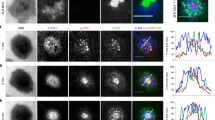
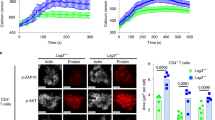
Abstract
Although the Src family tyrosine kinase Lck is essential for T cell receptor (TCR) signaling, whether or how Lck is activated is unknown. Using a phosphospecific antiserum to Lck, we show here that Lck becomes autophosphorylated when T cells are stimulated by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). We found that TCR cross-linking alone could not stimulate Lck autophosphorylation and CD45 was not required for this process. Instead, the T cell accessory molecules CD4 and CD28 cooperated to induce autophosphorylation of Lck. CD4 recruited Lck to the T cell–APC interface, whereas CD28 sustained Lck activation. These data show how the multiple interactions afforded by the immunological synapse drive efficient and highly specific signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delon, J. & Germain, R. N. Information transfer at the immunological synapse. Curr. Biol. 10, 923–933 (2000).
van Oers, N. S. T cell receptor-mediated signs and signals governing T cell development. Semin. Immunol. 11, 227–237 (1999).
Alexander, D. R. The CD45 tyrosine phosphatase: a positive and negative regulator of immune cell function. Semin. Immunol. 12, 349–359 (2000).
Ostergaard, H. L. et al. Expression of CD45 alters phosphorylation of the Lck encoded tyrosine protein kinase in murine lymphoma T cell lines. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 8959–8963 (1989).
McFarland, E. D. et al. Correlation between Src family member regulation by the protein tyrosine phosphatase CD45 and transmembrane signaling through the T cell receptor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 1402–1406 (1993).
Shaw, A. S., Gauen, L. K. & Zhu, Y. Interactions of TCR tyrosine based activation motifs with tyrosine kinases. Semin. Immunol. 7, 13–20 (1995).
Porter, M., Schindler, T., Kuriyan, J. & Miller, W. T. Reciprocal regulation of Hck activity by phosphorylation of Tyr(527) and Tyr(416). Effect of introducing a high affinity intramolecular SH2 ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 2721–2726 (2000).
Moarefi, I. et al. Activation of the Src-family tyrosine kinase Hck by SH3 domain displacement. Nature 385, 650–653 (1997).
Holdorf, A. D. et al. Proline residues in CD28 and the Src homology (SH)3 domain of Lck are required for T cell costimulation. J. Exp. Med. 190, 375–384 (1999).
Caron, L., Abraham, N., Pawson, T. & Veillette, A. Structural requirements for enhancement of T cell responsiveness by the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase p56lck. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 2720–2729 (1992).
Veillette, A. & Fournel, M. The CD4 associated tyrosine protein kinase p56lck is positively regulated through its site of autophosphorylation. Oncogene 5, 1455–1462 (1990).
Schindler, T. et al. Crystal structure of Hck in complex with a Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Mol. Cell 3, 639–648 (1999).
Xu, W., Doshi, A., Lei, M., Eck, M. J. & Harrison, S. C. Crystal structures of c-Src reveal features of its autoinhibitory mechanism. Mol. Cell 3, 629–638 (1999).
Samelson, L. E., Phillips, A. F., Luong, E. T. & Klausner, R. D. Association of the Fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T cell antigen receptor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 4358–4362 (1990).
O'Shea, J. J., McVicar, D. W., Bailey, T. L., Burns, C. & Smyth, M. J. Activation of human peripheral blood T lymphocytes by pharmacological induction of protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10306–10310 (1992).
Straus, D. B. & Weiss, A. Genetic evidence for the involvement of the Lck tyrosine kinase in signal transduction through the T cell antigen receptor. Cell 70, 585–593 (1992).
Murphy, K. M., Heimberger, A. B. & Loh, D. Y. Induction by antigen of intrathymic apoptosis of CD4+CD8+TCRlo thymocytes in vivo. Science 250, 1720–1723 (1990).
Kersh, G. J. & Allen, P. M. Structural basis for T cell recognition of altered peptide ligands: a single T cell receptor can productively recognize a large continuum of related ligands. J. Exp. Med. 184, 1259–1268 (1996).
Grakoui, A. et al. The immunological synapse: a molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science 285, 221–227 (1999).
Klausner, R. D. & Samelson, L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell 64, 875–878 (1991).
Veillette, A., Horak, I. D., Horak, E. M., Bookman, M. A. & Bolen, J. B. Alterations of the lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (p56lck) during T cell activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8, 4353–4561 (1988).
Danielian, S., Fagard, R., Alcover, A., Acuto, O. & Fischer, S. The lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase p56lck is hyperphosphorylated on serine and tyrosine residues within minutes after activation via T cell receptor or CD2. Eur. J. Immunol. 19, 2183–2189 (1989).
Soula, M. et al. Anti-CD3 and phorbol ester induce distinct phosphorylated sites in the SH2 domain of p56lck. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 27420–27427 (1993).
Veillette, A., Bookman, M. A., Horak, E. M. & Bolen, J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell 55, 301–308 (1988).
Veillette, A., Bolen, J. B. & Bookman, M. A. Alterations in tyrosine protein phosphorylation induced by antibody mediated cross-linking of the CD4 receptor of T lymphocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 9, 4441–4446 (1989).
Luo, K. X. & Sefton, B. M. Cross-linking of T cell surface molecules CD4 and CD8 stimulates phosphorylation of the Lck tyrosine protein kinase at the autophosphorylation site. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10, 5305–5313 (1990).
Rudd, C. E. et al. Molecular analysis of the interaction of p56lck with the CD4 and CD8 antigens. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 292, 85–96 (1991).
Holdorf, A. D., Kanagawa, O. & Shaw, A. S. CD28 and T cell co-stimulation. Rev. Immunogenet. 2, 175–184 (2000).
Nunes, J. A., Truneh, A., Olive, D. & Cantrell, D. A. Signal transduction by CD28 costimulatory receptor on T cells. B7-1 and B7-2 regulation of tyrosine kinase adaptor molecules. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 1591–1598 (1996).
Viola, A., Schroeder, S., Sakakibara, Y. & Lanzavecchia, A. T lymphocyte costimulation mediated by reorganization of membrane microdomains. Science 283, 680–682 (1999).
Olszowy, M. W., Leuchtmann, P. L., Veillette, A. & Shaw, A. S. Comparison of p56lck and p59fyn protein expression in thymocyte subsets, peripheral T cells, NK cells, and lymphoid cell lines. J. Immunol. 155, 4236–4240 (1995).
Desai, D. M., Sap, J., Silvennoinen, O., Schlessinger, J. & Weiss, A. The catalytic activity of the CD45 membrane-proximal phosphatase domain is required for TCR signaling and regulation. EMBO J. 13, 4002–4010 (1994).
Young, M. A., Gonfloni, S., Superti-Furga, G., Roux, B. & Kuriyan, J. Dynamic coupling between the SH2 and SH3 domains of c-Src and Hck underlies their inactivation by C-terminal tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell 105, 115–126 (2001).
Koretzky, G. A., Picus, J., Schultz, T. & Weiss, A. Tyrosine phosphatase CD45 is required for T cell antigen receptor and CD2-mediated activation of a protein tyrosine kinase and interleukin 2 production. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 2037–2041 (1991).
Deans, J. P., Kanner, S. B., Torres, R. M. & Ledbetter, J. A. Interaction of CD4:Lck with the T cell receptor/CD3 complex induces early signaling events in the absence of CD45 tyrosine phosphatase. Eur. J. Immunol. 22, 661–668 (1992).
Vidal, K., Daniel, C., Hill, M., Littman, D. R. & Allen, P. M. Differential requirements for CD4 in TCR-ligand interactions. J. Immunol. 163, 4811–4818 (1999).
Green, J. M., Karpitskiy, V., Kimzey, S. L. & Shaw, A. S. Coordinate regulation of T cell activation by CD2 and CD28. J. Immunol. 164, 3591–3595 (2000).
Monks, C. R., Freiberg, B. A., Kupfer, H., Sciaky, N. & Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 395, 82–86 (1998).
Krummel, M. F., Sjaastad, M. D., Wulfing, C. & Davis, M. M. Differential clustering of CD4 and CD3ζ during T cell recognition. Science 289, 1349–1352 (2000).
Bromley, S. K. et al. The immunological synapse and CD28-CD80 interactions. Nature Immunol. 2, 1159–1166 (2001).
Hernandez-Hoyos, G., Sohn, S. J., Rothenberg, E. V. & Alberola-Ila, J. Lck activity controls CD4/CD8 T cell lineage commitment. Immunity 12, 313–322 (2000).
Sloan-Lancaster, J., Shaw, A. S., Rothbard, J. B. & Allen, P. M. Partial T cell signaling: altered phospho-ζ and lack of ZAP70 recruitment in APL-induced T cell anergy. Cell 79, 913–922 (1994).
Kersh, E. N., Shaw, A. S. & Allen, P. M. Fidelity of T cell activation through multistep T cell receptor ζ phosphorylation. Science 281, 572–575 (1998).
Bromley, S. K. et al. The immunological synapse. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 375–396 (2001).
van der Merwe, P. A. The TCR Triggering Puzzle. Immunity 14, 665–668 (2001).
Delon, J. et al. CD8 expression allows T cell signaling by monomeric peptide-MHC complexes. Immunity 9, 467–473 (1998).
Block, M. S., Johnson, A. J., Mendez-Fernandez, Y. & Pease, L. R. Monomeric class I molecules mediate TCR/CD3ɛ/CD8 interaction on the surface of T cells. J. Immunol. 167, 821–826 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Chan, E. Unanue and J. Kim for critical review of the manuscript; S. Ranganath and D. Donermeyer for assistance with the T cell cultures; and J. Green for the CD28-deficient DO11.10 mice. Supported by the NIH (A. S.), the Cancer Research Institute (A. H.) and the Burroughs-Wellcome Fund (W. R. B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holdorf, A., Lee, KH., Burack, W. et al. Regulation of Lck activity by CD4 and CD28 in the immunological synapse. Nat Immunol 3, 259–264 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni761
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni761
This article is cited by
-
INPP5E regulates CD3ζ enrichment at the immune synapse by phosphoinositide distribution control
Communications Biology (2023)
-
A phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate redistribution-based sensing mechanism initiates a phagocytosis programing
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Identification and characterization of two CD4 alleles in Microminipigs
BMC Veterinary Research (2016)
-
Kupfer‐type immunological synapses in vivo: Raison D’être of SMAC
Immunology & Cell Biology (2015)
-
The pool of preactivated Lck in the initiation of T‐cell signaling: a critical re‐evaluation of the Lck standby model
Immunology & Cell Biology (2015)