Abstract
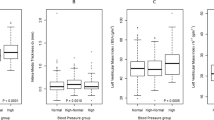
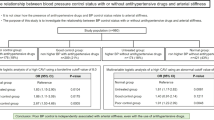
The aim of this study was to investigate whether resistant hypertension differs from uncontrolled and controlled hypertension in terms of target organ damage. Hypertensive subjects with antihypertensive medication (n=385) were identified in a population survey conducted in southwestern Finland. None of the study subjects had previously diagnosed cardiovascular or renal disease or diabetes. Ankle-brachial index, estimated glomerular filtration rate, electrocardiogram-determined left ventricular hypertrophy and cardiometabolic risk factors were assessed. The prevalence of peripheral arterial disease among subjects with resistant, uncontrolled and controlled hypertension was 6/37 (16%), 22/275 (8%) and 0/73 (0%), respectively (P=0.006). There were no differences in the prevalence of renal insufficiency, left ventricular hypertrophy or metabolic parameters between the groups. Resistant hypertension affects vasculature more than uncontrolled hypertension, and thus it can be regarded as a marker of more severe disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 2013; 31: 1281–1357.
Cuspidi C, Macca G, Sampieri L, Michev I, Salerno M, Fusi V et al. High prevalence of cardiac and extracardiac target organ damage in refractory hypertension. J Hypertens 2001; 19: 2063–2070.
de la Sierra A, Banegas JR, Oliveras A, Gorostidi M, Segura J, de la Cruz JJ et al. Clinical differences between resistant hypertensives and patients treated and controlled with three or less drugs. J Hypertens 2012; 30: 1211–1216.
Daugherty SL, Powers JD, Magid DJ, Tavel HM, Masoudi FA, Margolis KL et al. Incidence and prognosis of resistant hypertension in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2012; 125: 1635–1642.
Persell SD . Prevalence of resistant hypertension in the United States, 2003–2008. Hypertension 2011; 57: 1076–1080.
Korhonen PE, Syvänen K, Vesalainen RE, Kantola IM, Kautiainen H, Järvenpää S et al. Ankle-brachial index is lower in hypertensive than in normotensive individuals in a cardiovascular risk population. J Hypertens 2009; 27: 2036–2043.
Espinola-Klein C, Rupprecht HJ, Bickel C, Lackner K, Savvidis S, Messow CM et al. Different calculations of ankle-brachial index and their impact on cardiovascular risk prediction. Circulation 2008; 118: 961–967.
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang Y, Castro AF, Feldman HI et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 2009; 150: 604–612.
Sokolow M, Lyon T . The ventricular complex in left ventricular hypertrophy as obtained by unipolar precordial and limb leads. Am Heart J 1949; 37: 161–186.
Molloy TJ, Okin PM, Devereux RB, Kligfield P . Electrocardiographic detection of left ventricular hypertrophy by the simple QRS voltage-duration product. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992; 20: 1180–1186.
Korhonen P, Kivelä S-L, Aarnio P, Kautiainen H, Järvenpää S, Kantola I . Estimating glomerular filtration rate in hypertensive subjects: comparison of the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) study equations. Ann Med 2012; 44: 487–493.
Varis J, Savola H, Vesalainen R, Kantola I . Hypertension treatment in Finland still not optimal. Finn Med J 2008; 40: 3294–3289.
Chobanian AV . Control of hypertension—an important national priority. New Engl J Med 2001; 345: 534–535.
de la Sierra A, Segura J, Banegas JR, Gorostidi M, de la Cruz JJ, Amario P et al. Clinical features of 8295 patients with resistant hypertension classified on the basis of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Hypertension 2011; 57: 898–902.
Oliveras A, de la Sierra A . Resistant hypertension: patient characteristics, risk factors, co-morbidities and outcomes. J Hum Hypertens 2014; 28: 213–217.
De Buyzere ML, Clement DL . Management of hypertension in peripheral arterial disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2008; 50: 238–263.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Satakunta Hospital District.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korhonen, P., Kautiainen, H. & Kantola, I. Patients with resistant hypertension have more peripheral arterial disease than other uncontrolled hypertensives. J Hum Hypertens 29, 46–49 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2014.65
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2014.65