ, Villanueva CJ, Wroblewski K, Tontonoz P . (2008). Inhibition of adipocyte differentiation by Nur77, Nurr1, and Nor1. Mol Endocrinol 22: 2596–2608.
Cho SD, Yoon K, Chintharlapalli S, Abdelrahim M, Lei P, Hamilton S et al. (2007). Nur77 agonists induce proapoptotic genes and responses in colon cancer cells through nuclear receptor-dependent and nuclear receptor-independent pathways. Cancer Res 67: 674–683.
Chtarbova S, Nimmrich I, Erdmann S, Herter P, Renner M, Kitajewski J et al. (2002). Murine Nr4a1 and Herpud1 are up-regulated by Wnt-1, but the homologous human genes are independent from beta-catenin activation. Biochem J 367: 723–728.
Dawson MI, Hobbs PD, Peterson VJ, Leid M, Lange CW, Feng KC et al. (2001). Apoptosis induction in cancer cells by a novel analogue of 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]-2-naphthalenecarboxylic acid lacking retinoid receptor transcriptional activation activity. Cancer Res 61: 4723–4730.
Dillard AC, Lane MA . (2007). Retinol decreases beta-catenin protein levels in retinoic acid-resistant colon cancer cell lines. Mol Carcinog 46: 315–329.
Dillard AC, Lane MA . (2008). Retinol increases beta-catenin-RXRalpha binding leading to the increased proteasomal degradation of beta-catenin and RXRalpha. Nutr Cancer 60: 97–108.
Forman BM, Umesono K, Chen J, Evans RM . (1995). Unique response pathways are established by allosteric interactions among nuclear hormone receptors. Cell 81: 541–550.
Fu M, Wang C, Li Z, Sakamaki T, Pestell RG . (2004). Minireview: cyclin D1: normal and abnormal functions. Endocrinology 145: 5439–5447.
Han YH, Cao X, Lin B, Lin F, Kolluri SK, Stebbins J et al. (2006). Regulation of Nur77 nuclear export by c-Jun N-terminal kinase and Akt. Oncogene 25: 2974–2986.
Hart M, Concordet JP, Lassot I, Albert I, del los Santos R, Durand H et al. (1999). The F-box protein beta-TrCP associates with phosphorylated beta-catenin and regulates its activity in the cell. Curr Biol 9: 207–210.
Hutchinson DA, Mori A, Savitzky AH, Burghardt GM, Wu X, Meinwald J et al. (2007). Dietary sequestration of defensive steroids in nuchal glands of the Asian snake Rhabdophis tigrinus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 2265–2270.
Ilyas M, Tomlinson IP, Rowan A, Pignatelli M, Bodmer WF . (1997). Beta-catenin mutations in cell lines established from human colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 10330–10334.
Jiang MM, Dai Y, Gao H, Zhang X, Wang GH, He JY et al. (2008). Cardenolides from Antiaris toxicaria as potent selective Nur77 modulators. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 56: 1005–1008.
Katagiri Y, Takeda K, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Ozato K, Guroff G . (2000). Modulation of retinoid signalling through NGF-induced nuclear export of NGFI-B. Nat Cell Biol 2: 435–440.
Ke N, Claassen G, Yu DH, Albers A, Fan W, Tan P et al. (2004). Nuclear hormone receptor NR4A2 is involved in cell transformation and apoptosis. Cancer Res 64: 8208–8212.
Kitagawa H, Ray WJ, Glantschnig H, Nantermet PV, Yu Y, Leu CT et al. (2007). A regulatory circuit mediating convergence between Nurr1 transcriptional regulation and Wnt signaling. Mol Cell Biol 27: 7486–7496.
Klein PS, Melton DA . (1996). A molecular mechanism for the effect of lithium on development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 8455–8459.
Kolluri SK, Cao X, Bruey-Sedano N, Lin B, Lin F, Han Y et al. (2003). Mitogenic effect of orphan receptor TR3 and its regulation by MEKK1 in lung cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 23: 8651–8667.
Kolluri SK, Zhu X, Zhou X, Lin B, Chen Y, Sun K et al. (2008). A short Nur77-derived peptide converts Bcl-2 from a protector to a killer. Cancer Cell 14: 285–298.
Kudo N, Matsumori N, Taoka H, Fujiwara D, Schreiner EP, Wolff B et al. (1999). Leptomycin B inactivates CRM1/exportin 1 by covalent modification at a cysteine residue in the central conserved region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 9112–9117.
Lee SO, Abdelrahim M, Yoon K, Chintharlapalli S, Papineni S, Kim K et al. (2010). Inactivation of the orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell and tumor growth. Cancer Res 70: 6824–6836.
Li H, Kolluri SK, Gu J, Dawson MI, Cao X, Hobbs PD et al. (2000). Cytochrome c release and apoptosis induced by mitochondrial targeting of nuclear orphan receptor TR3. Science 289: 1159–1164.
Liang B, Song X, Liu G, Li R, Xie J, Xiao L et al. (2007). Involvement of TR3/Nur77 translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum in ER stress-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 313: 2833–2844.
Lin B, Kolluri S, Lin F, Liu W, Han YH, Cao X et al. (2004). Conversion of Bcl-2 from protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor Nur77/TR3. Cell 116: 527–540.
Liu C, Kato Y, Zhang Z, Do VM, Yankner BA, He X . (1999). beta-Trcp couples beta-catenin phosphorylation-degradation and regulates Xenopus axis formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 6273–6278.
Liu J, Stevens J, Rote CA, Yost HJ, Hu Y, Neufeld KL et al. (2001). Siah-1 mediates a novel beta-catenin degradation pathway linking p53 to the adenomatous polyposis coli protein. Mol Cell 7: 927–936.
Liu ZG, Smith SW, McLaughlin KA, Schwartz LM, Osborne BA . (1994). Apoptotic signals delivered through the T-cell receptor of a T-cell hybrid require the immediate-early gene nur77. Nature 367: 281–284.
Logan CY, Nusse R . (2004). The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20: 781–810.
Lopez-Lazaro M . (2007). Digitoxin as an anticancer agent with selectivity for cancer cells: possible mechanisms involved. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11: 1043–1053.
Matsuzawa SI, Reed JC . (2001). Siah-1, SIP, and Ebi collaborate in a novel pathway for beta-catenin degradation linked to p53 responses. Mol Cell 7: 915–926.
Maxwell MA, Muscat GE . (2006). The NR4A subgroup: immediate early response genes with pleiotropic physiological roles. Nucl Recept Signal 4: e002.
Moon RT, Bowerman B, Boutros M, Perrimon N . (2002). The promise and perils of Wnt signaling through beta-catenin. Science 296: 1644–1646.
Mullican SE, Zhang S, Konopleva M, Ruvolo V, Andreeff M, Milbrandt J et al. (2007). Abrogation of nuclear receptors Nr4a3 and Nr4a1 leads to development of acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med 13: 730–735.
Nesher M, Shpolansky U, Rosen H, Lichtstein D . (2007). The digitalis-like steroid hormones: new mechanisms of action and biological significance. Life Sci 80: 2093–2107.
Peifer M . (1997). Beta-catenin as oncogene: the smoking gun. Science 275: 1752–1753.
Peifer M, Polakis P . (2000). Wnt signaling in oncogenesis and embryogenesis–a look outside the nucleus. Science 287: 1606–1609.
Philips A, Lesage S, Gingras R, Maira MH, Gauthier Y, Hugo P et al. (1997). Novel dimeric Nur77 signaling mechanism in endocrine and lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol 17: 5946–5951.
Polakis P . (2000). Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev 14: 1837–1851.
Polakis P . (2007). The many ways of Wnt in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17: 45–51.
Ramaswamy S, Ross KN, Lander ES, Golub TR . (2003). A molecular signature of metastasis in primary solid tumors. Nat Genet 33: 49–54.
Safe S, Papineni S, Chintharlapalli S . (2008). Cancer chemotherapy with indole-3-carbinol, bis(3′-indolyl)methane and synthetic analogs. Cancer Lett 269: 326–338.
Shipp MA, Ross KN, Tamayo P, Weng AP, Kutok JL, Aguiar RC et al. (2002). Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma outcome prediction by gene-expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat Med 8: 68–74.
Steyn PS, van Heerden FR . (1998). Bufadienolides of plant and animal origin. Nat Prod Rep 15: 397–413.
Uemura H, Chang C . (1998). Antisense TR3 orphan receptor can increase prostate cancer cell viability with etoposide treatment. Endocrinology 139: 2329–2334.
Ward RD, Weigel NL . (2009). Steroid receptor phosphorylation: assigning function to site-specific phosphorylation. Biofactors 35: 528–536.
Wilson AJ, Arango D, Mariadason JM, Heerdt BG, Augenlicht LH . (2003). TR3/Nur77 in colon cancer cell apoptosis. Cancer Res 63: 5401–5407.
Wilson TE, Fahrner TJ, Johnston M, Milbrandt J . (1991). Identification of the DNA binding site for NGFI-B by genetic selection in yeast. Science 252: 1296–1300.
Woronicz JD, Calnan B, Ngo V, Winoto A . (1994). Requirement for the orphan steroid receptor Nur77 in apoptosis of T-cell hybridomas. Nature 367: 277–281.
Wu F, Mo YY . (2007). Ubiquitin-like protein modifications in prostate and breast cancer. Front Biosci 12: 700–711.
Wu H, Lin Y, Li W, Sun Z, Gao W, Zhang H et al. (2011). Regulation of Nur77 expression by {beta}-catenin and its mitogenic effect in colon cancer cells. FASEB J 25: 192–205.
Wu Q, Dawson MI, Zheng Y, Hobbs PD, Agadir A, Jong L et al. (1997a). Inhibition of trans-retinoic acid-resistant human breast cancer cell growth by retinoid X receptor-selective retinoids. Mol Cell Biol 17: 6598–6608.
Wu Q, Li Y, Liu R, Agadir A, Lee MO, Liu Y et al. (1997b). Modulation of retinoic acid sensitivity in lung cancer cells through dynamic balance of orphan receptors nur77 and COUP-TF and their heterodimerization. Embo J 16: 1656–1669.
Xiao JH, Ghosn C, Hinchman C, Forbes C, Wang J, Snider N et al. (2003). Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC)-independent regulation of beta-catenin degradation via a retinoid X receptor-mediated pathway. J Biol Chem 278: 29954–29962.
Yochum GS, Cleland R, McWeeney S, Goodman RH . (2007). An antisense transcript induced by Wnt/beta-catenin signaling decreases E2F4. J Biol Chem 282: 871–878.
Zhan Y, Du X, Chen H, Liu J, Zhao B, Huang D et al. (2008). Cytosporone B is an agonist for nuclear orphan receptor Nur77. Nat Chem Biol 4: 548–556.
Zhang XK . (2007). Targeting Nur77 translocation. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11: 69–79.
Zhao HY, Wu FK, Qiu YK, Wu Z, Jiang YT, Chen JY . (2010). Studies on cytotoxic constituents from the skin of the toad Bufo bufo gargarizans. J Asian Nat Prod Res 12: 793–800.
Zhao Y, Bruemmer D . (2010). NR4A orphan nuclear receptors: transcriptional regulators of gene expression in metabolism and vascular biology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30: 1535–1541.
Zhou H, Liu W, Su Y, Wei Z, Liu J, Kolluri SK et al. (2010). NSAID sulindac and its analog bind RXRalpha and inhibit RXRalpha-dependent AKT signaling. Cancer Cell 17: 560–573.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Zhuohua Zhang for providing β-catenin expression vectors and TOPFLASH reporter plasmid. This work is in part supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (CA140980, GM089927), the US Army Medical Research and Material Command, the 985 Project from Xiamen University, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC; 30971445 and NSCF-81001373) and NSFC/Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC; 30931160431) and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2009J01198).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Cao, X., Jiang, MM. et al. Inhibition of β-catenin signaling by nongenomic action of orphan nuclear receptor Nur77. Oncogene 31, 2653–2667 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.448
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.448
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
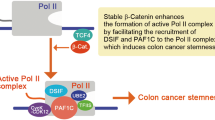
Delineating the role of nuclear receptors in colorectal cancer, a focused review
Discover Oncology (2024)
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine modification mediates downregulation of NR4A1 to facilitate malignancy of cervical cancer
Cell & Bioscience (2022)
-
Interplay between transforming growth factor-β and Nur77 in dual regulations of inhibitor of differentiation 1 for colonic tumorigenesis
Nature Communications (2021)
-
The nuclear receptor 4A family members: mediators in human disease and autophagy
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2020)
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase Trim13 regulates Nur77 stability via casein kinase 2α
Scientific Reports (2018)