Abstract
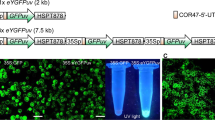
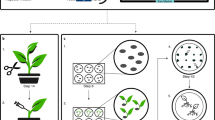
We describe a transgenic plant–based assay to study the genetic effects of heavy metals. Arabidopsis thaliana plants carrying a β-glucuronidase (GUS) marker gene either with a point mutation or as a recombination substrate were used to analyze the frequency of somatic point mutations and homologous recombination in whole plants. Transgenic test plants sown on media contaminated by the salts of the heavy metals Cd2+, Pb2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, and As2O3 exhibited a pronounced uptake-dependent increase in the frequencies of both somatic intrachromosomal recombination and point mutation. The test was applied to monitor the genotoxicity of soils sampled in sites contaminated with several heavy metals. Our results indicate that this is a highly sensitive system for monitoring metal contamination in soils and water.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thiele, D. Metal-regulated transcription in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 1183–1191 (1992).
Horn, N. Copper metabolism in Menke's disease. In Metabolism of trace metals in man, Vol. 2. (eds Rennert, O.M. & Chan W.-Y.) 26–52 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL; 1984).
Alloway, B.J. & Ayres, D.C. Chemical principles of environmental pollution. (Chapman and Hall, London; 1993).
Knasmüller, S. et al. Detection of genotoxic effects of heavy metal contaminated soils with plant bioassays. Mutat. Res. 420, 37–48 (1998).
Hartwig, A. Current aspects in metal genotoxicity. BioMetals 8, 3–11 (1995).
Schaaper, R.M. & Dunn, R.L. Spontaneous mutation in the Escherichia coli lacI gene. Genetics 129, 317–326 (1991).
Lewin, D.E. & Ames, B.N. Classifying mutagens as to their specificity in causing the six possible transitions and transversions: a simple analysis using the Salmonella mutagenicity assay. Environ. Mutagen. 8, 9–28 (1986).
Rossman, T.G. et al. Performance of 133 compounds in the lambda prophage induction endpoint of the Microscreen assay and a comparison with S. typhimurium mutagenicity and rodent carcinogenicity assays. Mutat. Res. 260, 349–367 (1991).
Hartmann, A. & Speit, G. Comparative investigations of the genotoxic effects of metals in the single cell gell (SCG) assay and the sister chromatid exchange (SCE) test. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 23, 299–305 (1994).
Siviková, K., Dianovsky, J. Sister chromatid exchanges after exposure to metal-containing emissions. Mutat. Res. 327, 17–22 (1995).
Rasmuson, A. Mutagenic effects of some water-soluble metal compounds in a somatic eye-color test system in Drosophila melanogaster. Mutat. Res. 157, 157–162 (1985).
Sacco, M.G. et al. A transgenic mouse model for the detection of cellular stress induced by toxic inorganic compounds. Nat. Biotechnol. 15, 1392–1397 (1997).
Mayer, C., Klein, R.G., Wesch, H. & Schmezer, P. Nickel subsulfide is genotoxic in vitro but shows no mutagenic potential in respiratory tract tissues of BigBlue rats and Muta Mouse mice in vivo after inhalation. Mutat. Res. 420, 85–98 (1998).
Rossman, T.G. Metal mutagenesis. In Toxicology of metals. (eds Goyer R.A. & Cherian, G.C.) 373–403 (Springer-Verlag, New York, NY; 1995).
Steinkellner, H. et al. Genotoxic effects of heavy metals: comparative investigation with plant bioassays. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 31, 183–191 (1998).
Grant, W.F. Higher plant assays for the detection of chromosomal aberrations and gene mutations-a brief historical background on their use for screening and monitoring environmental chemicals. Mutat. Res. 426, 107–112 (1999).
Fiskesjö, G. The Allium test—an alternative in environmental studies: the relative toxicity of metal ions. Mutat. Res. 197, 243–260 (1988).
Puchta, H., Swoboda, P. & Hohn, B. Induction of homologous DNA recombination in whole plants. Plant J. 7, 203–210 (1995).
Kovalchuk, I., Kovalchuk, O., Arkhipov, A. & Hohn, B. Transgenic plants are sensitive bioindicators of nuclear pollution caused by the Chernobyl accident. Nat. Biotechnol. 16, 1054–1059 (1998).
Kovalchuk, I., Kovalchuk, O. & Hohn, B. Genome-wide variation of the somatic mutation frequency in transgenic plants. EMBO J. 19, 4431–4438 (2000).
Swoboda, P., Gal., S., Hohn, B. & Puchta, H. Intrachromosomal homologous recombination in whole plants. EMBO J. 13, 484–489 (1994).
Peterhans, A., Schlupmann, H., Basse, C. & Paszkowski, J. Intrachromosomal recombination in plants. EMBO J. 9, 3437–3445 (1990).
Masson, J.E., Paszkowski, J. Arabidopsis thaliana mutants altered in homologous recombination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 11731–11735 (1997).
Imlay, J.A. & Linn, S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science 240, 1302–1309 (1988).
Lee, Y.-W., Broday, L. & Costa, M. Effects of nickel on DNA methyltransferase activity levels and genomic DNA methylation. Mutat. Res. 415, 213–218 (1998).
Mass, M.J. & Wang, L. Arsenic alters cytosine methylation patterns of the promoter of the tumor suppressor gene p53 in human lung cells: a model for a mechanism of carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. 386, 263–277 (1997).
Rank, J. & Nielsen, M.N. Evaluation of the Allium cepa anaphase–telophase test in relation to genotoxicity screening of industrial wastewater. Mutat. Res. 312, 17–24 (1994).
Bitton, G. & Koopman, B. Bacterial and enzymatic bioassays for toxicity testing in the environment. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 125, 1–22 (1992).
Bitton, G., Jung, K. & Koopman, B. Evaluation of a microplate assay specific for heavy metal toxicity. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 27, 25–28 (1994).
Codina, J.C., Perez-Garcia, A., Romero, R & de Vincente, A. A comparison of microbial bioassays for the detection of metal toxicity. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 25, 250–254 (1993).
Helleday, T., Nilsson, R. & Jenssen, D. Arsenic [III] and heavy metal ions induce intrachromosomal homologous recombination in the hprt gene of V79 Chinese hamster cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 35, 114–122 (2000).
Kong, I.-C., Bitton, G., Koopman, B. & Jung, K.-H. Heavy metal toxicity testing in environmental samples. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 125, 1–22 (1995).
Dmitriev, M.T., Kaznina, N.I., & Piniginina, I.A. Sanitary chemical analysis of the pollutants in the environment. (Khimiya, Moscow, USSR; 1989).
Jefferson, R.A., Bevan, M. & Kavanagh, T. The use of the Escherichia coli beta-glucuronidase as a gene fusion marker for studies of gene expression in higher plants. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 15, 17–18 (1987).
Sokal, R. & Rohlf, F. Biometry. (W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, NY; 1995).
Acknowledgements
We want to thank H. Rothnie, M. Pugin, L. Valentine, and Karin Wiebauer for critical reading of the manuscript. We wish to acknowledge an EMBO long-term fellowship to I.K., and we thank the Novartis Research Foundation for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovalchuk, O., Titov, V., Hohn, B. et al. A sensitive transgenic plant system to detect toxic inorganic compounds in the environment. Nat Biotechnol 19, 568–572 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/89327
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/89327
This article is cited by
-
The role of epicuticular waxes on foliar metal transfer and phytotoxicity in edible vegetables: case of Brassica oleracea species exposed to manufactured particles
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2019)
-
Determination by molecular methods of genetic and epigenetic changes caused by heavy metals released from thermal power plants
Applied Biological Chemistry (2018)
-
Genotoxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Plants Demonstrated Using Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana
Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (2018)
-
Cadmium stress in Dongying wild soybean seedlings: growth, Cd accumulation, and photosynthesis
Photosynthetica (2018)
-
Natural history of the narrow endemics Ipomoea cavalcantei and I. marabaensis from Amazon Canga savannahs
Scientific Reports (2017)