Abstract
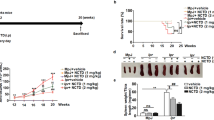
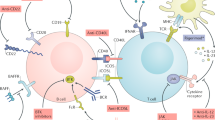
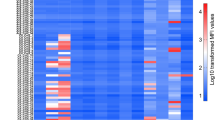
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem chronic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that affects many organs, including the kidney. The presence of multiple autoantibodies and other immunological abnormalities point to basic defects in immunoregulatory controls that normally maintain self-tolerance. The deposition on kidney tissue of autoantibodies as immune complexes (ICs) through the interaction with Fc-receptor γ-chains is thought to trigger an inflammatory response typical of SLE, leading to glomerulonephritis. Using combinatorial chemistry approaches, we have identified a peptide able to bind to immunoglobulins and to interfere with Fcγ-receptor recognition. Administration of this peptide to MRL/lpr mice, an animal model used to study SLE, resulted in a remarkable enhancement of the survival rate (80%) compared to placebo-treated animals (10%). Consistent with this was a significant reduction of proteinuria, a clinical sign of SLE. Kidney histological examination of treated animals confirmed the preservation of tissue integrity and a remarkable reduction in IC deposition. These results support the role of Fcγ receptors in SLE pathogenesis and open new avenues for the development of drugs to treat autoimmune disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Dell, J.R. & Kotzin, B.L. Systemic lupus erythematosus. In Samter's immunologic diseases. (eds Frank, M.M., Austen, K.F., Claman, H.N., & Unanue, E. R.) 667–697 (Little, Brown, Boston; 1995).
Baccala, R., Quang, T.V., Gilbert, M., Ternyck, T. & Avrameas, S. Two murine natural polyreactive autoantibodies are encoded by non-mutated germ-line genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 86, 4624–4628 (1989).
Marion, T.N., Bothwell, A.L.M., Briles, D.E. & Janeway, C.A. IgG anti-DNA autoantobodies within an individual autoimmune mouse are the products of clonal selection. J. Immunol. 142, 4269–4274 (1989).
Schett, G. et al. The lupus erythematosus cell phenomenon: comparative analysis of antichromatin antibody specificity in lupus erythematosus cell-positive and -negative sera. Arthritis Rheum. 43, 420–428 (2000).
Reichlin, M. Current perspectives on serological reactions in SLE patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 44, 1–10 (1981).
Franceschini, F. et al. Chilblain lupus erythematosus is associated with antibodies to SSA/Ro. Lupus 8, 215–219 (1999).
Mattioli, M. & Rechlin, M. Heterogeneity of RNA protein antigens reactive with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 17, 421–429 (1974).
Reichlin, M. et al. Prevalence of autoantibodies to ribosomal P proteins in juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus compared with the adult disease. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 69–75 (1999).
Hasegawa, H. et al. High frequency of antibody activity against ribosomal protein S10 in anti-Sm sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 8, 439–443 (1999).
Tsao, B.P. et al. Failed self-tolerance and autoimmunity in IgG anti-DNA transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 149, 350–358 (1992).
Mannik, M. Pathophysiology of circulating immune complexes. Arthritis Rheum. 25, 783–787 (1982).
Baumann, U. et al. A codominant role of Fc gamma RI/III and C5aR in the reverse Arthus reaction. J. Immunol. 164, 1065–1070 (2000).
Szalai, A. J. et al. The Arthus reaction in rodents: species-specific requirement of complement. J. Immunol. 164, 463–468 (2000).
Jazwinska, E.C., Banyer, J.L., Gatenby, P.A. & Serjeantson, S.W. Fc gamma RII alpha: sequencing of the ligand binding domain in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 86, 199–202 (1991).
Clynes, R., Dumitru, C. & Ravetch, J.V. Uncoupling of immune complex formation and kidney damage in autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Science 279, 1052–1054 (1998).
Ravetch, J.V. & Clynes, R.A. Divergent roles for Fc receptors and complement in vivo. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16, 421–432 (1998).
Sylvestre, D.L. & Ravetch, J.V. Fc receptors initiate the Arthus reaction: redefining the inflammatory cascade. Science 265, 1095–1098 (1994).
Fassina, G., Verdoliva, A., Odierna, M.R., Ruvo, M. & Cassani, G. Protein A mimetic peptide ligand for affinity purification of antibodies. J. Mol. Recog. 9, 564–569 (1996).
Fassina, G., Verdoliva, A., Palombo, G., Ruvo, M. & Cassani, G. Immunoglobulin specificity of TG19318: a novel synthetic ligand for antibody affinity purification. J. Mol. Recog. 11, 128–133 (1998).
Burton, D.R., Jefferis, R., Partridge, L.J. & Woof, J.M., Molecular recognition of antibody (IgG) by cellular Fc receptor (FcRI). Molec. Immunol. 25, 1175–1181 (1988).
Lund, J. et al. Oligosaccharide-protein interactions in IgG can modulate recognition by Fc gamma receptors. FASEB J. 9, 115–119 (1995).
Theofilopoulos, A.N. Murine models of lupus. In Systemic lupus erythematosus. (ed. Lahita, R.G.) 121–194 (Churchill Livingstone, New York, NY; 1992).
Watanabe-Fukunaga, R., Brannan, C.I., Copeland, N.G., Jekins, N.A. & Nagata, S. Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by effects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature 356, 314–317 (1992).
Lemay, S., Mao, C. & Singh, A. Cytokine gene expression in the MRL/lpr model of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 50, 85–93 (1996).
Mannik, M., Agodoa, L.Y. & David, K.A. Rearrangement of immune complexes in glomeruli leads to persistence and development of electron dense deposits. J. Exp. Med. 157, 1516–1528 (1983).
Gauthier, V.J. & Mannik, M. Only the initial binding of cationic immune complexes to glomerular anionic sites is mediated by charge–charge interactions. J. Immunol. 136, 3266–3271 (1986).
Wang, Y. et al. Amelioration of lupus-like autoimmune disease in NZB/W F1 mice after treatment with a blocking monoclonal antibody specific for complement component C5. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 8563–8568 (1996).
Baylink, D.J. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 309, 306–308 (1983).
Piper, J.M., Ray, W.A., Daugherty, J.R. & Griffin, M.R. Corticosteroid use and peptic ulcer disease: role of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Ann. Intern. Med. 114, 735–740 (1991).
Pryor, B.D., Bologna, S.G. & Kahl, L.E. Risk factors for serious infection during treatment with cyclophosphamide and high-dose corticosteroids for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 39, 1475–1482 (1996).
Hoover, R.G. et al. Autoregulatory circuits in myeloma. Tumor cell cytotoxicity mediated by soluble CD16. J. Clin. Invest 95, 241–247 (1995).
Fearon, D.T. & Wong, W.W. Complement ligand–receptor interactions that mediate biological responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1, 243–271 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marino, M., Ruvo, M., De Falco, S. et al. Prevention of systemic lupus erythematosus in MRL/lpr mice by administration of an immunoglobulin-binding peptide. Nat Biotechnol 18, 735–739 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/77296
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/77296
This article is cited by
-
Effect of enzymatic hydrolysate of cottonseed protein supplementation on growth performance and intestinal health of nursery pigs in Thailand
Tropical Animal Health and Production (2020)
-
Myeloid Populations in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2017)
-
Human IgG1 antibodies suppress angiogenesis in a target-independent manner
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2016)
-
The neonatal Fc receptor as therapeutic target in IgG-mediated autoimmune diseases
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2010)
-
FcRn: the neonatal Fc receptor comes of age
Nature Reviews Immunology (2007)