Abstract
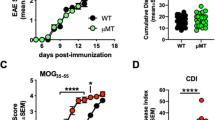
The aim of this work was to induce permanent tolerance toward self-antigens involved in autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS). We hypothesized that the stable auto-antigen presentation by dendritic cells (DCs) would tolerize auto-reactive T cells and, therefore, prevent disease development in a mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), which closely resembles MS. Specifically, our strategy included the ex vivo modification of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) with self-inactivating (SIN) lentivirus vectors that transcriptionally target the expression of myelin antigens to DCs. As SIN lentivirus vectors support the genomic integration of transgene sequences in HSC, the transduced and transplanted HSC may provide a constant supply of antigen expressing steady-state DCs. Here, we demonstrate that targeting myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) expression to DCs indeed resulted in complete and stable protection from EAE. No histological signs of EAE, such as demyelination, axonal damage, or infiltration of leukocytes in brain, spinal cord and optical nerve, were observed in tolerized mice. Tolerance induction was concomitant with the efficient deletion of MOG-specific T cells and the generation of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and, most importantly, directed toward a specific self-antigen while T-cell reactivity to unrelated foreign antigens was fully preserved.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin R, McFarland HF, McFarlin DE . Immunological aspects of demyelinating diseases. Annu Rev Immunol 1992; 10: 153–187.
Olerup O, Hillert J . HLA class II-associated genetic susceptibility in multiple sclerosis: a critical evaluation. Tissue Antigen 1991; 38: 1–15.
Bielekova B, Sung MH, Kadom N, Simon R, McFarland H, Martin R . Expansion and functional relevance of high-avidity myelin-specific CD4+ T cells in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 2004; 172: 3893–3904.
Weissert R, Kuhle J, de Graaf KL, Wienhold W, Herrmann MM, Muller C et al. High immunogenicity of intracellular myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein epitopes. J Immunol 2002; 169: 548–556.
Akirav EM, Xu Y, Ruddle NH . Resident B cells regulate thymic expression of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. J Neuroimmunol 235: 33–39.
Bruno R, Sabater L, Sospedra M, Ferrer-Francesch X, Escudero D, Martinez-Caceres E et al. Multiple sclerosis candidate autoantigens except myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein are transcribed in human thymus. Eur J Immunol 2002; 32: 2737–2747.
Anderson AC, Nicholson LB, Legge KL, Turchin V, Zaghouani H, Kuchroo VK . High frequency of autoreactive myelin proteolipid protein-specific T cells in the periphery of naive mice: mechanisms of selection of the self-reactive repertoire. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 761–770.
Klein L, Klugmann M, Nave KA, Tuohy VK, Kyewski B . Shaping of the autoreactive T-cell repertoire by a splice variant of self protein expressed in thymic epithelial cells. Nat Med 2000; 6: 56–61.
Bielekova B, Goodwin B, Richert N, Cortese I, Kondo T, Afshar G et al. Encephalitogenic potential of the myelin basic protein peptide (amino acids 83-99) in multiple sclerosis: results of a phase II clinical trial with an altered peptide ligand. Nat Med 2000; 6: 1167–1175.
Fassas A, Passweg JR, Anagnostopoulos A, Kazis A, Kozak T, Havrdova E et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for multiple sclerosis. A retrospective multicenter study. J Neurol 2002; 249: 1088–1097.
Sabatos-Peyton CA, Verhagen J, Wraith DC . Antigen-specific immunotherapy of autoimmune and allergic diseases. Curr Opin Immunol 22: 609–615.
Chan J, Ban EJ, Chun KH, Wang S, Backstrom BT, Bernard CC et al. Transplantation of bone marrow transduced to express self-antigen establishes deletional tolerance and permanently remits autoimmune disease. J Immunol 2008; 181: 7571–7580.
Xu B, Haviernik P, Wolfraim LA, Bunting KD, Scott DW . Bone marrow transplantation combined with gene therapy to induce antigen-specific tolerance and ameliorate EAE. Mol Ther 2006; 13: 42–48.
Eixarch H, Espejo C, Gomez A, Mansilla MJ, Castillo M, Mildner A et al. Tolerance induction in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis using non-myeloablative hematopoietic gene therapy with autoantigen. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 897–905.
Bosticardo M, Ghosh A, Du Y, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Candotti F . Self-inactivating retroviral vector-mediated gene transfer induces oncogene activation and immortalization of primary murine bone marrow cells. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 1910–1918.
Ko HJ, Chung JY, Nasa Z, Chan J, Siatskas C, Toh BH et al. Targeting MOG expression to dendritic cells delays onset of experimental autoimmune disease. Autoimmunity 2010; 44: 177–187.
Dresch C, Edelmann SL, Marconi P, Brocker T . Lentiviral-mediated transcriptional targeting of dendritic cells for induction of T cell tolerance in vivo. J Immunol 2008; 181: 4495–4506.
Bettelli E, Pagany M, Weiner HL, Linington C, Sobel RA, Kuchroo VK . Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific T cell receptor transgenic mice develop spontaneous autoimmune optic neuritis. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 1073–1081.
Alderuccio F, Nasa Z, Chung J, Ko HJ, Chan J, Toh BH . Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy as a treatment for autoimmune diseases. Mol Pharm 2011; 8: 1488–1494.
Naldini L, Blomer U, Gallay P, Ory D, Mulligan R, Gage FH et al. In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral vector. Science 1996; 272: 263–267.
Pfeifer A, Ikawa M, Dayn Y, Verma IM . Transgenesis by lentiviral vectors: lack of gene silencing in mammalian embryonic stem cells and preimplantation embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 2140–2145.
Hawiger D, Masilamani RF, Bettelli E, Kuchroo VK, Nussenzweig MC . Immunological unresponsiveness characterized by increased expression of CD5 on peripheral T cells induced by dendritic cells in vivo. Immunity 2004; 20: 695–705.
Goverman JM . Immune tolerance in multiple sclerosis. Immunol Rev 2011; 241: 228–240.
Acknowledgements
We thank Burkhard Becher, Martin Pruschy, Carla Rohrer-Bley and Kati Zlinszky for scientific and technical support, Dana Salathe and Maricello Rios for assistance with mice, and Craig Chappell for helpful comments on this manuscript. This work was supported by funds from the Swiss Multiple Sclerosis Society and the University of Zurich.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Andrade Pereira, B., Fraefel, C., Hilbe, M. et al. Transcriptional targeting of DCs with lentiviral vectors induces antigen-specific tolerance in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Gene Ther 20, 556–566 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2012.73
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2012.73
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Clinical and immunological control of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by tolerogenic dendritic cells loaded with MOG-encoding mRNA
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2019)
-
Tolerance of activated pathogenic CD4+ T cells by transcriptional targeting of dendritic cells
Gene Therapy (2015)
-
Dendritic Cell Immune Therapy to Break or Induce Tolerance
Current Stem Cell Reports (2015)
-
Development of gene transfer for induction of antigen-specific tolerance
Molecular Therapy - Methods & Clinical Development (2014)