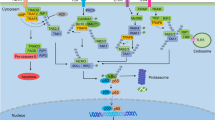
Abstract
Metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1), a master chromatin modifier, has been shown to regulate cancer progression and is widely upregulated in human cancer, including hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs). Here we provide evidence that hepatitis B virus transactivator protein HBx stimulates the expression of MTA1 but not of MTA2 or MTA3. The underlying mechanism of HBx stimulation of MTA1 involves HBx targeting of transcription factor nuclear factor (NF)-κB and the recruitment of HBx/p65 complex to the NF-κB consensus motif on the relaxed MTA1 gene chromatin. We also discovered that MTA1 depletion in HBx-expressing cells severely impairs the ability of HBx to stimulate NF-κB signaling and the expression of target proinflammatory molecules. Furthermore, the presence of HBx in HBx-infected HCCs correlated well with increased MTA1 and NF-κB-p65. Collectively, these findings revealed a previously unrecognized integral role of MTA1 in HBx stimulation of NF-κB signaling and consequently, the expression of NF-κB targets gene products with functions in inflammation and tumorigenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson P, Kedersha N . (2007). On again, off again: the SRC-3 transcriptional coactivator moonlights as a translational corepressor. Mol Cell 25: 796–797.
Bagheri-Yarmand R, Talukder AH, Wang RA, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R . (2004). Metastasis-associated protein 1 deregulation causes inappropriate mammary gland development and tumorigenesis. Development 131: 3469–3479.
Bergametti F, Prigent S, Luber B, Benoit A, Tiollais P, Sarasin A et al. (1999). The proapoptotic effect of hepatitis B virus HBx protein correlates with its transactivation activity in stably transfected cell lines. Oncogene 18: 2860–2871.
Bouchard MJ, Schneider RJ . (2004). The enigmatic X gene of hepatitis B virus. J Virol 78: 12725–12734.
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN et al. (2006). Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 295: 65–73.
Cheng AS, Chan HL, Leung WK, To KF, Go MY, Chan JY et al. (2004). Expression of HBx and COX-2 in chronic hepatitis B, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma: implication of HBx in upregulation of COX-2. Mod Pathol 17: 1169–1179.
Chirillo P, Falco M, Puri PL, Artini M, Balsano C, Levrero M et al. (1996). Hepatitis B virus pX activates NF-kappa B-dependent transcription through a Raf-independent pathway. J Virol 70: 641–646.
Ding Q, Xia W, Liu JC, Yang JY, Lee DF, Xia J et al. (2005). Erk associates with and primes GSK-3beta for its inactivation resulting in upregulation of beta-catenin. Mol Cell 19: 159–170.
Dvorchik I, Demetris AJ, Geller DA, Carr BI, Fontes P, Finkelstein SD et al. (2007). Prognostic models in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and statistical methodologies behind them. Curr Pharm Des 13: 1527–1532.
Giannini R, Cavallini A . (2005). Expression analysis of a subset of coregulators and three nuclear receptors in human colorectal carcinoma. Anticancer Res 25: 4287–4292.
Gururaj AE, Singh RR, Rayala SK, Holm C, den Hollander P, Zhang H et al. (2006). MTA1, a transcriptional activator of breast cancer amplified sequence 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 6670–6675.
Hamatsu T, Rikimaru T, Yamashita Y, Aishima S, Tanaka S, Shirabe K et al. (2003). The role of MTA1 gene expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 10: 599–604.
Hoffmann A, Baltimore D . (2006). Circuitry of nuclear factor kappaB signaling. Immunol Rev 210: 171–186.
Jang KS, Paik SS, Chung H, Oh YH, Kong G . (2006). MTA1 overexpression correlates significantly with tumor grade and angiogenesis in human breast cancers. Cancer Sci 97: 374–379.
Keasler VV, Hodgson AJ, Madden CR, Slagle BL . (2007). Enhancement of hepatitis B virus replication by the regulatory X protein in vitro and in vivo. J Virol 81: 2656–2662.
Kidd M, Modlin IM, Mane SM, Camp RL, Eick G, Latich I . (2006). The role of genetic markers—NAP1L1, MAGE-D2, and MTA1—in defining small-intestinal carcinoid neoplasia. Ann Surg Oncol 13: 253–262.
Kim SY, Kim JC, Kim JK, Kim HJ, Lee HM, Choi MS et al. (2008). Hepatitis B virus X protein enhances NFkappaB activity through cooperating with VBP1. BMB Rep 41: 158–163.
Lee T-h, Elledge SJ, Butel JS . (1995). Hepatitis B virus X protein interacts with a probable cellular DNA repair protein. J Virol 69: 1107–1114.
Li Q, Verma IM . (2002). Identification of 14-3-3sigma mutation causing cutaneous abnormality in repeated-epilation mutant mouse. Nat Rev Immunol 2: 725–734.
Li Da-Q, Ohshiro K, Reddy SDN, Pakala SB, Lee MH, Zhang Y et al. (2009). E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 regulates the stability and functions of MTA1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116: 17493–17498.
Lucito R, Schneider RJ . (1992). Hepatitis B virus X protein activates transcription factor NF-kappa B without a requirement for protein kinase C. J Virol 66: 983–991.
Lupberger J, Hildt E . (2007). A novel system for efficient gene transfer into primary human hepatocytes via cell-permeable hepatitis B virus-like particle. World J Gastroenterol 13: 74–81.
Maeda S, Kamata H, Luo JL, Leffert H, Karin M . (2005). IKKbeta couples hepatocyte death to cytokine-driven compensatory proliferation that promotes chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell 121: 977–990.
Manavathi B, Kumar R . (2007). Metastasis tumor antigens, an emerging family of multifaceted master coregulators. J Biol Chem 282: 1529–1533.
Manavathi B, Peng S, Rayala SK, Talukder AH, Wang MH, Wang RA et al. (2007a). Repression of Six3 by a corepressor regulates rhodopsin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 13128–13133.
Manavathi B, Singh K, Kumar R . (2007b). MTA family of coregulators in nuclear receptor biology and pathology. Nucl Recept Signal 5: e010.
Moon EJ, Jeong CH, Jeong JW, Kim KR, Yu DY, Murakami S et al. (2004). Hepatitis B virus X protein induces angiogenesis by stabilizing hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. FASEB J 18: 382–384.
Pahl HL . (1999). Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 18: 6853–6866.
Ray RB, Ray R . (2001). Hepatitis C virus core protein: intriguing properties and functional relevance. FEMS Microbiol Lett 202: 149–156.
Ryu SH, Chung YH, Lee H, Kim JA, Shin HD, Min HJ et al. (2008). Metastatic tumor antigen 1 is closely associated with frequent postoperative recurrence and poor survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 47: 929–936.
Schreiber E, Matthias P, Muller MM, Schaffner W . (1989). Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with ‘mini-extracts’, prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res 17: 6419.
Slagle BL, Zhou Y-Z, Butel JS . (1991). Hepatitis B virus integration event in human chromosome 17p near the p53 gene identifies the region of the chromosome commonly deleted in virus-positive hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res 51: 49–54.
Su F, Schneider RJ . (1996). Hepatitis B virus HBx protein activates transcription factor NF-kappaB by acting on multiple cytoplasmic inhibitors of rel-related proteins. J Virol 70: 4558–4566.
Toh Y, Pencil SD, Nicolson GL . (1995). Analysis of the complete sequence of the novel metastasis-associated candidate gene, mta1, differentially expressed in mammary adenocarcinoma and breast cancer cell lines. Gene 159: 97–104.
Weil R, Sirma H, Giannini C, Kremsdorf D, Bessia C, Dargemont C et al. (1999). Direct association and nuclear import of the Hepatitis B virus X protein with the NF-B inhibitor IB. Mol Cell Biol 19: 6345–6354.
Yoo YG, Na TY, Seo HW, Seong JK, Park CK, Shin YK et al. (2008). Hepatitis B virus X protein induces the expression of MTA1 and HDAC1, which enhances hypoxia signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene 27: 3405–3413.
Yun C, Um HR, Jin YH, Wang JH, Lee MO, Park S et al. (2002). NF-kappaB activation by hepatitis B virus X (HBx) protein shifts the cellular fate toward survival. Cancer Lett 184: 97–104.
Zhang X, Zhang H, Ye L . (2006). Effects of hepatitis B virus X protein on the development of liver cancer. J Lab Clin Med 147: 58–66.
Acknowledgements
We thank Aleem Siddiqui for pCMVXF and pCMV-Core constructs, Ranjit Banerjee for the HVC core plasmid, Amanda J Hodgson for technical assistance and Xuemei Wang for statistical analysis. The work was supported by NIH Grant CA98823 (RK). Work in Dr Betty L Slagle laboratory is supported by the NIH Grant 95388.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bui-Nguyen, T., Pakala, S., Sirigiri, R. et al. NF-κB signaling mediates the induction of MTA1 by hepatitis B virus transactivator protein HBx. Oncogene 29, 1179–1189 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.404
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.404
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Elevated MTA1 induced the migration and invasion of renal cell carcinoma through the NF-κB pathway
BMC Urology (2020)
-
Wogonin inhibits in vitro herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 infection by modulating cellular NF-κB and MAPK pathways
BMC Microbiology (2020)
-
Dynamic expression of ZNF382 and its tumor-suppressor role in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinogenesis
Oncogene (2019)
-
Hepatic SATB1 induces paracrine activation of hepatic stellate cells and is upregulated by HBx
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2/3 interacts with p65 and stabilizes it in the cytoplasm in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma
BMC Cancer (2015)