Abstract
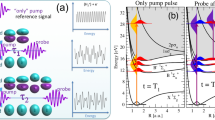
High-harmonic spectroscopy uses attosecond techniques to measure single-atom or molecule photorecombination cross-sections. Whereas the amplitude of the extreme-ultraviolet light is easily measurable, the phase is more challenging to access. However, the phase contains information necessary for tomographic imaging of the molecular orbital wavefunction with attosecond–ångström resolution. Present techniques cannot simultaneously measure the phase as a function of molecular angle and photon frequency, which is necessary for a full reconstruction of the wavefunction. We overcome this limitation with an all-optical method that does not require any ad hoc assumptions about the phase. We apply it to record the full phase map of aligned bromine molecules relative to reference xenon atoms. It allows us to resolve, both spectrally and angularly, the participation of multiple molecular orbitals, and infer a phase of ionization. This method opens a path to time-resolved molecular orbital tomography.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corkum, P. B. & Krausz, F. Attosecond science. Nature Phys. 3, 381–387 (2007).
Le, A-T., Lucchese, R. R., Tonzani, S., Morishita, T. & Lin, C. D. Quantitative rescattering theory for high-order harmonic generation from molecules. Phys. Rev. A 80, 013401 (2009).
Popmintchev, T., Chen, M-C., Arpin, P., Murnane, M. M. & Kapteyn, H. C. The attosecond nonlinear optics of bright coherent X-ray generation. Nature Photon. 4, 822–832 (2010).
Frolov, M. V., Manakov, N. L., Sarantseva, T. S. & Starace, A. F. Analytic confirmation that the factorized formula for harmonic generation involves the exact photorecombination cross section. Phys. Rev. A 83, 043416 (2011).
Shiner, A. D. et al. Probing collective multi-electron dynamics in xenon with high-harmonic spectroscopy. Nature Phys. 7, 464–467 (2011).
Mairesse, Y. et al. Attosecond synchronization of high-harmonic soft X-rays. Science 302, 1540–1543 (2003).
Wörner, H. J., Bertrand, J. B., Corkum, P. B. & Villeneuve, D. M. High-harmonic homodyne detection of the ultrafast dissociation of BR2 molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 103002 (2010).
Boutu, W. et al. Coherent control of attosecond emission from aligned molecules. Nature Phys. 4, 545–549 (2008).
Smirnova, O. et al. High harmonic interferometry of multi-electron dynamics in molecules. Nature 460, 972–977 (2009).
Mairesse, Y. et al. High harmonic spectroscopy of multichannel dynamics in strong-field ionization. Phy. Rev. Lett. 104, 213601 (2010).
Wörner, H. J., Bertrand, J. B., Kartashov, D. V., Corkum, P. B. & Villeneuve, D. M. Following a chemical reaction using high-harmonic interferometry. Nature 466, 604–607 (2010).
Itatani, J. et al. Tomographic imaging of molecular orbitals. Nature 432, 867–871 (2004).
Haessler, S. et al. Attosecond imaging of molecular electronic wavepackets. Nature Phys. 6, 200–2006 (2010).
Vozzi, C. et al. Generalized molecular orbital tomography. Nature Phys. 7, 822–826 (2011).
Haessler, S., Caillat, J. & Salières, P. Self-probing of molecules with high harmonic generation. J. Phys. B 44, 203001 (2011).
Paul, P. M. et al. Observation of a train of attosecond pulses from high harmonic generation. Science 292, 1689–1692 (2001).
Mairesse, Y. & Quéré, F. Frequency-resolved optical gating for complete reconstruction of attosecond bursts. Phys. Rev. A 71, 011401 (2005).
Zhou, X. et al. Molecular recollision interferometry in high harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 073902 (2008).
McFarland, B. K., Farrell, J. P., Bucksbaum, P. H. & Gühr, M. High-order harmonic phase in molecular nitrogen. Phys. Rev. A 80, 033412 (2009).
Wagner, N. et al. Extracting the phase of high-order harmonic emission from a molecule using transient alignment in mixed samples. Phys. Rev. A 76, 061403 (2007).
Stapelfeldt, H. & Seideman, T. Aligning molecules with strong laser pulses. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 543–557 (2003).
Lewenstein, M., Balcou, P., Ivanov, M. Y., L’Huillier, A. & Corkum, P. B. Theory of high-harmonic generation by low-frequency laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 49, 2117–2132 (1994).
Kanai, T., Takahashi, E. J., Nabekawa, Y. & Midorikawa, K. Destructive interference during high harmonic generation in mixed gases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 153904 (2007).
McFarland, B. K., Farrell, J. P., Bucksbaum, P. H. & Gühr, M. High harmonic generation from multiple orbitals in N2 . Science 322, 1232–1235 (2008).
Wörner, H. J., Bertrand, J. B., Hockett, P., Corkum, P. B. & Villeneuve, D. M. Controlling the interference of multiple molecular orbitals in high-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 233904 (2010).
Yakovlev, V. S., Ivanov, M. & Krausz, F. Enhanced phase-matching for generation of soft X-ray harmonics and attosecond pulses in atomic gases. Opt. Express 15, 15351–15364 (2007).
Gianturco, F. A., Lucchese, R. R. & Sanna, N. Calculation of low-energy elastic cross sections for electron-CF4 scattering. J. Chem. Phys. 100, 6464–6471 (1994).
Natalense, A. P. P. & Lucchese, R. R. Cross section and asymmetry parameter calculation for sulphur 1s photoionization of SF6 . J. Chem. Phys. 111, 5344–5348 (1999).
Lein, M., Hay, N., Velotta, R., Marangos, J. & Knight, P. Role of the intramolecular phase in high-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 183903 (2002).
Lee, K. F., Villeneuve, D. M., Corkum, P. B., Stolow, A. & Underwood, J. G. Field-free three-dimensional alignment of polyatomic molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 173001 (2006).
De, S. et al. Field-free orientation of CO molecules by femtosecond two-colour laser fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 153002 (2009).
Wörner, H. J. et al. Conical intersection dynamics in NO2 probed by homodyne high-harmonic spectroscopy. Science 334, 208–212 (2011).
Whitaker, B. J. Shining light on diabolic points. Science 334, 187–188 (2011).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from NSERC, CIPI, AFOSR and the NRC-CEA agreement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.B.B., H.J.W., P.S., D.M.V. and P.B.C. conceived the experiment and helped prepare the manuscript. J.B.B. and H.J.W. performed all experiments. J.B.B. and D.M.V. developed the LAPIN algorithm. J.B.B. did all data analysis and calculations, prepared all figures and led the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1424 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertrand, J., Wörner, H., Salières, P. et al. Linked attosecond phase interferometry for molecular frame measurements. Nature Phys 9, 174–178 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2540
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2540
This article is cited by
-
Electronic wavefunctions probed by all-optical attosecond interferometry
Nature Photonics (2019)
-
Attosecond imaging of molecules using high harmonic spectroscopy
Nature Reviews Physics (2019)
-
Controlling the orbital angular momentum of high harmonic vortices
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Petahertz optical oscilloscope
Nature Photonics (2013)