Abstract
Replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing three major glycoproteins (gB, gC, and gD) of pseudorabies virus (PrV) were constructed and used to examine the ability of these glycoproteins to induce protective immunity against a lethal challenge. Among three constructs, recombinant adenovirus expressing gB (rAd-gB) was found to induce the most potent immunity biased to Th1-type, as determined by the IgG isotype ratio and the profile of the Th1/Th2 cytokine production. Conversely, the gC-expressing adenovirus (rAd-gC) revealed Th2-type immunity and the gD-expressing adenovirus (rAd-gD) induced lower levels of IFN-γ and IL-4 production than other constructs, except IL-2 production. Mucosal delivery of rAd-gB induced mucosal IgA and serum IgG responses and biased toward Th2-type immune responses. However, these effects were not observed in response to systemic delivery of rAd-gB. In addition, rAd-gB appeared to induce effective protective immunity against a virulent viral infection, regardless of whether it was administered via the muscular or systemic route. These results suggest that administration of replication-incompetent adenoviruses can induce different types of immunity depending on the expressed antigen and that recombinant adenoviruses expressing gB induced the most potent Th1-biased humoral and cellular immunity and provided effective protection against PrV infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Adenovirus (Ad) is double-stranded linear DNA viruses with genomes of approximately 36 kb in length. Ad is used in the expression of genes of interest for gene therapy and vaccine development (Shiver et al., 2002; Mizuguchi, 2004; Plog et al., 2006; Khanam et al., 2007). In one such method, foreign genes are cloned into regions that are dispensable for viral replication, such as the E3 gene, or into the intersection between E4 and the right inverted terminal repeat (ITR) (Babiuk et al., 2000), which results in replication-competent viruses. However, the biosafety of such viruses remains to be addressed. In another method, a large deletion in the E1 and E3 genes was employed to create a replication-incompetent adenovirus. Such replication-incompetent adenoviruses can grow only in cells that contain the complement E1 region of the adenovirus genome (Babiuk et al., 2000), and this increases their biosafety for experimental use. Also, high levels of expression are achieved in replication-incompetent adenoviruses when the foreign genes are under the control of constitutive promoters such as the CMV promoter (Ambriovic et al., 1997). Other advantages of recombinant adenoviruses include their broad host range and, in the case of livestock, the lack of maternally derived antibodies that interfere with vaccine efficacy in young and growing animals (Monteil et al., 1997).
The pseudorabies virus (PrV) is a porcine alpha-herpesvirus that causes the fatal Aujeszky's disease in swine. Aujeszky's disease is an important infectious disease in the swine industry (Kluge et al., 1999), and control of disease outbreaks in swine by immunization with active, modified live, and inactivated vaccines have been attempted (Kit, 1988; Mettenleiter, 1996). Attenuated vaccines, which generally induce long-lasting immunity, carry a risk of insufficient attenuation and genetic instability. Inactivated vaccines are less efficient than attenuated vaccines and require repeat doses. Therefore, the use of live recombinant vaccines carrying individual PrV genes may provide a safe alternative to the use of attenuated live vaccine strains.
Three major glycoproteins (gB, gC, and gD) are involved in the essential steps in the progress of PrV infection because of their roles in the induction of protective immune responses against virus infection, as noted in vaccination experiments with mouse or pig models (Monteil et al., 1997; van Rooij et al., 1998; Hong et al., 2002; Yoon et al., 2006). Several B-cell epitopes detected on PrV gB and gC glycoproteins (Ober et al., 1998; Zaripov et al., 1998, 1999; Ober et al., 2000) and T-cell epitopes detected on the PrV gC glycoprotein (Ober et al., 1998; Ober et al., 2000) induce both humoral and cytotoxic responses (van Rooij et al., 1998, 2000). Additionally, vaccination of mice or pigs with either purified recombinant gD or recombinant gD-expressing virus vectors conferred protection to the animals (Eloit et al., 1995; Gonin et al., 1996; Monteil et al., 1997, 2000). However, the relative potency of recombinant viral vectors expressing the three major glycoproteins has not yet been investigated. Therefore, we constructed replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing these gB, gC, and gD, and examined their ability to induce immune responses against PrV. Among three recombinant adenovirus constructs, the gB-expressing adenovirus was found to induce the most potent Th1-type immunity. Further, we investigated the nature of the protective immunity induced by systemic and mucosal delivery of a replication-incompetent gB-expressing adenovirus.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Female C57BL/6 (H-2b) mice of 5 to 6 weeks of age were purchased from KOATECH (Pyeongtaek, Republic of Korea). Mice were maintained according to Institutional Guidelines at the animal facility of Chonbuk National University under standard conditions. All experiments were performed according to the guidelines of the committee on the Care of Laboratory Animal Resources, Commission on Life Science, National Research Council.
Cells and viruses
The wild-type pseudorabies virus (PrV) Yangsan (YS) strain was generously supplied by the National Veterinary Research and Quarantine Service of the Republic of Korea. PrV was propagated in a porcine kidney cell line, PK-15, using DMEM supplemented with 2.5% FBS, penicillin (100 U/ml), and streptomycin (100 U/ml). The PK-15 cultures were infected with PrV at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01, and then incubated in a humidified CO2 incubator for 1 h at 37℃. The inoculum was removed after adsorption and 10 ml of a maintenance medium containing 2.5% FBS was added. Cultures of host cells showing 80-90% cytopathic effect (CPE) were harvested at approximately 48 to 72 h post-infection. Virus stocks were concentrated by centrifugation at 50,000 g, titrated by a plaque assay, and stored in aliquots at -80℃ until needed.
Construction of replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing glycoproteins
The Gateway cloning technique was used to construct replication-defective adenoviruses expressing PrV glycoproteins (Walhout et al., 2000; Suzuki et al., 2005). We constructed recombinant entry vectors (pENTR; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) containing PrV glycoprotein genes by PCR amplification. Specific primers were used to amplify the gB, gC, and gD genes of the PrV as described in Table 1. Each fragment of the glycoprotein gene was amplified in 50 µl of a PCR buffer [2 mM each primer, 1 mM MgCl2, 100 µM each deoxynucleoside triphosphate, 2.5 U of i-pfu DNA polymerase (iNtRON Biotech, Daejeon, Korea), 100 ng PrV genome DNA as template]. The first cycle was performed at 96℃ for 3 min, 58℃ for 30 s, and 68℃ for 3 min. The DNA was then amplified for 34 cycles (94℃ for 1 min, 58℃ for 30 s, 68℃ for 3 min) followed by a final extension step at 72℃ for 10 min. The recombinant entry vector pENTR11 containing each glycoprotein gene was mixed with the adenoviral destination vector (pAd/CMV/V5-DEST; Invitrogen) to generate the recombinant adenoviral DNA plasmid containing PrV glycoprotein genes in the presence of LR Clonase (Invitrogen) for catalysis. The recombinant adenoviral plasmid DNA was transformed into competent E. coli and putative positive clones were selected by M13 primer-PCR amplification and detection by electrophoresis. Those putative clones were also cultured on LB plates containing 30 µg/ml chloramphenicol since true expression clones would be ampicillin-resistant and chloramphenicol-sensitive. Following digestion of recombinant adenoviral plasmid DNAs with the Pac I restriction enzyme, human embryonal kidney 293A cells were transfected to generate replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing gB (rAd-gB), gC (rAd-gC), and gD (rAD-gD). Viruses were then purified using an Adeno-X mini purification kit (Clontech, Mountain View, CA), titrated by plaque assay, and stored at -80℃ until use. Recombinant viruses (rAd-gB, rAd-gC, and rAd-gD) were used to infect NIH3T3 cells, and the expression of each glycoprotein was identified by immunoblot using polyclonal antibodies.
Immunization and sample collection
Groups of female mice were immunized with replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing PrV glycoproteins (rAd-gB, rAd-gC, and rAd-gD) by either the intranasal (i.n.) or intramuscular (i.m.) route. For i.m. administration, recombinant adenoviruses (106 pfu/mouse) were injected into the anterior tibialis muscle three times at weekly intervals (0, 7, and 14 days). The i.n. immunizations were also performed three times at weekly intervals (0, 7, and 14 days) by depositing 106 pfu of recombinant adenovirus onto the nares of deeply anesthetized mice. Control mice were immunized with replication-incompetent adenovirus expressing the LacZ gene (rAd-LacZ). Serum samples were collected 7 days after each immunization by retro-orbital bleeding and stored at -80℃ until needed. Vaginal lavage fluid samples were obtained by infusing 100 µl of PBS (pH 7.2) into the vaginal canal and then recovering fluid with a micropipette. Vaginal lavages were collected once per day for 3 days, and combined on day 7 post-immunization. Fecal samples were collected, weighed, and suspended at a concentration of 100 mg/ml in PBS containing 0.1% sodium azide. Each sample was stored at -80℃ until use.
ELISA for PrV-specific antibodies, IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, and IgA
A standard ELISA was used to determine the levels of PrV-specific antibodies in the serum, vaginal lavage contents, and feces. Briefly, ELISA plates were coated overnight at 4℃ with an optimal dilution (0.5 to 1.0 µg/well) of semi-purified PrV antigen to the sample wells, and either goat anti-mouse IgG (Southern Biotechnology Associate Inc., Birmingham, AL) or rabbit anti-mouse IgA (Zymed, San Francisco, CA) to the standard wells. The viral antigen for coating was prepared by semipurification of the viral stock by centrifugation at 50,000 × g after treatment with 0.5% Triton X-100 (Sigma, St Louis, MO) (Bianchi et al., 1998). Next, the plates were washed three times with PBS-Tween 20 (PBST) and blocked with 3% dehydrated milk. The samples were serially diluted twofold, incubated for 2 h at 37℃, and finally incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG for 1 h. Biotinylated goat-anti-mouse IgA was added to the samples for 2 h at 37℃ to measure IgA levels in vaginal lavage fluid and in fecal samples, followed by the addition of peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, West Grove, PA). Color was developed by the addition of a suitable substrate (11 mg of 2,2-azinobis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid in a mixture of 25 ml of 0.1 M citric acid, 25 ml of 0.1 M sodium phosphate, and 10 µl of hydrogen peroxide). The concentration of PrV-specific antibodies was determined using an automated ELISA reader and the SOFTmax Pro4.3 program and results were compared with two concentrations of standard immunoglobulin proteins.
Th1- and Th2-type cytokine ELISA following in vitro stimulation of CD4+ T cells
Mice were sacrificed two weeks after the final immunization for preparation of splenocytes and lymph node (LN) cells. Erythrocytes were depleted by the treatment of single cell suspensions with ammonium chloride containing Tris buffer (NH4Cl-Tris) for 5 min at 37℃, and these cells were used as responder cells. Enriched antigen-presenting cell (APC) populations were obtained using previously described methods (Eo et al., 2001) and were used as stimulators. Briefly, splenocytes from naїve female mice were depleted of erythrocytes, and 107 cells suspended in 3 ml of media were layered over 2 ml of a metrizamide gradient (Accurate Chemical and Sci., Westbury, NY; analytical grade with 14.5 g metrimazide added to 100 ml of PBS, pH 7.2). Cells were centrifuged at 600 × g for 10 min and the cell interface was collected. Next, enriched APC populations were pulsed with UV-inactivated PrV at 5.0 moi for 3 h (prior to inactivation), and cells were washed and counted. The responder cells and the PrV-pulsed APCs were combined at responder-to-stimulator ratios of 5:1, 2.5:1, and 1.25:1 in 200 µl of RPMI medium. Culture supernatants were harvested after 3 days of incubation, and a similar number of responder cells were stimulated for 48 h with 5 µg of concanavalin A as a polyclonal positive stimulator.
Cytokine levels in the culture supernatants were measured with ELISA. Briefly, ELISA plates were coated with IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-γ anti-mouse antibodies (Pharmingen, San Diego, CA; clone no. JES6-1A12, 11B11, and R4-6A2, respectively) and incubated overnight at 4℃. The plates were washed three times with PBST and then blocked with 3% nonfat-dried milk for 2 h at 37℃. The culture supernatants and standards for recombinant IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-γ proteins (Pharmingen) were added to the plates, which were incubated for 2 h at 37℃. Biotinylated IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-γ antibodies (Pharmingen; clone no. JES6-5H4, BVD6-24G2, and XMG1.2, respectively) were then added and incubated overnight at 4℃. The plates were then washed and incubated with peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin (Pharmingen) for 1 h, followed by color development. The cytokine concentration was determined using an automated ELISA reader.
Virus challenge experiment
The immunized mice were infected i.n. with the virulent PrV YS strain (10 LD50) two weeks after the final immunization. The challenged mice were examined daily to quantify the number of dead animals. Mice generally began to exhibit clinical signs of illness 3 to 4 days post-challenge.
Statistical analysis
Where specified, the data were analyzed for statistical significance using a Student's t-test. A P value < 0.05 was considered significant. Kaplan-Meier curves were generated for mice that survived a lethal challenge with PrV. The survival time of mice that were alive at the end of the study was regarded as censored. Time data were analyzed using the log rank statistic to compare the two survival curves, and P values were computed with the chi-square method. The survival rates of the two groups were considered to be significantly different if the two-side P value was less than 0.05.
Results
Construction of replication-incompetent adenovirus expressing glycoproteins
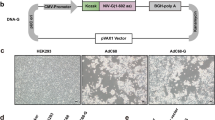
PCR products of each glycoprotein were amplified using specific primers, cloned, and sequenced to identify the ORF in order to construct replication-incompetent adenoviruses that express PrV gB, gC, and gD proteins (Figure 1A). Recombinant adenoviral expression plasmid DNA encoding glymbination of recombinant entry vectors in the presence of LR Clonase (Figure 1B). Following Pac I digestion and transfection into 293A cells, cells were observed to approximately 50-70% CPE. Recombinant adenoviruses expressing gB (rAd-gB), gC (rAd-gC), and gD (rAd-gD) were harvested and protein extracts from NIH3T3 cells infected with purified replication-incompetent adenoviruses were subjected to immunoblot analysis with polyclonal antibodies against gB, gC, and gD. The corresponding protein products of gB (~100 kD), gC (~51 kD), and gD (~44 kD) were detected in the reaction (Figure 1C), which indicated that replication-incompetent adenoviruses successfully expressed glycoproteins.
The rAd constructs used for this study. (A) PCR products of PrV glycoprotein genes (gB, gC, and gD). M, 1 kb DNA size marker ladder; 1, PrV gB gene (2901 bp); PrV gC gene (1615 bp); PrV gD gene (1323 bp). (B) Schematic representation of the linear genomes of the rAd expressing glycoproteins (gp) of PrV. The dashed line at the left end of the figure represents the position of region E1. The open box located toward the right end represents an approximately 2.7 kb deletion in the non-essential E3 region (ΔE3). The hatched boxes at either end represent the left and right inverted terminal repeats (5'ITR and 3'ITR, respectively), and the open circle near the 5'ITR represents the packaging signal (ψ). In the rAds, region E1 is replaced with the gp gene of the entry vector through recombination sites (attL1/R1, attL2/attR2) in the presence of LR clonase. CMV, CMV promoter; pA, SV40 polyadenylation signal. (C) Identification of the expression of glycoprotein genes from rAds by immunoblot analysis. The protein extracts from NIH3T3 cells infected with purified replication-incompetent adenoviruses were analyzed by immunoblot analysis using polyclonal antibodies against gB, gC, and gD.
Comparison of immunity induced by replication-incompetent adenovirus expressing glycoproteins
In order to assess humoral responses induced by replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing PrV glycoproteins, mice were immunized i.m. with rAd-gB, rAd-gC, and rAd-gD (106 pfu/mouse) through both tibialis muscles three times at 7 day intervals. PrV-specific IgG levels in the sera were quantified on the seventh day after each immunization, as described in Table 2. The control construct, replication-incompetent adenovirus expressing LacZ (rAd-LacZ), induced no significant PrV-specific IgG responses, while adenoviruses expressing each of the glycoproteins (rAd-gB, rAd-gC, and rAd-gD) produced detectable IgG levels after the first injection. Subsequent injections boosted the primary IgG responses. Replication-incompetent adenovirus expressing PrV gB (rAd-gB) induced the strongest responses of PrV-specific IgGs among the three constructs. In addition, both rAd-gC and rAd-gD revealed comarable levels of PrV-specific IgG in sera (Table 2). Evaluation of the PrV-specific IgG isotypes (IgG2a and IgG1) induced by each construct revealed that different isotype level patterns were observed in response to constructs expressing different immunogens (Table 2). The rAd-gB construct produced significantly higher amounts of the IgG2a isotype than rAd-gC and rAd-gD, resulting in the highest IgG2a to IgG1 ratio, which was indicative of a Th1-type immune response. Conversely, rAd-gC had a low IgG2a to IgG1 ratio as a result of higher production of the PrV-specific IgG1 isotype when compared to the IgG2a isotype (Table 2). In addition, rAd-gD induced similar levels of IgG2a and IgG1 and produced a median IgG2a:IgG1 ratio. These results demonstrate that replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing PrV glycoproteins successfully induced PrV-specific immunity. Further, different humoral responses were induced by adenoviruses that expressed different immunogens.
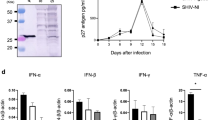
We examined the profile of Th1 (IL-2 and IFN-γ) and Th2 (IL-4) cytokines produced by CD4+ T cells stimulated with the PrV antigen protein, which is known to induce the predominant expansion of immune CD4+ T cells (Eo et al., 2001). Replication-incompetent adenoviruses consistently induced a different pattern of Th1- and Th2-type cytokine production according to the expressed antigen (Figure 2). Animals immunized with rAd-gB displayed higher levels of IFN-γ production than those treated with rAd-gC and rAd-gD, and rAd-gC administration induced marginally higher IL-4 production than treatment with rAd-gB. Additionally, treatment with rAd-gD resulted in production of lower amounts of IFN-γ and IL-4, but not IL-2. These results and associated antibody responses indicated that rAd-gB induced Th1-type responses and rAd-gC induced Th2-type responses. In addition, rAd-gB was the most potent inducer of humoral and cellular immunity.
The profile of cytokine production (IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-γ) by splenocytes (A, B, and C) and popliteal LN cells (D, E, and F) from animals immunized with rAd expressing glycoproteins (rAd-gB, rAd-gC, and rAd-gD). The responder cells (splenocytes and LN cells from the immunized mice) were mixed with irradiated syngeneic enriched APCs that had been pulsed with UV-inactivated PrV, and incubated for 3 days at 2 weeks after the final immunization. The levels of cytokines in the supernatants of the stimulated T cells were determined by cytokine ELISA. The test was carried out in quadruplicate wells. The bars represent the average ± SD from three independent experiments. P-values in the graphs were calculated using the Student's t-test.
Immunity induced by systemic and mucosal delivery of replication-incompetent adenovirus expressing gB
The immunity induced by systemic and mucosal delivery of replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing gB (rAd-gB), which was the most potent immunogen among three constructs tested, was further evaluated. Groups of mice were immunized with rAd-gB by either the intramuscular (systemic) or intranasal (mucosal) route. The i.n. immunization was performed by depositing rAd-gB onto the nares of deeply anesthetized mice. Detectable PrV-specific IgG antibodies in sera were produced by primary i.m. or i.n. administration of rAd-gB and boosted by subsequent immunizations (Figure 3A, B and C). However, the i.m. administration of rAd-gB showed stronger IgG responses than i.n. administration. In addition, when PrV-specific IgG isotype ratios were examined, i.n. administration induced a reduction in IgG2a to IgG1 ratios (Figure 3D).
Serum PrV-specific IgG levels and associated isotype distributions in animals immunized by rAd-gB systemic and mucosal delivery. Groups of C57BL/6 (H-2b) mice were immunized with rAd-gB (106 pfu/mouse) by either the i.m. or i.n. route three times at 7 day intervals. On the seventh day after each immunization, the PrV-specific IgG levels in the sera were evaluated by ELISA. The levels of IgG2a and IgG1 were compared 7 days after the final immunization. The circles on the graph represent the individual IgG levels and the height of the bar shows the average of each group (n = 7). P-values in the graphs were calculated using the Student's t-test.
Conversely, when IgA responses at mucosal sites were analyzed on the seventh day following the final immunization, induced IgA response levels displayed different patterns that were likely not a result of the serum IgG responses (Figure 4). Mice immunized i.m. with rAd-gB did not show significantly detectable PrV-specific IgA antibodies in the vaginal fluid or intestinal tract. However, i.n. administration of rAd-gB strongly induced secretory IgA responses at the mucosal site. These results suggest that mucosal IgA as well as serum IgG responses can be induced by mucosal delivery of rAd-gB. In addition, i.m. administration of rAd-gB produced strong serum PrV-specific IgG responses but not IgA responses at mucosal sites.
Mucosal IgA responses induced by systemic and mucosal delivery of rAd-gB. Groups of C57BL/6 (n = 7) mice were immunized with rAd-gB (106 pfu/mouse) by either the i.m. or i.n. route three times at 7 day intervals. Seven days after the final immunization, mucosal IgA levels in samples from both the vaginal tract (A) and feces (B) were measured by ELISA. The circles on the graph represent the individual IgG levels and the height of the bar shows the average of each group (n = 7). P-values in the graphs were calculated using the Student's t-test.
To further evaluate the nature of immunity induced by systemic and mucosal delivery of rAd-gB, the Th1 (IL-2 and IFN-γ)- and Th2 (IL-4)-type cytokines produced by CD4+ T cells stimulated with antigen proteins were evaluated. Systemic and mucosal delivery of rAd-gB induced different patterns of Th1- and Th2-type cytokine production (Figure 5). Intramuscular administration of rAd-gB induced strong Th1-type cytokine (IFN-γ and IL-2) production. However, i.n. rAd-gB delivery revealed enhanced IL-4 production and reduced IFN-γ production. This pattern of Th1- and Th2-type cytokine production was consistent with those from PrV-specific IgG isotypes. Therefore, i.m. administration of rAd-gB induced Th1-type immunity and this was reduced by the i.n. delivery of rAd-gB.
The profile of cytokine production (IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-γ) by splenocytes (A, B, and C) and draining LN cells (D, E, and F) of the animals immunized with rAd-gB via the systemic and mucosal routes. Responder cells (splenocytes and draining LN cells from the immunized mice) were mixed with the irradiated syngeneic enriched APCs, which had been pulsed with UV-inactivated PrV and then incubated for 3 days at two weeks after the final immunization. The levels of cytokines in the supernatants of the stimulated T cells were determined by cytokine ELISA. The test was carried out in quadruplicate wells. The bars represented the average ± SD of three independent experiments. P-values in the graphs were calculated using the Student's t-test.
Protective immunity induced by replication-incompetent adenovirus expressing glycoproteins against viral challenge
In order to compare the protective efficacy of immunity conferred by systemic and mucosal delivery of gB-expressing replication-incompetent adenovirus against a virulent viral infection, groups of mice that received i.m. and i.n. administration of rAd-gB were then challenged i.n. with the virulent PrV YS strain (10 LD50) 2 weeks post-immunization. Anamnestic PrV-specific IgG and IgA in sera and vaginal lavages were evaluated 3 days after challenge, and serum IgG antibody levels in mice that received rAd-gB was comparable, regardless of i.m. or i.n. administration (Figure 6A). Mice immunized i.m. with rAd-gB had significantly detectable IgA levels in the vaginal tract following challenge, although IgA levels in mice subjected to i.m. administration were marginally lower than in mice that received the i.n. administration (Figure 6B).
Serum PrV-specific IgG and mucosal IgA determined at 3 days post-challenge with the virulent PrV YS strain. Two weeks after the final immunization, groups of mice (n = 7) were challenged i.n. with the PrV YS strain (10 LD50) and the sera and vaginal lavages were collected at 3 days post-challenge. PrV-specific IgG and IgA were determined by conventional ELISA. The circles on the graph represent the individual IgG levels and the height of the bar shows the average of each group. P-values in graphs were calculated using the Student's t-test.
Survival curves of mice immunized with recombinant glycoprotein-expressing adenoviruses were examined. Both i.m. and i.n. delivery of rAd-gB provided effective resistance against viral challenge (P = 0.0002), as shown in Figure 7. In addition, the protective efficacy of rAd-gC administered via the i.m. route was inferior to that of the rAd-gB-immunized group (P = 0.0468), whereas the rAd-gD-immunized group showed marginally less protective immunity than the rAd-gB-immunized group (P = 0.1279). These results suggest that recombinant adenovirus expressing gB provides the most potent protection against a lethal challenge of virus. Further, rAd-gB delivered by both systemic and mucosal routes conferred comparable protective immunity.
Susceptibility of animals immunized with rAd-gB via systemic and mucosal routes. Two weeks after the final immunization, groups of mice (n = 7) were challenged i.n. with the PrV YS strain (10LD50). The challenged mice were then examined daily for any signs of inflammation, illness, and death until 14 days post-challenge. Kaplan-Meiers survival curves were computed and analyzed using the chi-square test.
Discussion
Overall, this study suggests that replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing three major glycoproteins (gB, gC, and gD) of PrV induced both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses. Different patterns of immune responses emerged in response to adenoviruses that expressed different antigens. The recombinant adenovirus expressing gB (rAd-gB) elicited the most potent immune responses biased to Th1-type. Conversely, the adenovirus that expressed gC favored Th2-type responses, and the adenovirus that expressed rAd-gD induced lower IFN-γ and IL-4 levels than the other constructs, but revealed comparable IL-2 production. Mucosal delivery of rAd-gB induced mucosal IgA as well as serum IgG responses, and resulted in Th2-type immune responses. However, similar effects were not observed in response to systemic delivery. Finally, recombinant adenoviruses expressing gB conferred the most effective protection against a lethal viral challenge, regardless of systemic or mucosal administration.
A better knowledge of protective immunological parameters is a precondition in the development and effectiveness of anti-herpesvirus vaccines in general and against PrV in particular. There is increasing evidence that cell-mediated immunity is important in effective induction of protective immunity against herpesviruses (Bianchi et al., 1998; Fischer et al., 2000; Eo et al., 2001; van Rooil et al., 2004; La et al., 2005), and the significance of Th1-type CD4+ effector T cells in protective immunity has been demonstrated with a PrV-infected murine model (Bianchi et al., 1998; Yoon et al., 2006). In our study, the replication-incompetent adenoviruses expressing gB showed Th1-biased immunity, which provided protection against PrV infection. This finding supports results from a previous report that illustrated the substantial role that gB plays as a dominant immunogen in the effective protection of a PrV DNA vaccination (Yoon et al., 2006). In addition, the strongest responses of Th1-type CD4+ T cells observed in this study were noted in mice that received gB-expressing plasmid DNA, which provided effective protection against a virulent viral infection (Yoon et al., 2006). However, our results differed from another study which found that recombinant gD-expressing adenoviruses induced the most potent responses of neutralizing antibody of the three major glycoproteins (Monteil et al., 1997), but with no absolute correlation between the presence of detectable neutralizing antibodies to gD prior to challenge and protection from disease. This suggests that protection from PrV infection may be dependent on cell-mediated immunity. Therefore, our study results support previous studies that have demonstrated the important role that cell-mediated immunity, particularly Th1-type responses, plays in protective immunity against PrV infections.
Our study also suggested that different types of immunity were induced depending on the type of expressed antigen. Treatment with a replication-incompetent gB-expressing adenovirus biased to the Th1-type immunity and gC-expressing adenovirus induced a Th2-type responses. However, gD-expressing adenoviruses created confused immunity since rAd-gD induced production of the median ratio of IgG isotypes (IgG2a to IgG1) as well as production of IL-2 by stimulated CD4+ T cells, which are one of the Th1-type cytokines. The nature of immunity induced by plasmid DNA expressing gD was biased towards Th2-type cells in a previous study of a PrV DNA vaccine (Yoon et al., 2006). This difference in observation may result from properties of the vehicles expressing the antigens (plasmid DNA vs. adenovirus). A primary difference between transfers of plasmid- and adenovirus-mediated transgenes is that plasmid-mediated transgenes rely on the target cells expressing the foreign protein. The primary target cells for transfection upon i.m. inoculation of plasmid DNA are differentiated muscular cells. However, their role in stimulating a naїve immune system remains unclear because muscle cells express only low levels of MHC class I antigen and show no MHC class II antigen presentation (Shedlock et al., 2000; Howarth et al., 2004). It is therefore likely that antigen-presenting cells (APCs) are recruited into the plasmid DNA injection sites and initiate immune responses in draining LNs (Shedlock et al., 2000; Howarth et al., 2004), and even CpG motifs in the backbone of plasmid DNA may affect the APC function in modulating immune responses to encoded antigens (Klinman et al., 2006). Conversely, adenoviruses have a broad host cell range and can infect a wide spectrum of cells including quiescent or terminally differentiated cells (Davis et al., 1993; Ali et al., 1994; Randrianarison-Jewtoukoff et al., 1995; Rocha et al., 2004; Barouch et al., 2005). Large numbers of small mononucleated cells were located within the endomysial spaces of muscle injected with adenovirus, and significant numbers of these cells expressed the reporter gene of the recombinant adenovirus (Davis et al., 1993). These mononucleated cells are not present in normal or regenerating muscle injected with plasmid DNA and were identified as blood cells (Davis et al., 1993). These results suggest that there are important differences in the initiation of immune responses between plasmid- and adenovirus-mediated vaccines.
The nasal mucosa is an important arm of the mucosal immune system and is generally the first entry site of several inhaled pathogens including PrV (Davis, 2001). Therefore, the nasal mucosa represents an attractive, noninvasive delivery route for several vaccines. A particular advantage of i.n. vaccine delivery is the requirement for a smaller quantity of antigen by this route when compared to the amount needed for oral immunization (Davis, 2001). Results from our study suggest that the i.n. delivery of replication-incompetent gB-expressing adenoviruses engaged the common mucosal immune system and induced significant immunity at both the systemic and distal mucosal sites, but that i.m. injection produced no IgA at the mucosal site. Further, mucosal delivery of rAd-gB induced Th2-type immunity when compared to systemic delivery. This suggests that the delivery route of vaccines may partially determine the nature of induced immune responses to antigens, as supported by previous studies (McCluskie et al., 1999; Okamba et al., 2007; Yoon et al., 2008). Both systemic and mucosal delivery of rAd-gB provided comparable protection. Curiously, the i.m. delivery of rAd-gB elicited detectable IgA production similar to that in groups that received treatment by the i.n. route 3 days after PrV challenge (Figure 6B). However, as was documented previously, it appears that immunity to PrV may depend more on a functioning T-cell defense system in infected tissues rather than on mucosal IgA function in the mucosal tissues (Bianchi et al., 1998; van Rooij et al., 2000). This is supported by a study that found similar protective immunity against human herpesvirus in both IgA knockout and wild-type mice (Parr et al., 1998). Therefore, both the cell-mediated and humoral immune responses systemically induced by rAd-gB may play critical roles in protection against PrV infection.
Adenovirus vectors are increasingly used for a variety of in vivo gene transfer experiments including vaccination. Replication-incompetent recombinants do not disseminate further because they undergo no additional rounds of replication, and thereby this replication-incompetent adenovirus vector is biologically safe (Babiuk et al., 2000). Recombinant adenovirus vaccines are particularly useful in the vaccination of neonates immediately after birth independent of the presence or absence of maternal antibodies (Monteil et al., 1997, 2000; Wesley et al., 2004; Liu et al., 2007). Therefore, there is significant veterinary utility for recombinant adenovirus vaccination of pigs slaughtered within a few months of birth and of pigs as young as 1 day of age, as such vaccines will not encounter maternal antibody interference. The data obtained from the PrV infection using murine models may reflect the same immunological parameters that allow vaccine for protection of pigs, since the importance of Th1-type CD4+ T cells and their IFN-γ production have been observed in both species (Bianchi et al., 1998; Ficher et al., 2000; Eo et al., 2001; van RooiJ et al., 2004). In conclusion, the results of this study suggest that replication-incompetent gB-expressing adenovirus induces Th1-biased humoral and cellular immune responses and provides effective protection against virulent virus infection. Further development of vaccine protocols using recombinant adenoviruses and DNA vaccines will sharpen their usefulness in the protection against pathogens such as PrV.
Abbreviations
- Ad:
-
adenovirus
- CMV:
-
cytomegalovirus
- CPE:
-
cytopathic effect
- i.n.:
-
intranasal
- ITR:
-
inverted terminal repeat
- LN:
-
lymph node
- PrV:
-
pseudorabies virus
- rAd:
-
recombinant adenovirus
References
Ali M, Lemoine NR, Ring CJ . The use of DNA viruses as vectors for gene therapy . Gene therapy 1994 ; 1 : 367 - 384
Ambriovic A, Adam M, Monteil M, Paulin D, Eloit M . Efficacy of replication-defective adenovirus-vectored vaccines: protection following intramuscular injection is linked to promoter efficiency in muscle representative cells . Virology 1997 ; 238 : 327 - 335
Babiuk LA, Tikoo SK . Adenoviruses as vectors for delivering vaccines to mucosal surfaces . Journal of biotechnology 2000 ; 83 : 105 - 113
Barouch DH, Nabel GJ . Adenovirus vector-based vaccines for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 . Human gene therapy 2005 ; 16 : 149 - 156
Bianchi AT, Moonen-Leusen HW, van Milligen FJ, Savelkoul HF, Zwart RJ, Kimman TG . A mouse model to study immunity against pseudorabies virus infection: significance of CD4+ and CD8+ cells in protective immunity . Vaccine 1998 ; 16 : 1550 - 1558
Davis HL, Demeneix BA, Quantin B, Coulombe J, Whalen RG . Plasmid DNA is superior to viral vectors for direct gene transfer into adult mouse skeletal muscle . Human gene therapy 1993 ; 4 : 733 - 740
Davis SS . Nasal vaccines . Advanced drug delivery reviews 2001 ; 51 : 21 - 42
Eloit M, Adam M . Isogenic adenoviruses type 5 expressing or not expressing the E1A gene: efficiency as virus vectors in the vaccination of permissive and non-permissive species . The Journal of general virology 1995 ; 76 : 1583 - 1589
Eo SK, Lee S, Chun S, Rouse BT . Modulation of immunity against herpes simplex virus infection via mucosal genetic transfer of plasmid DNA encoding chemokines . Journal of virology 2001 ; 75 : 569 - 578
Fischer T, Buttner M, Rziha HJ . T helper 1-type cytokine transcription in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of pseudorabies virus (Suid herpesvirus 1)-primed swine indicates efficient immunization . Immunology 2000 ; 101 : 378 - 387
Gonin P, Oualikene W, Fournier A, Eloit M . Comparison of the efficacy of replication-defective adenovirus and Nyvac poxvirus as vaccine vectors in mice . Vaccine 1996 ; 14 : 1083 - 1087
Hong W, Xiao S, Zhou R, Fang L, He Q, Wu B, Zhou F, Chen H . Protection induced by intramuscular immunization with DNA vaccines of pseudorabies in mice, rabbits and piglets . Vaccine 2002 ; 20 : 1205 - 1214
Howarth M, Elliott T . The processing of antigens delivered as DNA vaccines . Immunological reviews 2004 ; 199 : 27 - 39
Khanam S, Rajendra P, Khanna N, Swaminathan S . An adenovirus prime/plasmid boost strategy for induction of equipotent immune responses to two dengue virus serotypes . BMC biotechnology 2007 ; 7 : 10 -
Kit S, Oirschot T. J. V. . Safety, efficacy of genetically engineered Aujeszky's disease vaccines . Vaccination and Control of Aujeszky's Disease 1988 ; : 45 - 55
Klinman DM . Adjuvant activity of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides . International reviews of immunology 2006 ; 25 : 135 - 154
Kluge JP, Beran G, Hill GT, Platt KB, Straw B. E., S D. A., Mengeling W. L., Taylor D. J . Pseudorabies (Aujeszky's Disease) . Disease of Swine 1999 ; : 233 - 246
La S, Kim E, Kwon B . In vivo ligation of glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor enhances the T-cell immunity to herpes simplex virus type 1 . Experimental & molecular medicine 2005 ; 37 : 193 - 198
Liu Y, Okada T, Nomoto T, Ke X, Kume A, Ozawa K, Xiao S . Promoter effects of adeno-associated viral vector for transgene expression in the cochlea in vivo . Experimental & molecular medicine 2007 ; 39 : 170 - 175
Mettenleiter TC . Immunobiology of pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) . Veterinary immunology and immunopathology 1996 ; 54 : 221 - 229
Mizuguchi H, Hayakawa T . Targeted adenovirus vectors . Human gene therapy 2004 ; 15 : 1034 - 1044
Monteil M, Le Potier MF, Cariolet R, Houdayer C, Eloit M . Effective priming of neonates born to immune dams against the immunogenic pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gD by replication-incompetent adenovirus-mediated gene transfer at birth . The Journal of general virology 1997 ; 78 : 3303 - 3310
Monteil M, Le Pottier MF, Ristov AA, Cariolet R, L'Hospitalier R, Klonjkowski B, Eloit M . Single inoculation of replication-defective adenovirus-vectored vaccines at birth in piglets with maternal antibodies induces high level of antibodies and protection against pseudorabies . Vaccine 2000 ; 18 : 1738 - 1742
Ober BT, Summerfield A, Mattlinger C, Wiesmuller KH, Jung G, Pfaff E, Saalmuller A, Rziha HJ . Vaccine-induced, pseudorabies virus-specific, extrathymic CD4+ CD8+ memory T-helper cells in swine . Journal of Virology 1998 ; 72 : 4866 - 4873
Ober BT, Teufel B, Wiesmuller KH, Jung G, Pfaff E, Saalmuller A, Rziha HJ . The porcine humoral immune response against pseudorabies virus specifically targets attachment sites on glycoprotein gC . Journal of Virology 2000 ; 74 : 1752 - 1760
Parr MB, Harriman GR, Parr EL . Immunity to vaginal HSV-2 infection in immunoglobulin A knockout mice . Immunology 1998 ; 95 : 208 - 213
Plog MS, Guyre CA, Roberts BL, Goldberg M, St George JA, Perricone MA . Preclinical safety and biodistribution of adenovirus-based cancer vaccines after intradermal delivery . Human Gene Therapy 2006 ; 17 : 705 - 716
Randrianarison-Jewtoukoff V, Perricaudet M . Recombinant adenoviruses as vaccines . Biologicals 1995 ; 23 : 145 - 157
Rocha CD, Caetano BC, Machado AV, Bruna-Romero O . Recombinant viruses as tools to induce protective cellular immunity against infectious diseases . Int Microbiol 2004 ; 7 : 83 - 94
Shedlock DJ, Weiner DB . DNA vaccination: antigen presentation and the induction of immunity . Journal of Leukocyte Biology 2000 ; 68 : 793 - 806
Shiver JW, Fu TM, Chen L, Casimiro DR, Davies ME, Evans RK, Zhang ZQ, Simon AJ, Trigona WL, Dubey SA, Huang L, Harris VA, Long RS, Liang X, Handt L, Schleif WA, Zhu L, Freed DC, Persaud NV, Guan L, Punt KS, Tang A, Chen M, Wilson KA, Collins KB, Heidecker GJ, Fernandez VR, Perry HC, Joyce JG, Grimm KM, Cook JC, Keller PM, Kresock DS, Mach H, Troutman RD, Isopi LA, Williams DM, Xu Z, Bohannon KE, Volkin DB, Montefiori DC, Miura A, Krivulka GR, Lifton MA, Kuroda MJ, Schmitz JE, Letvin NL, Caulfield MJ, Bett AJ, Youil R, Kaslow DC, Emini EA . Replication-incompetent adenoviral vaccine vector elicits effective anti-immunodeficiency-virus immunity . Nature 2002 ; 415 : 331 - 335
Suzuki Y, Kagawa N, Fujino T, Sumiya T, Andoh T, Ishikawa K, Kimura R, Kemmochi K, Ohta T, Tanaka S . A novel high-throughput (HTP) cloning strategy for site-directed designed chimeragenesis and mutation using the Gateway cloning system . Nucleic Acids Research 2005 ; 33 : e109 -
van Rooij EM, Haagmans BL, de Visser YE, de Bruin MG, Boersma W, Bianchi AT . Effect of vaccination route and composition of DNA vaccine on the induction of protective immunity against pseudorabies infection in pigs . Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 1998 ; 66 : 113 - 126
van Rooij EM, Haagmans BL, Glansbeek HL, de Visser YE, de Bruin MG, Boersma W, Bianchi AT . A DNA vaccine coding for glycoprotein B of pseudorabies virus induces cell-mediated immunity in pigs and reduces virus excretion early after infection . Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 2000 ; 74 : 121 - 136
van Rooij EM, de Bruin MG, de Visser YE, Middel WG, Boersma WJ, Bianchi AT . Vaccine-induced T cell-mediated immunity plays a critical role in early protection against pseudorabies virus (suid herpes virus type 1) infection in pigs . Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 2004 ; 99 : 113 - 125
Walhout AJ, Temple GF, Brasch MA, Hartley JL, Lorson MA, van den Heuvel S, Vidal M . GATEWAY recombinational cloning: application to the cloning of large numbers of open reading frames or ORFeomes . Methods in Enzymology 2000 ; 328 : 575 - 592
Wesley RD, Tang M, Lager KM . Protection of weaned pigs by vaccination with human adenovirus 5 recombinant viruses expressing the hemagglutinin and the nucleoprotein of H3N2 swine influenza virus . Vaccine 2004 ; 22 : 3427 - 3434
Yoon HA, Aleyas AG, George JA, Park SO, Han YW, Kang SH, Cho JG, Eo SK . Differential segregation of protective immunity by encoded antigen in DNA vaccine against pseudorabies virus . Immunology and Cell Biology 2006 ; 84 : 502 - 511
Zaripov MM, Morenkov OS, Siklodi B, Barna-Vetro I, Gyongyosi-Horvath A, Fodor I . Glycoprotein B of Aujeszky's disease virus: topographical epitope mapping and epitope-specific antibody response . Research in Virology 1998 ; 149 : 29 - 41
Zaripov MM, Morenkov OS, Fodor N, Braun A, Schmatchenko VV, Fodor I . Distribution of B-cell epitopes on the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein B . The Journal of General Virology 1999 ; 80 : 537 - 541
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant No. RTI05-03-02 from the Regional Technology Innovation Programme of the Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy (MOCIE), a research grant from the Bio-Safety Research Institute, Chonbuk National University, and the Brain Korea 21 Project in 2007, Republic of Korea. H.A. Yoon was supported in part by a grant from the Post-Doctoral Program, Chonbuk National University (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Aleyas, A., George, J. et al. Polarization of protective immunity induced by replication-incompetent adenovirus expressing glycoproteins of pseudorabies virus. Exp Mol Med 40, 583–595 (2008). https://doi.org/10.3858/emm.2008.40.6.583
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3858/emm.2008.40.6.583