Abstract
Background:
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) binds to IGF and thus modulates IGF signaling pathway. We have shown earlier that the IGFBP5 gene was downregulated in the adipose tissue after 12-week carbohydrate diet with low insulinemic response.
Objective:
The aim was to examine the putative contribution of genetic variation of the IGFBP5 gene to the characteristics of metabolic syndrome and incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study (DPS).
Methods:
DPS is a longitudinal study where 522 subjects with impaired glucose tolerance were randomized to either lifestyle intervention group or control group. DNA was available from 507 subjects (mean body mass index (BMI) 31.2±4.5 kg/m2, age 55±7 years). The eight single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were selected from HapMap database and genotyped by Taqman allelic discrimination protocol. The main results were confirmed in a larger cross-sectional study population (METSIM). In addition, the gene expression of IGFBP5 was studied in two previously published study populations (FUNGENUT and GENOBIN) of 124 subjects with insulin resistance (BMI 32.2±3.5 kg/m2, age 57.7±7.4 years).
Results:
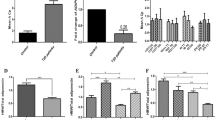
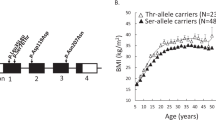
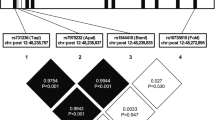
Three out of eight IGFBP5 markers (rs9341234, rs3276 and rs11575134) were significantly associated with circulating adiponectin concentrations in men. Furthermore, mRNA expression studies of subcutaneous adipose tissue showed that mRNA concentrations of IGFBP5 correlated with adiponectin concentrations in all subjects and in women. None of the IGFBP5 SNPs were associated with T2DM.
Conclusions:
Our findings show that IGFBP5 has a gender-specific association with adiponectin, which may modulate the development of metabolic syndrome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nair PP . Nutrients and the human genome: new frontiers for the next century. FASEB J 1993; 7: 501–502.
Delzenne N, Ferre P, Beylot M, Daubioul C, Declercq B, Diraison F et al. Study of the regulation by nutrients of the expression of genes involved in lipogenesis and obesity in humans and animals. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2001; 11: 118–121.
Corella D, Ordovas JM . Single nucleotide polymorphisms that influence lipid metabolism: interaction with dietary factors. Annu Rev Nutr 2005; 25: 341–390.
Ordovas JM . Genetic interactions with diet influence the risk of cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr 2006; 83: 443S–446S.
Jones JI, Clemmons DR . Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev 1995; 16: 3–34.
Renehan AG, Frystyk J, Flyvbjerg A . Obesity and cancer risk: the role of the insulin-IGF axis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2006; 17: 328–336.
Boulware SD, Tamborlane WV, Matthews LS, Sherwin RS . Diverse effects of insulin-like growth factor I on glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism. Am J Physiol 1992; 262: E130–E133.
Clemmons DR, Busby WH, Arai T, Nam TJ, Clarke JB, Jones JI et al. Role of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the control of IGF actions. Prog Growth Factor Res 1995; 6: 357–366.
Rosenfeld RG, Hwa V, Wilson E, Plymate SR, Oh Y . The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein superfamily. Growth Horm IGF Res 2000; 10 (Suppl A): S16–S17.
Quattrin T, Thrailkill K, Baker L, Kuntze J, Compton P, Martha P, rhIGF-I in IDDM Study Group. Improvement of HbA1c without increased hypoglycemia in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus treated with recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin. rhIGF-I in IDDM Study Group. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2001; 14: 267–277.
Schneider MR, Wolf E, Hoeflich A, Lahm H . IGF-binding protein-5: flexible player in the IGF system and effector on its own. J Endocrinol 2002; 172: 423–440.
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Deroo B et al. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer. Lancet 1998; 351: 1393–1396.
Wajapeyee N, Serra RW, Zhu X, Mahalingam M, Green MR . Oncogenic BRAF induces senescence and apoptosis through pathways mediated by the secreted protein IGFBP7. Cell 2008; 132: 363–374.
Chan SS, Twigg SM, Firth SM, Baxter RC . Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 leads to insulin resistance in adipocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 6588–6595.
Baxter RC, Martin JL, Beniac VA . High molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. Purification and properties of the acid-labile subunit from human serum. J Biol Chem 1989; 264: 11843–11848.
Twigg SM, Kiefer MC, Zapf J, Baxter RC . Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 complexes with the acid-labile subunit. Role of the carboxyl-terminal domain. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 28791–28798.
Kallio P, Kolehmainen M, Laaksonen DE, Kekalainen J, Salopuro T, Sivenius K et al. Dietary carbohydrate modification induces alterations in gene expression in abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue in persons with the metabolic syndrome: the FUNGENUT Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 85: 1417–1427.
Brand-Miller JC, Liu V, Petocz P, Baxter RC . The glycemic index of foods influences postprandial insulin-like growth factor-binding protein responses in lean young subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82: 350–354.
Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hamalainen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, et al., Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 1343–1350.
Eriksson J, Lindstrom J, Valle T, Aunola S, Hamalainen H, Ilanne-Parikka P et al. Prevention of Type II diabetes in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance: the Diabetes Prevention Study (DPS) in Finland. Study design and 1-year interim report on the feasibility of the lifestyle intervention programme. Diabetologia 1999; 42: 793–801.
World Health Organization. Diabetes Mellitus: Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Org: Geneva, 1985 (Tech. Rep. Ser. no. 727).
Wang J, Kuusisto J, Vanttinen M, Kuulasmaa T, Lindstrom J, Tuomilehto J et al. Variants of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene predict conversion to type 2 diabetes in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study and are associated with impaired glucose regulation and impaired insulin secretion. Diabetologia 2007; 50: 1192–1200.
World Health Organisation. Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications. Report of a WHO Consultation. Part 1. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Publication no. WHO/NCD/NCS/99.2, WHO: Geneva, 1999.
Kolehmainen M, Salopuro T, Schwab US, Kekalainen J, Kallio P, Laaksonen DE et al. Weight reduction modulates expression of genes involved in extracellular matrix and cell death: the GENOBIN study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008; 32: 292–303.
Mager U, Kolehmainen M, de Mello VD, Schwab U, Laaksonen DE, Rauramaa R et al. Expression of ghrelin gene in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and plasma ghrelin concentrations in patients with metabolic syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol 2008; 158: 499–510.
Thorisson GA, Smith AV, Krishnan L, Stein LD . The International HapMap Project Web site. Genome Res 2005; 15: 1592–1593.
de Bakker PI, Yelensky R, Pe'er I, Gabriel SB, Daly MJ, Altshuler D . Efficiency and power in genetic association studies. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 1217–1223.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
Storey JD, Tibshirani R . Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 9440–9445.
Tregouet DA, Garelle V . A new JAVA interface implementation of THESIAS: testing haplotype effects in association studies. Bioinformatics 2007; 23: 1038–1039.
Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K . cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript 1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 221: 286–289.
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 257: 79–83.
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE et al. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1930–1935.
Tworoger SS, Mantzoros C, Hankinson SE . Relationship of plasma adiponectin with sex hormone and insulin-like growth factor levels. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2007; 15: 2217–2224.
Yatagai T, Nagasaka S, Taniguchi A, Fukushima M, Nakamura T, Kuroe A et al. Hypoadiponectinemia is associated with visceral fat accumulation and insulin resistance in Japanese men with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2003; 52: 1274–1278.
Cnop M, Havel PJ, Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Sinha MK, Boyko EJ et al. Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia 2003; 46: 459–469.
Garner CP, Ding YC, John EM, Ingles SA, Olopade OI, Huo D et al. Genetic variation in IGFBP2 and IGFBP5 is associated with breast cancer in populations of African descent. Hum Genet 2008; 123: 247–255.
Wang H, Arun BK, Wang H, Fuller GN, Zhang W, Middleton LP et al. IGFBP2 and IGFBP5 overexpression correlates with the lymph node metastasis in T1 breast carcinomas. Breast J 2008; 14: 261–267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kallio, P., Tolppanen, AM., Kolehmainen, M. et al. Association of sequence variations in the gene encoding insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 with adiponectin. Int J Obes 33, 80–88 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.196
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.196
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo(4,5-b) pyridine (PhIP) induces gene expression changes in JAK/STAT and MAPK pathways related to inflammation, diabetes and cancer
Nutrition & Metabolism (2016)
-
Oilseeds ameliorate metabolic parameters in male mice, while contained lignans inhibit 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation in vitro
European Journal of Nutrition (2014)