Abstract
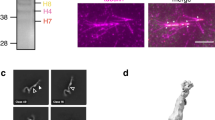
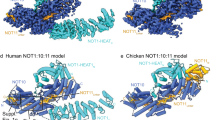
The origin licensing repressor geminin is a unique bifunctional protein providing a molecular link between cellular proliferation, differentiation and genomic stability. Here we report the first molecular structure of human geminin, determined by EM and image processing at a resolution of 17.5 Å. The geminin molecule is a tetramer formed by two dimers with monomers interacting via coiled-coil domains. The unusual structural organization of geminin provides molecular insight into its bifunctional nature.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell, S.P. & Dutta, A. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 333–374 (2002).
McGarry, T.J. & Kirschner, M.W. Cell 93, 1043–1053 (1998).
Kroll, K.L., Salic, A.N., Evans, L.M. & Kirschner, M.W. Development 125, 3247–3258 (1998).
Wohlschlegel, J.A. et al. Science 290, 2309–2312 (2000).
Tada, S., Li, A., Maiorano, D., Mechali, M. & Blow, J.J. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 107–113 (2001).
Quinn, L.M., Herr, A., McGarry, T.J. & Richardson, H. Genes Dev. 15, 2741–2754 (2001).
Shreeram, S., Sparks, A., Lane, D.P. & Blow, J.J. Oncogene 21, 6624–6632 (2002).
Vaziri, C. et al. Mol. Cell 11, 997–1008 (2003).
Melixetian, M. et al. J. Cell Biol. 165, 473–482 (2004).
Luo, L., Yang, X., Takihara, Y., Knoetgen, H. & Kessel, M. Nature 427, 749–753 (2004).
Del Bene, F., Tessmar-Raible, K. & Wittbrodt, J. Nature 427, 745–749 (2004).
Stoeber, K. et al. EMBO J. 17, 7219–7229 (1998).
van Heel, M., Harauz, G., Orlova, E.V., Schmidt, R. & Schatz, M. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 17–24 (1996).
Thepaut, M. et al. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1599, 149–151 (2002).
Walshaw, J. & Woolfson, D.N. J. Struct. Biol. 144, 349–361 (2003).
Yanagi, K., Mizuno, T., You, Z. & Hanaoka, F. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 40871–40880 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Dutta for geminin cDNA and H. Saibil, D. Madge and D. Selwood for stimulating discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. This work has been funded by Cancer Research UK scientific programme grant SP2360/0103 (G.H.W. and K.S.) and by UK Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council programme grant 31/SB09826 (A.L.O., E.V.O., C.B. and U.G.). S.R.K. is supported by a UK Medical Research Council studentship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Biochemical properties of recombinant geminin. (PDF 279 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Three-dimensional reconstruction of human geminin. (PDF 66 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Properties of an N-terminal truncated form of human geminin and modeling of geminin's dimeric coiled coil domain. (PDF 92 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okorokov, A., Orlova, E., Kingsbury, S. et al. Molecular structure of human geminin. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11, 1021–1022 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb835
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb835
This article is cited by
-
SPOP mutation induces replication over-firing by impairing Geminin ubiquitination and triggers replication catastrophe upon ATR inhibition
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Small-molecule mimics of an α-helix for efficient transport of proteins into cells
Nature Methods (2007)
-
A Cdt1–geminin complex licenses chromatin for DNA replication and prevents rereplication during S phase in Xenopus
The EMBO Journal (2006)
-
Preventing re-replication of chromosomal DNA
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2005)