Abstract
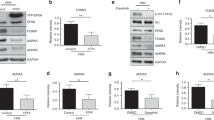
GRIM-19 (Gene associated with Retinoid-Interferon-induced Mortality 19) is a novel tumor suppressor regulated by interferon/retinoid combination. We have recently shown that GRIM-19 inhibits v-Src-induced oncogenic transformation and metastatic behavior of cells. Oncogenic v-Src induces cell motility by cytoskeletal remodeling, especially the formation of podosomes and. Here, we show that GRIM-19 inhibited the v-Src-induced cell motility by inhibiting cytoskeletal remodeling, that is, podosome formation. We also show that the N terminus of GRIM-19 played a major role in this process and identified critical residues in this region. More importantly, we show that tumor-associated GRIM-19 mutations disrupted its ability to inhibit v-Src-induced cell motility. These actions appear to occur independently of STAT3, a known target of GRIM-19-mediated inhibition. Lastly, tumor-associated GRIM-19 mutants significantly lost their ability to control v-Src-induced metastases in vivo, indicating the biological and pathological significance of these observations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alchanati I, Nallar SC, Sun P, Gao L, Hu J, Stein A et al. (2006). A proteomic analysis reveals the loss of expression of the cell death regulatory gene GRIM-19 in human renal cell carcinomas. Oncogene 25: 7138–7147.
Angell JE, Lindner DJ, Shapiro PS, Hofmann ER, Kalvakolanu DV . (2000). Identification of GRIM-19, a novel cell death-regulatory gene induced by the interferon-beta and retinoic acid combination, using a genetic approach. J Biol Chem 275: 33416–33426.
Bromberg JF, Horvath CM, Besser D, Lathem WW, Darnell Jr JE . (1998). Stat3 activation is required for cellular transformation by v-src. Mol Cell Biol 18: 2553–2558.
Coussens LM, Fingleton B, Matrisian LM . (2002). Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: trials and tribulations. Science 295: 2387–2392.
Ellis C, Moran M, McCormick F, Pawson T . (1990). Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature 343: 377–381.
Fearnley IM, Carroll J, Shannon RJ, Runswick MJ, Walker JE, Hirst J . (2001). GRIM-19, a cell death regulatory gene product, is a subunit of bovine mitochondrial NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I). J Biol Chem 276: 38345–38348.
Frame MC, Fincham VJ, Carragher NO, Wyke JA . (2002). v-Src's hold over actin and cell adhesions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 233–245.
Hakak Y, Hsu YS, Martin GS . (2000). Shp-2 mediates v-Src-induced morphological changes and activation of the anti-apoptotic protein kinase Akt. Oncogene 19: 3164–3171.
Head JA, Jiang D, Li M, Zorn LJ, Schaefer EM, Parsons JT et al. (2003). Cortactin tyrosine phosphorylation requires Rac1 activity and association with the cortical actin cytoskeleton. Mol Biol Cell 14: 3216–3229.
Huang C, Ni Y, Wang T, Gao Y, Haudenschild CC, Zhan X . (1997). Down-regulation of the filamentous actin cross-linking activity of cortactin by Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 272: 13911–13915.
Itoh M, Murata T, Suzuki T, Shindoh M, Nakajima K, Imai K et al. (2006). Requirement of STAT3 activation for maximal collagenase-1 (MMP-1) induction by epidermal growth factor and malignant characteristics in T24 bladder cancer cells. Oncogene 25: 1195–1204.
Jonasch E, Haluska FG . (2001). Interferon in oncological practice: review of interferon biology, clinical applications, and toxicities. Oncologist 6: 34–55.
Kalakonda S, Nallar SC, Gong P, Lindner DJ, Goldblum SE, Reddy SP et al. (2007a). Tumor suppressive protein gene associated with retinoid-interferon-induced mortality (GRIM)-19 inhibits src-induced oncogenic transformation at multiple levels. Am J Pathol 171: 1352–1368.
Kalakonda S, Nallar SC, Lindner DJ, Hu J, Reddy SP, Kalvakolanu DV . (2007b). Tumor-suppressive activity of the cell death activator GRIM-19 on a constitutively active signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Cancer Res 67: 6212–6220.
Kolla V, Lindner DJ, Xiao W, Borden EC, Kalvakolanu DV . (1996). Modulation of interferon (IFN)-inducible gene expression by retinoic acid. Up-regulation of STAT1 protein in IFN-unresponsive cells. J Biol Chem 271: 10508–10514.
Lindner DJ, Borden EC, Kalvakolanu DV . (1997). Synergistic antitumor effects of a combination of interferons and retinoic acid on human tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 3: 931–937.
Lufei C, Ma J, Huang G, Zhang T, Novotny-Diermayr V, Ong CT et al. (2003). GRIM-19, a death-regulatory gene product, suppresses Stat3 activity via functional interaction. EMBO J 22: 1325–1335.
Ma X, Karra S, Guo W, Lindner DJ, Hu J, Angell JE et al. (2001). Regulation of interferon and retinoic acid-induced cell death activation through thioredoxin reductase. J Biol Chem 276: 24843–24854.
Martin GS . (2001). The hunting of the Src. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 467–475.
Maximo V, Botelho T, Capela J, Soares P, Lima J, Taveira A et al. (2005). Somatic and germline mutation in GRIM-19, a dual function gene involved in mitochondrial metabolism and cell death, is linked to mitochondrion-rich (Hurthle cell) tumours of the thyroid. Br J Cancer 92: 1892–1898.
Mizutani K, Miki H, He H, Maruta H, Takenawa T . (2002). Essential role of neural Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein in podosome formation and degradation of extracellular matrix in src-transformed fibroblasts. Cancer Res 62: 669–674.
Monsky WL, Kelly T, Lin CY, Yeh Y, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Mueller SC et al. (1993). Binding and localization of M(r) 72,000 matrix metalloproteinase at cell surface invadopodia. Cancer Res 53: 3159–3164.
Ng DC, Lin BH, Lim CP, Huang G, Zhang T, Poli V et al. (2006). Stat3 regulates microtubules by antagonizing the depolymerization activity of stathmin. J Cell Biol 172: 245–257.
Rodriguez OC, Schaefer AW, Mandato CA, Forscher P, Bement WM, Waterman-Storer CM . (2003). Conserved microtubule–actin interactions in cell movement and morphogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 5: 599–609.
Scott LA, Vass JK, Parkinson EK, Gillespie DA, Winnie JN, Ozanne BW . (2004). Invasion of normal human fibroblasts induced by v-Fos is independent of proliferation, immortalization, and the tumor suppressors p16INK4a and p53. Mol Cell Biol 24: 1540–1559.
Seo T, Lee D, Shim YS, Angell JE, Chidambaram NV, Kalvakolanu DV et al. (2002). Viral interferon regulatory factor 1 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus interacts with a cell death regulator, GRIM19, and inhibits interferon/retinoic acid-induced cell death. J Virol 76: 8797–8807.
Tehrani S, Faccio R, Chandrasekar I, Ross FP, Cooper JA . (2006). Cortactin has an essential and specific role in osteoclast actin assembly. Mol Biol Cell 17: 2882–2895.
Tehrani S, Tomasevic N, Weed S, Sakowicz R, Cooper JA . (2007). Src phosphorylation of cortactin enhances actin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 11933–11938.
Wittmann T, Waterman-Storer CM . (2001). Cell motility: can Rho GTPases and microtubules point the way? J Cell Sci 114: 3795–3803.
Wu H, Parsons JT . (1993). Cortactin, an 80/85-kilodalton pp60src substrate, is a filamentous actin-binding protein enriched in the cell cortex. J Cell Biol 120: 1417–1426.
Wu H, Reynolds AB, Kanner SB, Vines RR, Parsons JT . (1991). Identification and characterization of a novel cytoskeleton-associated pp60src substrate. Mol Cell Biol 11: 5113–5124.
Zhang J, Yang J, Roy SK, Tininini S, Hu J, Bromberg JF et al. (2003). The cell death regulator GRIM-19 is an inhibitor of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 9342–9347.
Zhang L, Gao L, Li Y, Lin G, Shao Y, Ji K et al. (2008). Effects of plasmid-based Stat3-specific short hairpin RNA and GRIM-19 on PC-3M tumor cell growth. Clin Cancer Res 14: 559–568.
Acknowledgements
DVK thanks National Cancer Institute (CA105005) for the grant support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, P., Nallar, S., Kalakonda, S. et al. GRIM-19 inhibits v-Src-induced cell motility by interfering with cytoskeletal restructuring. Oncogene 28, 1339–1347 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.480
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.480
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
GRIM-19 mutations fail to inhibit v-Src-induced oncogenesis
Oncogene (2014)
-
Nicotine promotes apoptosis resistance of breast cancer cells and enrichment of side population cells with cancer stem cell-like properties via a signaling cascade involving galectin-3, α9 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and STAT3
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2014)
-
Ischemia-Induced Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex I in Rat Brain: Effect of Permeabilization Method and Electron Acceptor
Neurochemical Research (2012)
-
Identification of alternatively spliced GRIM-19 mRNA in kidney cancer tissues
Journal of Human Genetics (2010)