Abstract
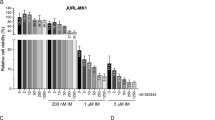
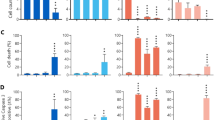
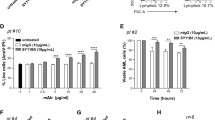
Imatinib is an effective first-line therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) that acts by targeting the tyrosine kinase activity of BCR–ABL. To overcome resistance, second-generation inhibitors of BCR–ABL have been developed. Among these, nilotinib is more potent against BCR–ABL than imatinib, and is effective against many imatinib-resistant BCR–ABL mutants. In this study, an in vitro flow cytometry assay to analyze imatinib- and nilotinib-induced apoptosis in CML cells has been developed. Both the drugs induced significant apoptosis in CD34+ cells from 36 CML bone marrow samples (P<10−4), whereas CD34+ cells from BCR–ABL negative samples were unaffected. When the experiments were carried out in the presence of a cocktail of cytokines, nilotinib- but not imatinib-induced apoptosis was inhibited. This differential inhibition was confirmed on K562 cells. A blocking anti-CD117 antibody alleviated the antiapoptotic effect of cytokines against nilotinib. Moreover, using short hairpin RNA against BCR–ABL, we showed that K562 cells were not dependent on BCR–ABL signaling as long as the stem cell factor (SCF) receptor pathway was activated. We conclude that the c-KIT pathway may substitute for BCR–ABL tyrosine kinase to activate survival signals, and that c-KIT must be inhibited besides Bcr–Abl to allow apoptosis of CML cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 994–1004.
Weisberg E, Manley PW, Breitenstein W, Bruggen J, Cowan-Jacob SW, Ray A et al. Characterization of AMN107, a selective inhibitor of native and mutant Bcr–Abl. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 129–141.
Branford S, Rudzki Z, Walsh S, Grigg A, Arthur C, Taylor K et al. High frequency of point mutations clustered within the adenosine triphosphate-binding region of BCR/ABL in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia or Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia who develop imatinib (STI571) resistance. Blood 2002; 99: 3472–3475.
Jorgensen HG, Allan EK, Jordanides NE, Mountford JC, Holyoake TL . Nilotinib exerts equipotent antiproliferative effects to imatinib and does not induce apoptosis in CD34+ CML cells. Blood 2007; 109: 4016–4019.
Amarante-Mendes GP, McGahon AJ, Nishioka WK, Afar DE, Witte ON, Green DR . Bcl-2-independent Bcr–Abl-mediated resistance to apoptosis: protection is correlated with up regulation of Bcl-xL. Oncogene 1998; 16: 1383–1390.
de Groot RP, Raaijmakers JA, Lammers JW, Koenderman L . STAT5-dependent CyclinD1 and Bcl-xL expression in Bcr–Abl-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun 2000; 3: 299–305.
Horita M, Andreu EJ, Benito A, Arbona C, Sanz C, Benet I et al. Blockade of the Bcr–Abl kinase activity induces apoptosis of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells by suppressing signal transducer and activator of transcription 5-dependent expression of Bcl-xL. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 977–984.
Aichberger KJ, Mayerhofer M, Krauth MT, Skvara H, Florian S, Sonneck K et al. Identification of mcl-1 as a BCR/ABL-dependent target in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): evidence for cooperative antileukemic effects of imatinib and mcl-1 antisense oligonucleotides. Blood 2005; 105: 3303–3311.
Kuribara R, Honda H, Matsui H, Shinjyo T, Inukai T, Sugita K et al. Roles of Bim in apoptosis of normal and Bcr–Abl-expressing hematopoietic progenitors. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 6172–6183.
Aichberger KJ, Mayerhofer M, Krauth MT, Vales A, Kondo R, Derdak S et al. Low-level expression of proapoptotic Bcl-2-interacting mediator in leukemic cells in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: role of BCR/ABL, characterization of underlying signaling pathways, and reexpression by novel pharmacologic compounds. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 9436–9444.
Belloc F, Moreau-Gaudry F, Uhalde M, Cazalis L, Jeanneteau M, Lacombe F et al. Imatinib and nilotinib induce apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells through a Bim-dependant pathway modulated by cytokines. Cancer Biol Ther 2007; 6: 912–919.
Inaba T . Cytokine-mediated cell survival. Int J Hematol 2004; 80: 210–214.
Graham SM, Jorgensen HG, Allan E, Pearson C, Alcorn MJ, Richmond L et al. Primitive, quiescent, Philadelphia-positive stem cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia are insensitive to STI571 in vitro. Blood 2002; 99: 319–325.
Holtz MS, Slovak ML, Zhang F, Sawyers CL, Forman SJ, Bhatia R . Imatinib mesylate (STI571) inhibits growth of primitive malignant progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia through reversal of abnormally increased proliferation. Blood 2002; 99: 3792–3800.
Chen R, Gandhi V, Plunkett W . A sequential blockade strategy for the design of combination therapies to overcome oncogene addiction in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 10959–10966.
Sharma SV, Gajowniczek P, Way IP, Lee DY, Jiang J, Yuza Y et al. A common signaling cascade may underlie ‘addiction’ to the Src, BCR–ABL, and EGF receptor oncogenes. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 425–435.
Carrion RP, Gracian AC, Hernandez PS . Erlotinib as a single agent in select subsets of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 2007; 8: 425–428.
Konig H, Holyoake TL, Bhatia R . Effective and selective inhibition of chronic myeloid leukemia primitive hematopoietic progenitors by the dual Src/Abl kinase inhibitor SKI-606. Blood 2008; 111: 2329–2338.
Konig H, Holtz M, Modi H, Manley P, Holyoake TL, Forman SJ et al. Enhanced BCR–ABL kinase inhibition does not result in increased inhibition of downstream signaling pathways or increased growth suppression in CML progenitors. Leukemia 2008; 22: 748–755.
Belloc F, Cotteret S, Labroille G, Schmit V, Jaloustre C, Dumain P et al. Bcr–abl translocation can occur during the induction of multidrug resistance and confers apoptosis resistance on myeloid leukemic cell lines. Cell Death Differ 1997; 4: 806–814.
Vayssiere JL, Petit PX, Risler Y, Mignotte B . Commitment to apoptosis is associated with changes in mitochondrial biogenesis and activity in cell lines conditionally immortalized with simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 11752–11756.
Copland M, Hamilton A, Elrick LJ, Baird JW, Allan EK, Jordanides N et al. Dasatinib (BMS-354825) targets an earlier progenitor population than imatinib in primary CML but does not eliminate the quiescent fraction. Blood 2006; 107: 4532–4539.
Martin-Henao GA, Ingles-Esteve J, Cancelas JA, Garcia J . Isolation of CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells in chronic myeloid leukemia by magnetic activated cell sorting (MACS). Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 18: 603–609.
Al-Ali HK, Heinrich MC, Lange T, Krahl R, Mueller M, Muller C et al. High incidence of BCR–ABL kinase domain mutations and absence of mutations of the PDGFR and KIT activation loops in CML patients with secondary resistance to imatinib. Hematol J 2004; 5: 55–60.
von Bubnoff N, Manley PW, Mestan J, Sanger J, Peschel C, Duyster J . Bcr–Abl resistance screening predicts a limited spectrum of point mutations to be associated with clinical resistance to the Abl kinase inhibitor nilotinib (AMN107). Blood 2006; 108: 1328–1333.
Tojyo A, Miyazaki Y, Usui N, Kobyashi Y, Okamoto S, Oyashiki K et al. Phase I study of nilotinib in patients (pts) from Japan with imatinib-resistant Ph+ chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) or acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). J Clin Oncol (Meet Abstr) 2007; 25 (suppl): 17511.
Kantarjian H, Giles F, Wunderle L, Bhalla K, O'Brien S, Wassmann B et al. Nilotinib in imatinib-resistant CML and Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 2542–2551.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Comité de Gironde de la Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer and the Fondation Laurette Fugain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belloc, F., Airiau, K., Jeanneteau, M. et al. The stem cell factor–c-KIT pathway must be inhibited to enable apoptosis induced by BCR–ABL inhibitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Leukemia 23, 679–685 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.364
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.364
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Expression differences of miR-142-5p between treatment-naïve chronic myeloid leukemia patients responding and non-responding to imatinib therapy suggest a link to oncogenic ABL2, SRI, cKIT and MCL1 signaling pathways critical for development of therapy resistance
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2020)
-
Effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on stemness in normal and chronic myeloid leukemia cells
Leukemia (2017)
-
Pharmacogenetics and Pharmacogenomics of Targeted Therapeutics in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2017)
-
Silencing stem cell factor attenuates stemness and inhibits migration of cancer stem cells derived from Lewis lung carcinoma cells
Tumor Biology (2016)
-
PI3K/mTOR pathway inhibitors sensitize chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells to nilotinib and restore the response of progenitors to nilotinib in the presence of stem cell factor
Cell Death & Disease (2013)