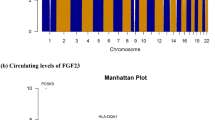
Abstract
This genome-wide association study (GWAS) utilises data from the Western Australian Pregnancy Cohort (Raine) Study for 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) levels measured in blood collected at age 6 years (n=673) and at age 14 years (n=1140). Replication of significantly associated genes from previous GWASs was found for both ages. Genome-wide significant associations were found both at age 6 and 14 with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on chromosome 11p15 in PDE3B/CYP2R1 (age 6: rs1007392, P=3.9 × 10−8; age14: rs11023332, P=2.2 × 10−10) and on chromosome 4q13 in GC (age 6: rs17467825, P=4.2 × 10−9; age14: rs1155563; P=3.9 × 10−9). In addition, a novel association was observed at age 6 with SNPs on chromosome 7p15 near NPY (age 6: rs156299, P=1.3 × 10−6) that could be of functional interest in highlighting alternative pathways for vitamin D metabolism in this age group and merits further analysis in other cohort studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu J . Vitamin D content of food and its contribution to vitamin D status: a brief overview and Australian focus. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2012; 11: 1802–1807.
Australian Bureau of Statistics. Australian Health Survey: Biomedical Results for Nutrients, 2011-12 cat. no. 4364.0.55.006 2014.
Daly RM, Gagnon C, Lu ZX, Magliano DJ, Dunstan DW, Sikaris KA et al. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its determinants in Australian adults aged 25 years and older: a national, population-based study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2012; 77: 26–35.
Munns CF, Simm PJ, Rodda CP, Garnett SP, Zacharin MR, Ward LM et al. Incidence of vitamin D deficiency rickets among Australian children: an Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit study. Med J Aust 2012; 196: 466–468.
Reid IR, Bolland MJ, Grey A . Effects of vitamin D supplements on bone mineral density: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2014; 383: 146–155.
Nowson CA, McGrath JJ, Ebeling PR, Haikerwal A, Daly RM, Sanders KM et al. Vitamin D and health in adults in Australia and New Zealand: a position statement. Med J Aust 2012; 196: 686–687.
Dastani Z, Li R, Richards B . Genetic regulation of vitamin D levels. Calcif Tissue Int 2013; 92: 106–117.
Ahn J, Yu K, Stolzenberg-Solomon R, Simon KC, McCullough ML, Gallicchio L et al. Genome-wide association study of circulating vitamin D levels. Hum Mol Genet 2010; 19: 2739–2745.
Engelman CD, Meyers KJ, Ziegler JT, Taylor KD, Palmer ND, Haffner SM et al. Genome-wide association study of vitamin D concentrations in Hispanic Americans: the IRAS family study. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2010; 122: 186–192.
Lasky-Su J, Lange N, Brehm JM, Damask A, Soto-Quiros M, Avila L et al. Genome-wide association analysis of circulating vitamin D levels in children with asthma. Hum Genet 2012; 131: 1495–1505.
Wang TJ, Zhang F, Richards JB, Kestenbaum B, van Meurs JB, Berry D et al. Common genetic determinants of vitamin D insufficiency: a genome-wide association study. Lancet 2010; 376: 180–188.
Newnham JP, Evans SF, Michael CA, Stanley FJ, Landau LI . Effects of frequent ultrasound during pregnancy: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 1993; 342: 887–891.
Knox S, Harris J, Calton L, Wallace AM . A simple automated solid-phase extraction procedure for measurement of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and D2 by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Ann Clin Biochem 2009; 46 (Pt 3): 226–230.
Chun RF . New perspectives on the vitamin D binding protein. Cell Biochem Funct 2012; 30: 445–456.
Shinkyo R, Sakaki T, Kamakura M, Ohta M, Inouye K . Metabolism of vitamin D by human microsomal CYP2R1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 324: 451–457.
McCarty MF, Thomas CA . PTH excess may promote weight gain by impeding catecholamine-induced lipolysis-implications for the impact of calcium, vitamin D, and alcohol on body weight. Med Hypotheses 2003; 61: 535–542.
Zemel MB, Shi H, Greer B, Dirienzo D, Zemel PC . Regulation of adiposity by dietary calcium. FASEB J 2000; 14: 1132–1138.
Reinehr T, de Sousa G, Alexy U, Kersting M, Andler W . Vitamin D status and parathyroid hormone in obese children before and after weight loss. Eur J Endocrinol 2007; 157: 225–232.
Lai JK, Lucas RM, Clements MS, Harrison SL, Banks E . Assessing vitamin D status: pitfalls for the unwary. Mol Nutr Food Res 2010; 54: 1062–1071.
Thorsell A, Heilig M . Diverse functions of neuropeptide Y revealed using genetically modified animals. Neuropeptides 2002; 36: 182–193.
Franquinho F, Liz MA, Nunes AF, Neto E, Lamghari M, Sousa MM . Neuropeptide Y and osteoblast differentiation—the balance between the neuro-osteogenic network and local control. FEBS J 2010; 277: 3664–3674.
Brothers SP, Wahlestedt C . Therapeutic potential of neuropeptide Y (NPY) receptor ligands. EMBO Mol Med 2010; 2: 429–439.
Wang Q, Nicholson PH, Suuriniemi M, Lyytikainen A, Helkala E, Alen M et al. Relationship of sex hormones to bone geometric properties and mineral density in early pubertal girls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1698–1703.
Zengin A, Zhang L, Herzog H, Baldock PA, Sainsbury A . Neuropeptide Y and sex hormone interactions in humoral and neuronal regulation of bone and fat. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2010; 21: 411–418.
Hollams EM, Hart PH, Holt BJ, Serralha M, Parsons F, de Klerk NH et al. Vitamin D and atopy and asthma phenotypes in children: a longitudinal cohort study. Eur Respir J 2011; 38: 1320–1327.
Maunsell Z, Wright DJ, Rainbow SJ . Routine isotope-dilution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay for simultaneous measurement of the 25-hydroxy metabolites of vitamins D2 and D3. Clin Chem 2005; 51: 1683–1690.
Clarke MW, Tuckey RC, Gorman S, Holt B, Hart PH . Optimized 25-hydroxyvitamin D analysis using liquid-liquid extraction with 2D separation with LC/MS/MS detection, provides superior precision compared to conventional assays. Metabolomics 2013; 9: 1031–1040.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Li Y, Willer CJ, Ding J, Scheet P, Abecasis GR . MaCH: using sequence and genotype data to estimate haplotypes and unobserved genotypes. Genet Epidemiol 2010; 34: 816–834.
R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing In R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013.
Manuilova E, Schuetzenmeister A, Model F . mcr: Method Comparison Regression. In. 2012.
Barnett A, Baker P, Dobson A . Season: Analysing Seasonal Data R Functions. In. R package version 0.3-2 ed, 2012.
van der Mei IA, Ponsonby AL, Dwyer T, Blizzard L, Taylor BV, Kilpatrick T et al. Vitamin D levels in people with multiple sclerosis and community controls in Tasmania, Australia. J Neurol 2007; 254: 581–590.
Aulchenko YS, Struchalin MV, van Duijn CM . ProbABEL package for genome-wide association analysis of imputed data. BMC Bioinformatics 2010; 11: 134.
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D . Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 904–909.
Hiersche M . postgwas: GWAS Post-Processing Utilities. In: R package version 1.02, 2012.
Panagiotou OA, Ioannidis JP . What should the genome-wide significance threshold be? Empirical replication of borderline genetic associations. Int J Epidemiol 2012; 41: 273–286.
Pruim RJ, Welch RP, Sanna S, Teslovich TM, Chines PS, Gliedt TP et al. LocusZoom: regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics 2010; 26: 2336–2337.
Melville S . NCBI2R: NCBI2R-An R package to navigate and annotate genes and SNPs. In. R package version 1.4.4 ed, 2012.
Acknowledgements
We are extremely grateful to all the families who took part in this study and the whole Raine Study team, which includes data collectors, cohort managers, data managers, clerical staff, research scientists and volunteers. The Raine Study has been supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council over the last 20 years with funding for core management provided by The University of Western Australia (UWA), Raine Medical Research Foundation, Telethon Kids Institute, UWA Faculty of Medicine, Dentistry and Health Sciences, Women and Infants Research Foundation, Curtin University and Edith Cowan University. The 5-year cohort review was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (ID 963209) and The Raine Foundation. The 14-year follow-up was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (ID 211912 and ID 003209) and The Raine Foundation. Genome-wide SNP genotyping data generated from samples collected at either the 14- or 17-year follow-ups were supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (ID 572613).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Genes and Immunity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, D., Holt, B., Pennell, C. et al. Genome-wide association study of vitamin D levels in children: replication in the Western Australian Pregnancy Cohort (Raine) study. Genes Immun 15, 578–583 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2014.52
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2014.52
This article is cited by
-
Investigation of genetic variation and lifestyle determinants in vitamin D levels in Arab individuals
Journal of Translational Medicine (2018)
-
SNPs related to vitamin D and breast cancer risk: a case-control study
Breast Cancer Research (2018)