Abstract
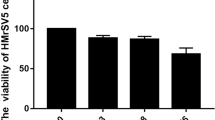
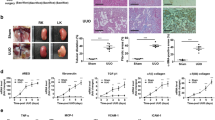
Gene therapies may be promising for the treatment of peritoneal fibrosis (PF) in subjects undergoing peritoneal dialysis (PD). However, a method of delivery of treatment genes to the peritoneum is lacking. We attempted to develop an in vivo small interfering RNA (siRNA) delivery system with liposome-based nanoparticles (NPs) to the peritoneum to inhibit PF. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1-siRNAs encapsulated in NPs (TGF-β1-siRNAs-NPs) dissolved in PD fluid were injected into the peritoneum of mice with PF three times a week for 2 weeks. TGF-β1-siRNAs-NPs knocked down TGF-β1 expression significantly in the peritoneum and inhibited peritoneal thickening with fibrous changes. TGF-β1-siRNAs-NPs also inhibited the increase of expression of α-smooth muscle actin-positive myofibroblasts. These results suggest that the TGF-β1-siRNA delivery system with NPs described here could be an effective therapeutic option for PF in subjects undergoing PD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krediet RT, Lindholm B, Rippe B . Pathophysiology of peritoneal membrane failure. Perit Dial Int 2000; 20: S22–S42.
Gandhi VC, Humayun HM, Ing TS, Daugirdas JT, Jablokow VR, Iwatsuki S et al. Sclerotic thickening of the peritoneal membrane in maintenance peritoneal dialysis patients. Arch Intern Med 1980; 140: 1201–1203.
Ronco C, Feriani M, Chiaramonte S, Brendolan A, Bragantini L, Conz P et al. Pathophysiology of ultrafiltration in peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int 1990; 10: 119–126.
Devuyst O, Margetts PJ, Topley N . The pathophysiology of the peritoneal membrane. J Am Soc Nephrol 2010; 21: 1077–1085.
Margetts PJ, Bonniaud P . Basic mechanisms and clinical implications of peritoneal fibrosis. Perit Dial Int 2003; 23: 530–541.
Hannon GJ . RNA interference. Nature 2002; 418: 244–251.
Tijsterman M, Ketting RF, Plasterk RH . The genetics of RNA silencing. Annu Rev Genet 2002; 36: 489–519.
Dykxhoorn DM, Lieberman J . The silent revolution: RNA interference as basic biology, research tool, and therapeutic. Annu Rev Med 2005; 56: 401–423.
Sledz CA, Williams BR . RNA interference in biology and disease. Blood 2005; 106: 787–794.
Leung RK, Whittaker PA . RNA interference: from gene silencing to gene-specific therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther 2005; 107: 222–239.
de Fougerolles A, Vornlocher HP, Maraganore J, Lieberman J . Interfering with disease: a progress report on siRNA-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007; 6: 443–453.
Soutschek J, Akinc A, Bramlage B, Charisse K, Constien R, Donoghue M et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 2004; 432: 173–178.
Palliser D, Chowdhury D, Wang QY, Lee SJ, Bronson RT, Knipe DM et al. An siRNA-based microbicide protects mice from lethal herpes simplex virus 2 infection. Nature 2006; 439: 89–94.
Stewart SA, Dykxhoorn DM, Palliser D, Mizuno H, Yu EY, An DS et al. Lentivirus-delivered stable gene silencing by RNAi in primary cells. RNA 2003; 9: 493–501.
Yao Q, Pawlaczyk K, Ayala ER, Styszynski A, Breborowicz A, Heimburger O et al. The role of the TGF/Smad signaling pathway in peritoneal fibrosis induced by peritoneal dialysis solutions. Nephron Exp Nephrol 2008; 109: e71–e78.
Loureiro J, Aguilera A, Selgas R, Sandoval P, Albar-Vizcaino P, Perez-Lozano ML et al. Blocking TGF-beta1 protects the peritoneal membrane from dialysate-induced damage. J Am Soc Nephrol 2011; 22: 1682–1695.
Li XJ, Sun L, Xiao L, Liu FY . Gene delivery in peritoneal dialysis related peritoneal fibrosis research. Chin Med J (Engl) 2012; 125: 2219–2224.
Motomura Y, Kanbayashi H, Khan WI, Deng Y, Blennerhassett PA, Margetts PJ et al. The gene transfer of soluble VEGF type I receptor (Flt-1) attenuates peritoneal fibrosis formation in mice but not soluble TGF-beta type II receptor gene transfer. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2005; 288: G143–G150.
Margetts PJ, Gyorffy S, Kolb M, Yu L, Hoff CM, Holmes CJ et al. Antiangiogenic and antifibrotic gene therapy in a chronic infusion model of peritoneal dialysis in rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 2002; 13: 721–728.
Nishino T, Miyazaki M, Abe K, Furusu A, Mishima Y, Harada T et al. Antisense oligonucleotides against collagen-binding stress protein HSP47 suppress peritoneal fibrosis in rats. Kidney Int 2003; 64: 887–896.
Guo H, Leung JC, Chan LY, Tsang AW, Lam MF, Lan HY et al. Ultrasound-contrast agent mediated naked gene delivery in the peritoneal cavity of adult rat. Gene Therapy 2007; 14: 1712–1720.
Kikuchi A, Aoki Y, Sugaya S, Serikawa T, Takakuwa K, Tanaka K et al. Development of novel cationic liposomes for efficient gene transfer into peritoneal disseminated tumor. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 947–955.
Sato Y, Murase K, Kato J, Kobune M, Sato T, Kawano Y et al. Resolution of liver cirrhosis using vitamin A-coupled liposomes to deliver siRNA against a collagen-specific chaperone. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 431–442.
Wang X, Podila R, Shannahan JH, Rao AM, Brown JM . Intravenously delivered graphene nanosheets and multiwalled carbon nanotubes induce site-specific Th2 inflammatory responses via the IL-33/ST2 axis. Int J Nanomedicine 2013; 8: 1733–1748.
Ban M, Langonne I, Huguet N, Guichard Y, Goutet M . Iron oxide particles modulate the ovalbumin-induced Th2 immune response in mice. Toxicol Lett 2013; 216: 31–39.
Morishige T, Yoshioka Y, Inakura H, Tanabe A, Narimatsu S, Yao X et al. Suppression of nanosilica particle-induced inflammation by surface modification of the particles. Arch Toxicol 2012; 86: 1297–1307.
Li J, Qu X, Bertram JF . Endothelial-myofibroblast transition contributes to the early development of diabetic renal interstitial fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Am J Pathol 2009; 175: 1380–1388.
Bellini A, Mattoli S . The role of the fibrocyte, a bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor, in reactive and reparative fibroses. Lab Invest 2007; 87: 858–870.
Desmouliere A, Geinoz A, Gabbiani F, Gabbiani G . Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 1993; 122: 103–111.
Wang X, Nie J, Jia Z, Feng M, Zheng Z, Chen W et al. Impaired TGF-beta signalling enhances peritoneal inflammation induced by E. coli in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2010; 25: 399–412.
Hirahara I, Kusano E, Yanagiba S, Miyata Y, Ando Y, Muto S et al. Peritoneal injury by methylglyoxal in peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int 2006; 26: 380–392.
Acknowledgements
We thank Motomu Shimaoka (Professor of Molecular Pathobiology, Mie University School of Medicine) for discussion and comments regarding the manuscript. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant number 25461252) and MEXT-Supported Program for Strategic Research Foundations at Private Universities, 2013–2017 (S1211029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Gene Therapy website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshizawa, H., Morishita, Y., Watanabe, M. et al. TGF-β1-siRNA delivery with nanoparticles inhibits peritoneal fibrosis. Gene Ther 22, 333–340 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2014.116
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2014.116
This article is cited by
-
Ameliorative role of SIRT1 in peritoneal fibrosis: an in vivo and in vitro study
Cell & Bioscience (2021)
-
The anti-scarring effect of corneal stromal stem cell therapy is mediated by transforming growth factor β3
Eye and Vision (2020)
-
Curcumin ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis via inhibition of transforming growth factor-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) pathway in a rat model of peritoneal dialysis
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2019)
-
Injectable and thermosensitive TGF-β1-loaded PCEC hydrogel system for in vivo cartilage repair
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Cationic microRNA-delivering nanocarriers for efficient treatment of colon carcinoma in xenograft model
Gene Therapy (2016)