Abstract
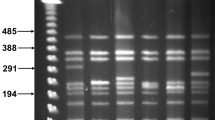
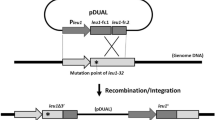
We have developed a system for the introduction and maintenance of novel tandem repeats in the chromosome of Streptomyces lividans 66. This was achieved by introducing, via transformation, Escherichia coli “suicide” vectors carrying manipulated S. lividans DNA fragments. Selection for antibiotic resistance markers carried on such plasmids permitted the isolation and maintenance of mutant strains containing novel tandem repeats formed by the integration into the chromosome of the plasmids, via homologous recombination between plasmid–borne chromosomal sequences and identical sequences on the chromosome. When novel repeats were introduced, and maintained, in regions of the chromosome which become deleted in unstable strains of S. lividans, those deletion events were blocked. Surprisingly, such strains were also 10 to 20–fold more stable than the parent even in the absence of selection. In stable regions of the chromosome, the maintenance of novel repeats had no obvious effect on the deletion events. This strategy could be generally applicable to industrial strains of Streptomyces, where instability is a common problem.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berdy, J. 1980. Recent advances in and prospects for antibiotic research. Proc. Biochem. 15: 28–35.
Ono, H., Hintermann, G., Crameri, R., Wallis, G. and Hütter, R. 1982. Reiterated DNA sequences in a mutant strain of Streptomyces glaucescens and cloning of the sequence in Escherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 186: 106–110.
Schrempf, H. 1982. Plasmid loss and changes within the chromosomal DNA of Streptomyces reticuli. J. Bacteriol. 151: 701–707.
Baltz, R.H. and Stonesifer, J. 1985. Phenotypic changes associated with loss of expression of tylosin biosynthesis and resistance genes in Streptomyces fradiae. J. Antibiotics 38: 1226–1236.
Demuyter, P., Leblond, P., Decaris, B. and Simonet, J.-M. 1988. Characterisation of two families of spontaneous amplifiable units of DNA in Streptomyces ambofaciens. J. Gen. Microbiol. 134: 2001–2007.
Dary, A., Bourget, N., Simonet, J.-M. and Decaris, B. 1992. The amplification of a specific DNA sequence reversibly prevents spiramycin production in Streptomyces ambofaciens RP181110. Res. Microbiol. 43: 99–112.
Leblond, P., Demuyter, P., Simonet, J.-M. and Decaris, B. 1991. Genetic instability and associated genome plasticity in Streptomyces ambofaciens: PFGE evidence for large alterations in a limited genomic region. J. Bacteriol. 173: 4229–4233.
Altenbuchner, J. and Cullum, J. 1984. DNA amplification and an unstable arginine gene in Streptomyces lividans 66. Mol. Gen. Genet. 195: 134–138.
Altenbuchner, J. and Cullum, J. 1985. Structure of an amplifiable DNA sequence in Streptomyces lividans 66. Mol. Gen. Genet. 201: 192–195.
Betzler, M., Dyson, P. and Schrempf, H. 1987. Relationship of an unstable argG gene to a 5.7 kb amplifiable DNA sequence in Streptomyces lividans 66. J. Bacteriol. 169: 4804–4810.
Mori, M., Hashiguchi, K.-I., Yoda, K. and Yamasaki, M. 1988. Designed gene amplification on the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J. Gen. Microbiol. 134: 85–95.
Niaudet, B., Goze, A. and Ehrlich, S.D. 1982. Insertional mutagenesis in Bacillus subtilis: mechanism and use in gene cloning. Gene 19: 277–284.
Altenbuchner, J. and Cullum, J. 1987. Amplification of cloned genes in Streptomyces. Bio/Technology 5: 1328–1329.
Chater, K.F. and Bruton, C.J. 1983. Mutational cloning in Streptomyces and the isolation of antibiotic production genes. Gene 26: 67–78.
Bolivar, F., Rodriguez, R.L., Greene, P.J., Betlach, M.C., Heyneker, H.L., Boyer, H.W., Crosa, J.H. and Falkow, S. 1977. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles, II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene 2: 95–113.
Thompson, C.J., Ward, M.J. and Hopwood, D.A. 1980. DNA cloning in Streptomyces: resistance genes from antibiotic-producing species. Nature 286: 525–527.
Beck, E., Ludwig, G., Auerswald, E.A., Reiss, B. and Schaller, H. 1982. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene 19: 327–336.
Ish-Horowitz, D. and Burke, J.F. 1981. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucl. Acids Res. 9: 2989–2998.
Cullum, J., Flett, F., Gravius, B., Hranueli, D., Miyashita, K., Pigac, J., Rauland, U. and Redenbach, M. 1991. Genetics and product formation in Streptomyces. Plenum Press, New York.
Campbell, A.M. 1962. The episomes. Adv. Genet. 11: 101–145.
Rudd, B.A.M. and Hopwood, D.A. 1979. Genetics of actinorhodin biosynthesis by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Gen. Microbiol. 114: 35–43.
Edlund, T. and Normark, S. 1981. Recombination between short DNA homologies causes tandem duplication. Nature 292: 269–271.
Hopwood, D.A., Bibb, M.J., Chater, K.F., Kieser, T., Bruton, C.J., Kieser, H.M., Lydiate, D.J., Smith, C.P., Ward, J.M. and Schrempf, H., 1985. Genetic Manipulation of Streptomyces–A Laboratory Manual. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich, UK.
Katz, E., Thompson, C.J. and Hopwood, D.A. 1983. Cloning and expression of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus in Streptomyces lividans. J. Gen. Microbiol. 129: 2703–2714.
Yanisch-Perron, C., Vieira, J. and Messing, J. 1985. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33: 103–119.
Gibson, T. 1984. Studies on the Epstein-Barr virus genome. Ph.D.Thesis, Cambridge University, England.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F. and Sambrook, J. 1982. Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaiser, P., Flett, F. & Cullum, J. Stabilization of Streptomyces lividans by Homologous Recombinational Insertion. Nat Biotechnol 10, 570–573 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0592-570
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0592-570