Abstract
Review of all medical literature dealing with delivery room management of meconium-stained infants. Additionally, the author contacted multiple individuals involved historically or clinically with the published studies or the persons who developed treatment guidelines. Although many therapies have been suggested as being effective, none have been definitively proven efficacious by the gold standard: a large, randomized, controlled trial (RCT). Further adequate investigations (RCTs) need to be performed to assess whether proposed management schemes are of benefit in the care of meconium-stained newborn infants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiswell TE, Bent RC . Meconium staining and the meconium aspiration syndrome. Pediatr Clin North Am 1993; 40: 955–981.
Wiswell TE, Fuloria M . Management of meconium stained amniotic fluid. Clin Perinatol 1999; 26: 659–668.
O’Donnell CPF, Gibson AT, Davis PG . Pinching, electrocution, ravens’ beaks, and positive pressure ventilation: a brief history of neonatal resuscitation. Arch Dis Child 2006; 91: F369–F373.
James LS . Resuscitation procedures in the delivery room. In: Abramson H (ed). Resuscitation of the Newborn Infant. CV Mosby Co: St Louis, 1960, pp 141–161.
Gregory GA, Gooding CA, Phibbs RH, Tooley WH . Meconium aspiration in infants: a prospective study. J Pediatr 1974; 85: 848–852.
Burke-Strickland M, Edwards NB . Meconium aspiration in the newborn. Minn Med 1973; 57: 1031–1035.
Ting P, Brady JP . Tracheal suction in meconium aspiration. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1975; 122: 767–771.
Carson B, Losey RW, Bowes Jr WA, Simmons MA . Combined obstetric and pediatric approach to prevent meconium aspiration syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1976; 126: 712–715.
Wiswell TE, Tuggle JM, Turner BS . Meconium aspiration syndrome: have we made a difference? Pediatrics 1990; 85: 715–721.
Bent RC, Wiswell TE, Chang A . Removing meconium from infant trachea. What works best? Am J Dis Child 1992; 146: 1085–1089.
Linder NJ, Aranda V, Tsur M, Matoth I, Yatsiv I, Mandelberg H et al. Need for endotracheal intubation and suction in meconium stained neonates. J Pediatr 1998; 112: 613–615.
Wiswell TE, Gannon CM, Jacob J, Goldsmith L, Szyld E, Weiss K et al. Delivery room management of the apparently vigorous meconium-stained neonate: results of the multicenter, international collaborative trial. Pediatrics 2000; 105: 1–7.
Falciglia HS . Failure to prevent meconium aspiration syndrome. Obstet Gynecol 1988; 71: 349–353.
Falciglia HS, Henderschott C, Potter P, Helmchen R . Does DeLee suction at the perineum prevent meconium aspiration syndrome? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992; 167: 1243–1249.
Vain N, Szyld E, Prudent L, Wiswell TE, Aguilar AM, Vivas NI . Oro- and nasopharyngeal suctioning of meconium-stained neonates before delivery of their shoulders: results of the international, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Lancet 2004; 364: 597–602.
Cleary GM, Wiswell TE . Meconium-stained amniotic fluid and the meconium aspiration syndrome. An update. Pediatr Clin North Am 1998; 45: 511–529.
Karlowicz MG . More on meconium aspiration. Pediatrics 1990; 86: 1007–1008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiswell, T. Delivery room management of the meconium-stained newborn. J Perinatol 28 (Suppl 3), S19–S26 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2008.143
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2008.143
This article is cited by
-
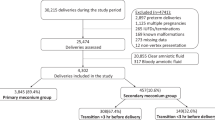
Neonatal outcomes of non-vigorous neonates with meconium-stained amniotic fluid before and after change in tracheal suctioning recommendation
Journal of Perinatology (2022)
-
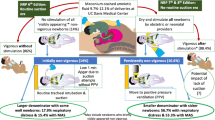
Notfälle im Kreißsaal
Der Gynäkologe (2012)