Abstract
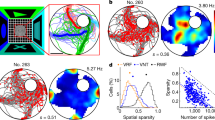
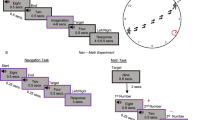
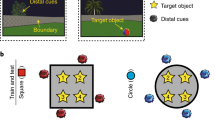
The spatial selectivity of hippocampal neurons suggests that they contribute to an internal representation of current location. The activity of hippocampal pyramidal cells was recorded while adult (10–13 months old) and aged (24–28 months old) rats performed a task in which two spatial reference frames were put in conflict. Rats attempted to find an unmarked goal whose position was fixed relative to only one of the two reference frames. The ability of a rat's hippocampus to adjust to the conflicting information and use the 'correct' position estimate (hippocampal map 'realignment') was correlated with the rat's ability to find the hidden goal. In addition, aged rats were impaired relative to adult rats in both goal-finding accuracy and map realignment. Thus, changes in the effectiveness with which the hippocampal spatial representation is updated on the basis of external cues may contribute to both within-age-group spatial learning variability and age-related spatial learning deficits.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Keefe, J. & Dostrovsky, J. The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res. 34, 171–175 (1971).
Wilson, M.A. & McNaughton, B.L. Dynamics of the hippocampal ensemble code for space. Science 261, 1055–1058 (1993).
O'Keefe, J. & Nadel, L. The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1978).
Pico, R.M., Gerbrandt, L.K., Pondel, M. & Ivy, G. During stepwise cue deletion, rat place behaviors correlate with place unit responses. Brain Res. 330, 369–372 (1985).
Shapiro, M.L. et al. Intrahippocampal grafts of fetal basal forebrain tissue alter place fields in the hippocampus of rats with fimbria-fornix lesions. Neuroscience 32, 1–18 (1989).
Markus, E.J., Barnes, C.A., McNaughton, B.L., Gladden, V.L. & Skaggs, W.E. Spatial information content and reliability of hippocampal CA1 neurons: Effects of visual input. Hippocampus 4, 410–421 (1994).
Mizumori, S.J.Y., Miya, D.Y. & Ward, K.E. Reversible inactivation of the lateral dorsal thalamus disrupts hippocampal place representation and impairs spatial learning. Brain Res. 644, 168–174 (1994).
Lenck-Santini, P.P., Save, E. & Poucet, B. Evidence for a relationship between place-cell spatial firing and spatial memory performance. Hippocampus 11, 377–390 (2001).
Cooper, B.G. & Mizumori, S.J. Temporary inactivation of the retrosplenial cortex causes a transient reorganization of spatial coding in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 21, 3986–4001 (2001).
Wilson, M.A. & Tonegawa, S. Synaptic plasticity, place cells and spatial memory: Study with second generation knockouts. Trends Neurosci. 20, 102–106 (1997).
Rotenberg, A., Abel, T., Hawkins, R.D., Kandel, E.R. & Muller, R.U. Parallel instabilities of long-term potentiation, place cells, and learning caused by decreased protein kinase A activity. J. Neurosci. 20, 8096–8102 (2000).
Bures, J., Fenton, A.A., Kaminsky, Y. & Zinyuk, L. Place cells and place navigation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 343–350 (1997).
Jeffery, K.J., Gilbert, A., Burton, S. & Strudwick, A. Preserved performance in a hippocampal-dependent spatial task despite complete place cell remapping. Hippocampus 13, 133–147 (2003).
O'Keefe, J. & Speakman, A. Single unit activity in the rat hippocampus during a spatial memory task. Exp. Brain Res. 68, 1–27 (1987).
Lenck-Santini, P.P., Muller, R.U., Save, E. & Poucet, B. Relationships between place cell firing fields and navigational decisions by rats. J. Neurosci. 22, 9035–9047 (2002).
Gallagher, M. & Pelleymounter, M.A. Spatial learning deficits in old rats: A model for memory decline in the aged. Neurobiol. Aging 9, 363–369 (1988).
Barnes, C.A. Animal models of age-related cognitive decline. in Handbook of Neuropsychology (eds. Boller, F. & Grafman, J.) 169–196 (Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, 1990).
Rosenzweig, E.S. & Barnes, C.A. Impact of aging on hippocampal function: Plasticity, network dynamics, and cognition. Prog. Neurobiol. in press (2003).
Foster, T.C. Involvement of hippocampal synaptic plasticity in age-related memory decline. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 30, 236–249 (1999).
Bliss, T.V.P. & Gardner-Medwin, A.R. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the unanaesthetised rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J. Physiol. (Lond). 232, 357–374 (1973).
Bliss, T.V.P. & Lomo, T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J. Physiol. (Lond). 232, 331–356 (1973).
Levy, W.B. & Steward, O. Synapses as associative memory elements in the hippocampal formation. Brain Res. 175, 233–245 (1979).
McNaughton, B.L., Douglas, R.M. & Goddard, G.V. Synaptic enhancement in fascia dentata: Cooperativity among coactive afferents. Brain Res. 157, 277–293 (1978).
McNaughton, B.L. et al. Deciphering the hippocampal polyglot: The hippocampus as a path integration system. J. Exp. Biol. 199, 173–185 (1996).
Samsonovich, A. & McNaughton, B.L. Path integration and cognitive mapping in a continuous attractor neural network model. J. Neurosci. 17, 5900–5920 (1997).
Redish, A.D. & Touretzky, D.S. Cognitive maps beyond the hippocampus. Hippocampus 7, 1–21 (1997).
Redish, A.D. Beyond the Cognitive Map: From Place Cells to Episodic Memory (MIT Press, Cambridge, 1999).
Touretzky, D.S. & Redish, A.D. Theory of rodent navigation based on interacting representations of space. Hippocampus 6, 247–270 (1996).
Muller, R.U. & Kubie, J.L. The effects of changes in the environment on the spatial firing of hippocampal complex-spike cells. J. Neurosci. 7, 1951–1968 (1987).
Knierim, J.J., Kudrimoti, H.S. & McNaughton, B.L. Place cells, head direction cells, and the learning of landmark stability. J. Neurosci. 15, 1648–1659 (1995).
O'Keefe, J. & Conway, D.H. Hippocampal place units in the freely moving rat: Why they fire where they fire. Exp. Brain Res. 31, 573–590 (1978).
Gothard, K.M., Skaggs, W.E. & McNaughton, B.L. Dynamics of mismatch correction in the hippocampal ensemble code for space: Interaction between path integration and environmental cues. J. Neurosci. 16, 8027–8040 (1996).
Gothard, K.M., Hoffman, K.L., Battaglia, F.P. & McNaughton, B.L. Dentate gyrus and CA1 ensemble activity during spatial reference frame shifts in the presence and absence of visual input. J. Neurosci. 21, 7284–7292 (2001).
O'Keefe, J. & Burgess, N. Geometric determinants of the place fields of hippocampal neurons. Nature 381, 425–428 (1996).
Jeffery, K.J. & O'Keefe, J.M. Learned interaction of visual and idiothetic cues in the control of place field orientation. Exp. Brain Res. 127, 151–161 (1999).
Sharp, P.E., Blair, H.T., Etkin, D. & Tzanetos, D.B. Influences of vestibular and visual motion information on the spatial firing patterns of hippocampal place cells. J. Neurosci. 15, 173–189 (1995).
Redish, A.D., Rosenzweig, E.S., Bohanick, J.D., McNaughton, B.L. & Barnes, C.A. Dynamics of hippocampal ensemble activity realignment: Time vs. space. J. Neurosci. 20, 9298–9309 (2000).
Tanila, H., Sipilä, P., Shapiro, M. & Eichenbaum, H. Brain aging: Impaired coding of novel environmental cues. J. Neurosci. 17, 5167–5174 (1997).
Tanila, H., Shapiro, M., Gallagher, M. & Eichenbaum, H. Brain aging: changes in the nature of information coding by the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 17, 5155–5166 (1997).
Wilson, I.A. et al. Place cell rigidity correlates with impaired spatial learning in aged rats. Neurobiol. Aging 24, 297–305 (2003).
Redish, A.D. et al. Independence of firing correlates of anatomically proximate hippocampal pyramidal cells. J. Neurosci. 21, RC134, 1–6 (2001).
Gothard, K.M., Skaggs, W.E., Moore, K.M. & McNaughton, B.L. Binding of hippocampal CA1 neural activity to multiple reference frames in a landmark-based navigation task. J. Neurosci. 16, 823–835 (1996).
McNaughton, B.L., O'Keefe, J. & Barnes, C.A. The stereotrode: A new technique for simultaneous isolation of several single units in the central nervous system from multiple unit records. J. Neurosci. Methods 8, 391–397 (1983).
O'Keefe, J. & Recce, M.L. Phase relationships between hippocampal place units and the EEG theta rhythm. Hippocampus 3, 317–330 (1993).
Mizumori, S.J.Y., McNaughton, B.L. & Barnes, C.A. A comparison of supramammillary and medial septal influences on hippocampal field potentials and single-unit activity. J. Neurophysiol. 61, 15–31 (1989).
Ranck, J.B. Jr. Studies on single neurons in dorsal hippocampal formation and septum in unrestrained rats. I. Behavioral correlates and firing repertoires. Exp. Neurol. 41, 461–531 (1973).
Kubie, J.L. & Ranck, J.B. Jr. Sensory-behavioral correlates in individual hippocampus neurons in three situations: Space and context. in Neurobiology of the Hippocampus (ed. Seifert, W.) 433–447 (Academic Press, New York, 1983).
Markus, E.J. et al. Interactions between location and task affect the spatial and directional firing of hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 15, 7079–7094 (1995).
Vanderwolf, C.H. Hippocampal electrical activity and voluntary movement in the rat. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 26, 407–418 (1969).
Muller, R.U., Kubie, J.L. & Ranck, J.B. Jr. Spatial firing patterns of hippocampal complex-spike cells in a fixed environment. J. Neurosci. 77, 1935–1950 (1987).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank J. Bohanick, J. Gerrard, S. de Dios, J. Dees, J. Yuan, K. Hardesty, N. Insel, J. Meltzer, J. Wang and K. Weaver-Sommers for help running experiments and processing data. This research was supported by Public Health Service grants AG12609, AG05805 and MH01565.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenzweig, E., Redish, A., McNaughton, B. et al. Hippocampal map realignment and spatial learning. Nat Neurosci 6, 609–615 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1053
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1053
This article is cited by
-
The antipsychotic drug sulpiride in the ventral pallidum paradoxically impairs learning and induces place preference
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Impaired Spatial Reorientation in the 3xTg-AD Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Coherent encoding of subjective spatial position in visual cortex and hippocampus
Nature (2018)
-
Viewpoints: how the hippocampus contributes to memory, navigation and cognition
Nature Neuroscience (2017)
-
Targeting Adult Neurogenesis to Optimize Hippocampal Circuits in Aging
Neurotherapeutics (2017)