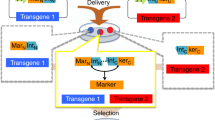
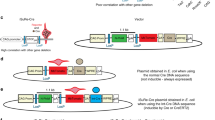
Abstract
Here we describe the generation of a double-fluorescent Cre/loxP indicator system. This protocol involves (i) all cloning steps to generate the plasmid vector (3–5 months); (ii) a guide to prepare high-efficiency transformation competent E. coli; (iii) generation of double-fluorescent reporter cell lines (3–4 weeks); and (iv) the functional testing of the indicator cell lines by application of cell-permeable Cre recombinase. The indicator is designed to monitor recombination events by switching the fluorescence light from red to green. The red fluorescence, indicating the nonrecombined state, is accompanied by the expression of a resistance gene against the antibiotic blasticidin. Appearance of green fluorescence concomitantly with the activation of puromycin-acetyltransferase monitors the recombination of the indicator construct by the Cre recombinase. In summary, we have developed a plasmid vector allowing a fast, stable and straightforward generation of transgenic clones. The expression of red fluorescent protein enables the selection of positive clones upon transfection and significantly shortens the time for identification of stable clones. This feature and the option to select for recombined cells by puromycin application are advantages compared with other alternative methods. Moreover, we developed a method utilizing cell-permeable Cre protein to validate the transgenic clones. Ultimately, this powerful methodology facilitates Cre/loxP-based applications such as cell lineage tracking or monitoring of cell fusion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoess, R.H. & Abremski, K. Interaction of the bacteriophage P1 recombinase Cre with the recombining site loxP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 1026–1029 (1984).
Sternberg, N. & Hamilton, D. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. I. Recombination between loxP sites. J. Mol. Biol. 150, 467–486 (1981).
Sternberg, N., Hamilton, D. & Hoess, R. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. II. Recombination between loxP and the bacterial chromosome. J. Mol. Biol. 150, 487–507 (1981).
Sauer, B. & Henderson, N. Site-specific DNA recombination in mammalian cells by the Cre recombinase of bacteriophage P1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 5166–5170 (1988).
Gu, H., Zou, Y.R. & Rajewsky, K. Independent control of immunoglobulin switch recombination at individual switch regions evidenced through Cre-loxP-mediated gene targeting. Cell 73, 1155–1164 (1993).
Gopaul, D.N., Guo, F. & Van Duyne, G.D. Structure of the Holliday junction intermediate in Cre-loxP site-specific recombination. EMBO J. 17, 4175–4187 (1998).
Alvarez-Dolado, M. et al. Fusion of bone-marrow-derived cells with Purkinje neurons, cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Nature 425, 968–973 (2003).
Kühn, R., Schwenk, F., Aguet, M. & Rajewsky, K. Inducible gene targeting in mice. Science 269, 1427–1429 (1995).
Schwenk, F., Kuhn, R., Angrand, P.O., Rajewsky, K. & Stewart, A.F. Temporally and spatially regulated somatic mutagenesis in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 1427–1432 (1998).
Buch, T. et al. A Cre-inducible diphtheria toxin receptor mediates cell lineage ablation after toxin administration. Nat. Methods 2, 419–426 (2005).
Nolden, L. et al. Site-specific recombination in human embryonic stem cells induced by cell-permeant Cre recombinase. Nat. Methods 3, 461–467 (2000).
Kolossov, E. et al. Engraftment of engineered ES cell-derived cardiomyocytes but not BM cells restores contractile function to the infarcted myocardium. J. Exp. Med. 203, 2315–2327 (2006).
Lakso, M. et al. Targeted oncogene activation by site-specific recombination in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 6232–6236 (1992).
Peitz, M., Pfannkuche, K., Rajewsky, K. & Edenhofer, F. Ability of the hydrophobic FGF and basic TAT peptides to promote cellular uptake of recombinant Cre recombinase: a tool for efficient genetic engineering of mammalian genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 4489–4494 (2002).
Peitz, M. et al. Enhanced purification of cell-permeant Cre and germline transmission after transduction into mouse embryonic stem cells. Genesis 45, 508–517 (2007).
Stoller, J.Z., Degenhardt, K.R., Huang, L., Zhou, D.D., Lu, M.M. & Epstein, J.A. Cre reporter mouse expressing a nuclear localized fusion of GFP and beta-galactosidase reveals new derivatives of Pax3-expressing precursors. Genesis 46, 200–204 (2008).
Soriano, P. Generalized lacZ expression with the ROSA26 Cre reporter strain. Nat. Genet. 21, 70–71 (1999).
Mao, X., Fujiwara, Y. & Orkin, S.H. Improved reporter strain for monitoring Cre recombinase-mediated DNA excisions in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 5037–5042 (1999).
Novak, A., Guo, C., Yang, W. & Nagy, A. Lobe CG.Z/EG, a double reporter mouse line that expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein upon Cre-mediated excision. Genesis 28, 147–155 (2000).
Laugwitz, K.L. et al. Postnatal isl1+ cardioblasts enter fully differentiated cardiomyocyte lineages. Nature 433, 647–653 (2005). Erratum in: Nature 446, 934 (2007).
Friedrich, G. & Soriano, P. Promoter traps in embryonic stem cells: a genetic screen to identify and mutate developmental genes in mice. Genes Dev. 5, 1513–1523 (1991).
Christ, N. & Dröge, P. Genetic manipulation of mouse embryonic stem cells by mutant lambda integrase. Genesis 32, 203–208 (2002).
Inoue, H., Nojima, H. & Okayama, H. High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. Gene 96, 23–28 (1990).
Chung, C.T., Niemela, S.L. & Miller, R.H. One-step preparation of competent Escherichia coli: transformation and storage of bacterial cells in the same solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 2172–2175 (1989).
Acknowledgements
The work presented here was supported by a grant from the Imhoff Stiftung to K.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfannkuche, K., Wunderlich, F., Doss, M. et al. Generation of a double-fluorescent double-selectable Cre/loxP indicator vector for monitoring of intracellular recombination events. Nat Protoc 3, 1510–1526 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.143
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.143
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.