Abstract
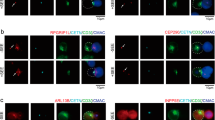
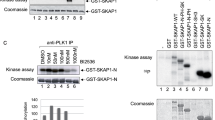
T cell receptor engagement activates p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) through a LAT–SLP-76–Nck–Vav-Rac–dependent pathway. A second independent pathway involving a GIT-PIX-PAK1 trimolecular complex is also activated by T cell receptor ligation. Here we show a Vav-independent pathway exists that leads to PAK1 activation. In addition, PAK1, PIX and GIT1 were recruited to the T cell–antigen-presenting cell contact site independently of SLP-76 and Vav1. PAK1 recruitment to the T cell–antigen-presenting cell interface required interaction with PIX, which also led to optimal PLC-γ1 activation and T cell receptor–dependent transcriptional responses. These data indicate that a pathway involving the GIT-PIX-PAK1 complex has a crucial function in PAK1 activation by recruiting PAK1 to the immunological synapse.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samelson, L.E. Signal transduction mediated by the T cell antigen receptor: the role of adapter proteins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 371–394 (2002).
Tomlinson, M.G., Lin, J. & Weiss, A. Lymphocytes with a complex: adapter proteins in antigen receptor signaling. Immunol. Today 21, 584–591 (2000).
Bubeck Wardenburg, J. et al. Regulation of PAK activation and the T cell cytoskeleton by the linker protein SLP-76. Immunity 9, 607–616 (1998).
Yablonski, D., Kane, L.P., Qian, D. & Weiss, A.A. Nck-Pak1 signaling module is required for T-cell receptor-mediated activation of NFAT, but not of JNK. EMBO J. 17, 5647–5657 (1998).
Chu, P. et al. Systematic identification of regulatory proteins critical for T-cell activation. J. Biol. 2, 21 (2003).
Chu, P.C. et al. A novel role for p21-activated protein kinase 2 in T cell activation. J. Immunol. 172, 7324–7334 (2004).
Bokoch, G.M. Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 743–781 (2003).
Monks, C.R., Freiberg, B.A., Kupfer, H., Sciaky, N. & Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 395, 82–86 (1998).
Jacobelli, J., Andres, P.G., Boisvert, J. & Krummel, M.F. New views of the immunological synapse: variations in assembly and function. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 16, 345–352 (2004).
Lee, K.H. et al. T cell receptor signaling precedes immunological synapse formation. Science 295, 1539–1542 (2002).
Montoya, M.C. et al. Role of ICAM-3 in the initial interaction of T lymphocytes and APCs. Nat. Immunol. 3, 159–168 (2002).
Bonello, G. et al. Dynamic recruitment of the adaptor protein LAT: LAT exists in two distinct intracellular pools and controls its own recruitment. J. Cell Sci. 117, 1009–1016 (2004).
Ku, G.M., Yablonski, D., Manser, E., Lim, L. & Weiss, A.A. PAK1-PIX-PKL complex is activated by the T-cell receptor independent of Nck, Slp-76 and LAT. EMBO J. 20, 457–465 (2001).
Manser, E., Leung, T., Salihuddin, H., Zhao, Z.S. & Lim, L. A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature 367, 40–46 (1994).
DeFranco, A.L. Vav and the B cell signalosome. Nat. Immunol. 2, 482–484 (2001).
Tybulewicz, V.L., Ardouin, L., Prisco, A. & Reynolds, L.F. Vav1: a key signal transducer downstream of the TCR. Immunol. Rev. 192, 42–52 (2003).
Crespo, P., Schuebel, K.E., Ostrom, A.A., Gutkind, J.S. & Bustelo, X.R. Phosphotyrosine-dependent activation of Rac-1 GDP/GTP exchange by the vav proto-oncogene product. Nature 385, 169–172 (1997).
Han, J. et al. Lck regulates Vav activation of members of the Rho family of GTPases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 1346–1353 (1997).
Zeng, R. et al. SLP-76 coordinates Nck-dependent Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein recruitment with Vav-1/Cdc42-dependent Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein activation at the T cell-APC contact site. J. Immunol. 171, 1360–1368 (2003).
Liu, S.K., Fang, N., Koretzky, G.A. & McGlade, C.J. The hematopoietic-specific adaptor protein gads functions in T-cell signaling via interactions with the SLP-76 and LAT adaptors. Curr. Biol. 9, 67–75 (1999).
Bagrodia, S., Taylor, S.J., Jordon, K.A., Van Aelst, L. & Cerione, R.A. A novel regulator of p21-activated kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 23633–23636 (1998).
Manser, E. et al. PAK kinases are directly coupled to the PIX family of nucleotide exchange factors. Mol. Cell 1, 183–192 (1998).
Zhao, Z.S., Manser, E. & Lim, L. Interaction between PAK and Nck: a template for Nck targets and role of PAK autophosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 3906–3917 (2000).
Premont, R.T. et al. β2-Adrenergic receptor regulation by GIT1, a G protein-coupled receptor kinase-associated ADP ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 14082–14087 (1998).
Bagrodia, S. et al. A tyrosine-phosphorylated protein that binds to an important regulatory region on the cool family of p21-activated kinase-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 22393–22400 (1999).
Premont, R.T., Claing, A., Vitale, N., Perry, S.J. & Lefkowitz, R.J. The GIT family of ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating proteins. Functional diversity of GIT2 through alternative splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 22373–22380 (2000).
Turner, C.E. et al. Paxillin LD4 motif binds PAK and PIX through a novel 95-kD ankyrin repeat, ARF-GAP protein: A role in cytoskeletal remodeling. J. Cell Biol. 145, 851–863 (1999).
Turner, C.E., West, K.A. & Brown, M.C. Paxillin-ARF GAP signaling and the cytoskeleton. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 593–599 (2001).
Natarajan, K., Yin, G. & Berk, B.C. Scaffolds direct Src-specific signaling in response to angiotensin II: new roles for Cas and GIT1. Mol. Pharmacol. 65, 822–825 (2004).
Zakaria, S. et al. Differential regulation of TCR-mediated gene transcription by Vav family members. J. Exp. Med. 199, 429–434 (2004).
Wu, J., Motto, D.G., Koretzky, G.A. & Weiss, A. Vav and SLP-76 interact and functionally cooperate in IL-2 gene activation. Immunity 4, 593–602 (1996).
Benard, V., Bohl, B.P. & Bokoch, G.M. Characterization of Rac and Cdc42 activation in chemoattractant-stimulated human neutrophils using a novel assay for active GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 13198–13204 (1999).
Kraynov, V.S. et al. Localized Rac activation dynamics visualized in living cells. Science 290, 333–337 (2000).
Ardouin, L. et al. Vav1 transduces TCR signals required for LFA-1 function and cell polarization at the immunological synapse. Eur. J. Immunol. 33, 790–797 (2003).
King, C.C. et al. p21-activated kinase (PAK1) is phosphorylated and activated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK1). J. Biol. Chem. 275, 41201–41209 (2000).
Chong, C., Tan, L., Lim, L. & Manser, E. The mechanism of PAK activation. Autophosphorylation events in both regulatory and kinase domains control activity. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17347–17353 (2001).
Krummel, M.F., Sjaastad, M.D., Wulfing, C. & Davis, M.M. Differential clustering of CD4 and CD3ζ during T cell recognition. Science 289, 1349–1352 (2000).
Kim, H.K. et al. PDGF stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis requires PLC-γ1 phosphorylation on tyrosine residues 783 and 1254. Cell 65, 435–441 (1991).
Fraser, J.D., Newton, M.E. & Weiss, A. CD28 and T cell antigen receptor signal transduction coordinately regulate interleukin 2 gene expression in response to superantigen stimulation. J. Exp. Med. 175, 1131–1134 (1992).
Shapiro, V.S., Truitt, K.E., Imboden, J.B. & Weiss, A. CD28 mediates transcriptional upregulation of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) promoter through a composite element containing the CD28RE and NF-IL-2B AP-1 sites. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 4051–4058 (1997).
Daniels, R.H., Hall, P.S. & Bokoch, G.M. Membrane targeting of p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) induces neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells. EMBO J. 17, 754–764 (1998).
Loo, T.H., Ng, Y.W., Lim, L. & Manser, E. GIT1 activates p21-activated kinase through a mechanism independent of p21 binding. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 3849–3859 (2004).
Dustin, M.L. & Cooper, J.A. The immunological synapse and the actin cytoskeleton: molecular hardware for T cell signaling. Nat. Immunol. 1, 23–29 (2000).
Bunnell, S.C., Kapoor, V., Trible, R.P., Zhang, W. & Samelson, L.E. Dynamic actin polymerization drives T cell receptor-induced spreading: a role for the signal transduction adaptor LAT. Immunity 14, 315–329 (2001).
Barda-Saad, M. et al. Dynamic molecular interactions linking the T cell antigen receptor to the actin cytoskeleton. Nat. Immunol. 6, 80–89 (2005).
Negulescu, P.A., Krasieva, T.B., Khan, A., Kerschbaum, H.H. & Cahalan, M.D. Polarity of T cell shape, motility, and sensitivity to antigen. Immunity 4, 421–430 (1996).
Weiss, A. & Stobo, J.D. Requirement for the coexpression of T3 and the T cell antigen receptor on a malignant human T cell line. J. Exp. Med. 160, 1284–1299 (1984).
Yablonski, D., Kuhne, M.R., Kadlecek, T. & Weiss, A. Uncoupling of nonreceptor tyrosine kinases from PLC-γ1 in an SLP-76-deficient T cell. Science 281, 413–416 (1998).
Cao, Y. et al. Pleiotropic defects in TCR signaling in a Vav-1-null Jurkat T-cell line. EMBO J. 21, 4809–4819 (2002).
Williams, B.L. et al. Genetic evidence for differential coupling of Syk family kinases to the T-cell receptor: reconstitution studies in a ZAP-70-deficient Jurkat T-cell line. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 1388–1399 (1998).
Kuhne, M.R., Ku, G. & Weiss, A. A guanine nucleotide exchange factor-independent function of Vav1 in transcriptional activation. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 2185–2190 (2000).
Takesono, A., Horai, R., Mandai, M., Dombroski, D. & Schwartzberg, P.L. Requirement for Tec kinases in chemokine-induced migration and activation of Cdc42 and Rac. Curr. Biol. 14, 917–922 (2004).
Shapiro, V.S., Mollenauer, M.N., Greene, W.C. & Weiss, A. c-rel regulation of IL-2 gene expression may be mediated through activation of AP-1. J. Exp. Med. 184, 1663–1669 (1996).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank A. Defranco, M. Krummel, T. Brdicka and S. Levin for reading this manuscript and for comments, and J. Jacobelli for helping with analysis of microscopy data for some of these studies. Supported in part by the National Cancer Institute (CA72531 to A.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Effects of Vav-C on endogenous Cdc42 activation and PAK in vitro kinase assay. (PDF 440 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phee, H., Abraham, R. & Weiss, A. Dynamic recruitment of PAK1 to the immunological synapse is mediated by PIX independently of SLP-76 and Vav1. Nat Immunol 6, 608–617 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1199
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1199
This article is cited by
-
Rapid increase in transferrin receptor recycling promotes adhesion during T cell activation
BMC Biology (2022)
-
Protein kinase C-η controls CTLA-4–mediated regulatory T cell function
Nature Immunology (2014)
-
New inhibitory signaling by CTLA-4
Nature Immunology (2014)
-
Coronin 1A promotes a cytoskeletal-based feedback loop that facilitates Rac1 translocation and activation
The EMBO Journal (2011)
-
Regulation of thymocyte positive selection and motility by GIT2
Nature Immunology (2010)