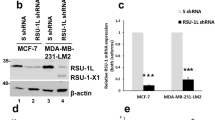
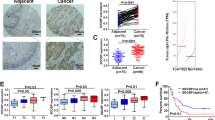
Abstract
The tyrosine kinase c-Src is upregulated in various human cancers; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying c-Src-mediated tumor progression remain unclear. Here we show that downregulation of microRNA (miR)-542-3p is tightly associated with tumor progression via c-Src-related oncogenic pathways. In c-Src-transformed fibroblasts and human cancer cells that overexpress c-Src, miR-542-3p is substantially downregulated, and the ectopic expression of miR-542-3p suppresses tumor growth. We identified the integrin-linked kinase (ILK) as a conserved target of miR-542-3p. ILK upregulation promotes cell adhesion and invasion by activating the integrin–focal adhesion kinase (FAK)/c-Src pathway, and can also contribute to tumor growth via the AKT and glycogen synthase kinase 3β pathways. MiR-542-3p expression is downregulated by the activation of c-Src-related signaling molecules, including epidermal growth factor receptor, K-Ras and Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase. In human colon cancer tissues, downregulation of miR-542-3p is significantly correlated with the upregulation of c-Src and ILK. Our results suggest that the novel c-Src–miR-542-3p–ILK–FAK circuit plays a crucial role in controlling tumor progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud ER, Coffelt SB, Figueroa YG, Zwezdaryk KJ, Nelson AB, Sullivan DE et al. (2007). Integrin-linked kinase: a hypoxia-induced anti-apoptotic factor exploited by cancer cells. Int J Oncol 30: 113–122.
Ambros V . (2004). The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431: 350–355.
Attwell S, Mills J, Troussard A, Wu C, Dedhar S . (2003). Integration of cell attachment, cytoskeletal localization, and signaling by integrin-linked kinase (ILK), CH-ILKBP, and the tumor suppressor PTEN. Mol Biol Cell 14: 4813–4825.
Bartel DP . (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297.
Bartel DP . (2009). MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136: 215–233.
Brown M, Cooper J . (1996). Regulation, substrates and functions of src. Biochim Biophys Acta 1287: 121–149.
Cabodi S, del Pilar Camacho-Leal M, Di Stefano P, Defilippi P . (2010a). Integrin signalling adaptors: not only figurants in the cancer story. Nat Rev Cancer 10: 858–870.
Cabodi S, Di Stefano P, Leal Mdel P, Tinnirello A, Bisaro B, Morello V et al. (2010b). Integrins and signal transduction. Adv Exp Med Biol 674: 43–54.
Calin GA, Croce CM . (2006). MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 857–866.
Di-Poi N, Tan NS, Michalik L, Wahli W, Desvergne B . (2002). Antiapoptotic role of PPARbeta in keratinocytes via transcriptional control of the Akt1 signaling pathway. Mol Cell 10: 721–733.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ . (2006). Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 259–269.
Frame M . (2002). Src in cancer: deregulation and consequences for cell behaviour. Biochim Biophy Acta 1602: 114–130.
Hannigan G, Troussard AA, Dedhar S . (2005). Integrin-linked kinase: a cancer therapeutic target unique among its ILK. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 51–63.
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Fitz-Gibbon L, Coppolino MG, Radeva G, Filmus J et al. (1996). Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a new beta 1-integrin-linked protein kinase. Nature 379: 91–96.
He L, Hannon GJ . (2004). MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5: 522–531.
Hehlgans S, Haase M, Cordes N . (2007). Signalling via integrins: implications for cell survival and anticancer strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1775: 163–180.
Iliopoulos D, Jaeger SA, Hirsch HA, Bulyk ML, Struhl K . (2010). STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer. Mol Cell 39: 493–506.
Ingley E . (2008). Src family kinases: regulation of their activities, levels and identification of new pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784: 56–65.
Irby R, Mao W, Coppola D, Kang J, Loubeau J, Trudeau W et al. (1999). Activating SRC mutation in a subset of advanced human colon cancers. Nat Genet 21: 187–190.
Irby R, Yeatman T . (2000). Role of Src expression and activation in human cancer. Oncogene 19: 5636–5642.
Ishizawar R, Parsons S . (2004). c-Src and cooperating partners in human cancer. Cancer Cell 6: 209–214.
Kim M, Lee KT, Jang HR, Kim JH, Noh SM, Song KS et al. (2008a). Epigenetic down-regulation and suppressive role of DCBLD2 in gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Mol Cancer Res 6: 222–230.
Kim YB, Choi S, Choi MC, Oh MA, Lee SA, Cho M et al. (2008b). Cell adhesion-dependent cofilin serine 3 phosphorylation by the integrin-linked kinase.c-Src complex. J Biol Chem 283: 10089–10096.
Legate KR, Montanez E, Kudlacek O, Fassler R . (2006). ILK, PINCH and parvin: the tIPP of integrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 20–31.
Li X, Shen Y, Ichikawa H, Antes T, Goldberg GS . (2009). Regulation of miRNA expression by Src and contact normalization: effects on nonanchored cell growth and migration. Oncogene 28: 4272–4283.
McDonald PC, Fielding AB, Dedhar S . (2008). Integrin-linked kinase—essential roles in physiology and cancer biology. J Cell Sci 121: 3121–3132.
Mitra SK, Schlaepfer DD . (2006). Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18: 516–523.
Okada M, Nada S, Yamanashi Y, Yamamoto T, Nakagawa H . (1991). CSK: a protein-tyrosine kinase involved in regulation of src family kinases. J Biol Chem 266: 24249–24252.
Oneyama C, Hikita T, Nada S, Okada M . (2008). Functional dissection of transformation by c-Src and v-Src. Genes Cells 13: 1–12.
Oneyama C, Ikeda J, Okuzaki D, Suzuki K, Kanou T, Shintani Y et al. (2011). MicroRNA-mediated downregulation of mTOR/FGFR3 controls tumor growth induced by Src-related oncogenic pathways. Oncogene 30: 3489–3501.
Persad S, Dedhar S . (2003). The role of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in cancer progression. Cancer Metast Rev 22: 375–384.
Pontier SM, Huck L, White DE, Rayment J, Sanguin-Gendreau V, Hennessy B et al. (2010). Integrin-linked kinase has a critical role in ErbB2 mammary tumor progression: implications for human breast cancer. Oncogene 29: 3374–3385.
Radeva G, Petrocelli T, Behrend E, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Filmus J, Slingerland J et al. (1997). Overexpression of the integrin-linked kinase promotes anchorage-independent cell cycle progression. J Biol Chem 272: 13937–13944.
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK . (2009). MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metast Rev 28: 369–378.
Toloubeydokhti T, Pan Q, Luo X, Bukulmez O, Chegini N . (2008). The expression and ovarian steroid regulation of endometrial micro-RNAs. Reprod Sci 15: 993–1001.
Troussard AA, McDonald PC, Wederell ED, Mawji NM, Filipenko NR, Gelmon KA et al. (2006). Preferential dependence of breast cancer cells versus normal cells on integrin-linked kinase for protein kinase B/Akt activation and cell survival. Cancer Res 66: 393–403.
Ventura A, Jacks T . (2009). MicroRNAs and cancer: short RNAs go a long way. Cell 136: 586–591.
White DE, Cardiff RD, Dedhar S, Muller WJ . (2001). Mammary epithelial-specific expression of the integrin-linked kinase (ILK) results in the induction of mammary gland hyperplasias and tumors in transgenic mice. Oncogene 20: 7064–7072.
Yang L, Olsson B, Pfeifer D, Jonsson JI, Zhou ZG, Jiang X et al. (2010). Knockdown of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-beta induces less differentiation and enhances cell-fibronectin adhesion of colon cancer cells. Oncogene 29: 516–526.
Yau CY, Wheeler JJ, Sutton KL, Hedley DW . (2005). Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase by a selective small molecule inhibitor, QLT0254, inhibits the PI3K/PKB/mTOR, Stat3, and FKHR pathways and tumor growth, and enhances gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in human orthotopic primary pancreatic cancer xenografts. Cancer Res 65: 1497–1504.
Yeatman TJ . (2004). A renaissance for SRC. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 470–480.
Yoganathan TN, Costello P, Chen X, Jabali M, Yan J, Leung D et al. (2000). Integrin-linked kinase (ILK): a ‘hot’ therapeutic target. Biochem Pharmacol 60: 1115–1119.
Yoon S, Choi YC, Lee S, Jeong Y, Yoon J, Baek K . (2010). Induction of growth arrest by miR-542-3p that targets survivin. FEBS Lett 584: 4048–4052.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs A Imamoto, T Akagi and M Yutsudo for their generous gifts of reagents. This work was supported by a Grant-in-aid for Young Scientists from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and The Exciting Leading-Edge Research Project at Osaka University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oneyama, C., Morii, E., Okuzaki, D. et al. MicroRNA-mediated upregulation of integrin-linked kinase promotes Src-induced tumor progression. Oncogene 31, 1623–1635 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.367
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.367
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Plantamajoside alleviates hypoxia-reoxygenation injury through integrin-linked kinase/c-Src/Akt and the mitochondrial apoptosis signaling pathways in H9c2 myocardial cells
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies (2023)
-
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK): the known vs. the unknown and perspectives
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
A prognostic index based on an eleven gene signature to predict systemic recurrences in colorectal cancer
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2019)
-
Loss of miR-542-3p enhances IGFBP-1 expression in decidualizing human endometrial stromal cells
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Fer tyrosine kinase oligomer mediates and amplifies Src-induced tumor progression
Oncogene (2016)