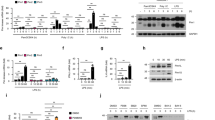
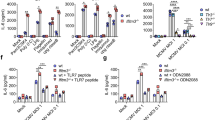
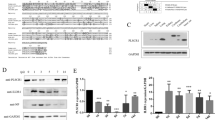
Abstract
Influenza A virus (IAV) infection is a major worldwide public health problem. However, the factors involved in mediating the inflammatory response to this infection and their relationships remain poorly understood. Here, we show that IAV infection stimulates the expression of the soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), a multifunctional protein involved in IL-6 signaling. Interestingly, sIL-6R expression upregulated the levels of its own ligand, IL-6 and those of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-32. shRNA-mediated knockdown of sIL-6R suppressed IL-6 and IL-32, indicating that this regulation is dependent on sIL-6R during IAV infection. Furthermore, our results demonstrate that IL-32 participates in a negative feedback loop that inhibits sIL-6R while upregulating IL-6 expression during IAV infection. Therefore, we show that sIL-6R is a critical cellular factor involved in the acute inflammatory response to viral infection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heitmeier MR, Scarim AL, Corbett JA . Double-stranded RNA-induced inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression and interleukin-1 release by murine macrophages requires NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 15301–15307.
Guillot L, Le Goffic R, Bloch S, Escriou N, Akira S, Chignard M et al. Involvement of toll-like receptor 3 in the immune response of lung epithelial cells to double-stranded RNA and influenza A virus. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 5571–5580.
Eliopoulos AG, Gallagher NJ, Blake SM, Dawson CW, Young LS . Activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by Epstein–Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 coregulates interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 production. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 16085–16096.
Kaiser L, Fritz RS, Straus SE, Gubareva L, Hayden FG . Symptom pathogenesis during acute influenza: interleukin-6 and other cytokine responses. J Med Virol 2001; 64: 262–268.
Tisoncik JR, Korth MJ, Simmons CP, Farrar J, Martin TR, Katze MG . Into the eye of the cytokine storm. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2012; 76: 16–32.
Kishimoto T . IL-6: from its discovery to clinical applications. Int Immunol 2010; 22: 347–352.
Scheller J, Chalaris A, Schmidt-Arras D, Rose-John S . The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011; 1813: 878–888.
Assier E, Boissier MC, Dayer JM . Interleukin-6: from identification of the cytokine to development of targeted treatments. Joint Bone Spine 2010; 77: 532–536.
Jones SA, Horiuchi S, Topley N, Yamamoto N, Fuller GM . The soluble interleukin 6 receptor: mechanisms of production and implications in disease. FASEB J 2001; 15: 43–58.
Chen Q, Fisher DT, Clancy KA, Gauguet JM, Wang WC, Unger E et al. Fever-range thermal stress promotes lymphocyte trafficking across high endothelial venules via an interleukin 6 trans-signaling mechanism. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 1299–1308.
Hurst SM, Wilkinson TS, McLoughlin RM, Jones S, Horiuchi S, Yamamoto N et al. IL-6 and its soluble receptor orchestrate a temporal switch in the pattern of leukocyte recruitment seen during acute inflammation. Immunity 2001; 14: 705–714.
Hou T, Tieu BC, Ray S, Recinos A Iii, Cui R, Tilton RG et al. Roles of IL-6-gp130 signaling in vascular inflammation. Curr Cardiol Rev 2008; 4: 179–192.
Fielding CA, McLoughlin RM, McLeod L, Colmont CS, Najdovska M, Grail D et al. IL-6 regulates neutrophil trafficking during acute inflammation via STAT3. J Immunol 2008; 181: 2189–2195.
Taga T, Kishimoto T . Gp130 and the interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol 1997; 15: 797–819.
Rose-John S, Neurath MF . IL-6 trans-signaling: the heat is on. Immunity 2004; 20: 2–4.
Nilsson MB, Langley RR, Fidler IJ . Interleukin-6, secreted by human ovarian carcinoma cells, is a potent proangiogenic cytokine. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 10794–10800.
Matthews V, Schuster B, Schutze S, Bussmeyer I, Ludwig A, Hundhausen C et al. Cellular cholesterol depletion triggers shedding of the human interleukin-6 receptor by ADAM10 and ADAM17 (TACE). J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 38829–38839.
Coodly L . Diverse cell surface protein ectodomains are shed by a system sensitive to metalloprotease inhibitors. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 11376–11382.
Bennett TA, Lynam EB, Sklar LA, Rogelj S . Hydroxamate-based metalloprotease inhibitor blocks shedding of L-selectin adhesion molecule from leukocytes: functional consequences for neutrophil aggregation. J Immunol 1996; 156: 3093–3097.
Mohler KM, Sleath PR, Fitzner JN, Cerretti DP, Alderson M, Kerwar SS et al. Protection against a lethal dose of endotoxin by an inhibitor of tumour necrosis factor processing. Nature 1994; 370: 218–220.
Müllberg J, Durie FH, Otten-Evans C, Alderson MR, Rose-John S, Cosman D et al. A metalloprotease inhibitor blocks shedding of the IL-6 receptor and the p60 TNF receptor. J Immunol 1995; 155: 5198–5205.
Jones SA, Horiuchi S, Novick D, Yamamoto N, Fuller GM . Shedding of the soluble IL-6 receptor is triggered by Ca2+ mobilization, while basal release is predominantly the product of differential mRNA splicing in THP-1 cells. Eur J Immunol 1998; 28: 3514–3522.
Chalaris A, Garbers C, Rabe B, Rose-John S, Scheller J . The soluble interleukin 6 receptor: generation and role in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cell Biol 2011; 90: 484–494.
Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, Lehr HA, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A et al. TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity 2004; 21: 491–501.
Knupfer H, Preiss R . sIL-6R: more than an agonist? Immunol Cell Biol 2008; 86: 87–91.
Netea MG, Azam T, Lewis EC, Joosten LA, Wang M, Langenberg D et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces interleukin-32 production through a caspase- 1/IL-18/interferon-gamma-dependent mechanism. PLoS Med 2006; 3: e277.
Li W, Liu Y, Mukhtar MM, Gong R, Pan Y, Rasool ST et al. Activation of interleukin-32 pro-inflammatory pathway in response to influenza A virus infection. PLoS One 2008; 3: e1985.
Dinarello CA, Kim SH . IL-32, a novel cytokine with a possible role in disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2006; 65( Suppl 3): iii61–iii64.
Joosten LA, Netea MG, Kim SH, Yoon DY, Oppers-Walgreen B, Radstake TR et al. IL-32, a proinflammatory cytokine in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 3298–3303.
Andoh A, Yagi Y, Shioya M, Nishida A, Tsujikawa T, Fujiyama Y . Mucosal cytokine network in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14: 5154–5161.
Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Pott GB, Zepp JA, Saavedra MT, Kim SH et al. Endogenous IL-32 controls cytokine and HIV-1 production. J Immunol 2008; 181: 557–565.
Netea MG, Azam T, Ferwerda G, Girardin SE, Walsh M, Park JS et al. IL-32 synergizes with nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD) 1 and NOD2 ligands for IL-1beta and IL-6 production through a caspase 1-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 16309–16314.
Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA . Interleukin-32: a cytokine and inducer of TNFalpha. Immunity 2005; 22: 131–142.
Li W, Sun W, Liu L, Yang F, Li Y, Chen Y et al. IL-32: a host proinflammatory factor against influenza viral replication is upregulated by aberrant epigenetic modifications during influenza A virus infection. J Immunol 2010; 185: 5056–5065.
Zepp JA, Nold-Petry CA, Dinarello CA, Nold MF . Protection from RNA and DNA viruses by IL-32. J Immunol 2011; 186: 4110–4118.
Liu L, Li R, Pan Y, Chen J, Li Y, Wu J et al. High-throughput screen of protein expression levels induced by cyclooxygenase-2 during influenza a virus infection. Clin Chim Acta 2011; 412: 1081–1085.
Yu Y, Gong R, Mu Y, Chen Y, Zhu C, Sun Z et al. Hepatitis B virus induces a novel inflammation network involving three inflammatory factors, IL-29, IL-8, and cyclooxygenase-2. J Immunol 2011; 187: 4844–4860.
Li Y, Xie J, Xu X, Liu L, Wan Y, Liu Y et al. Inducible interleukin 32 (IL-32) exerts extensive antiviral function via selective stimulation of interferon lambda1 (IFN-lambda1). J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 20927–20941.
Mohler KM, Sleath PR, Fitzner JN, Cerretti DP, Alderson M, Kerwar SS et al. Protection against a lethal dose of endotoxin by an inhibitor of tumour necrosis factor processing. Nature 1994; 370: 218–220.
Zhan M, Jin B, Chen SE, Reecy JM, Li YP . TACE release of TNF-alpha mediates mechanotransduction-induced activation of p38 MAPK and myogenesis. J Cell Sci 2007; 120: 692–701.
Wang Q, Chen X, Feng J, Cao Y, Song Y, Wang H et al. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor-mediated innate immune response to DNA and RNA viruses. J Virol 2013; 87: 11244–11254.
Hutchins AP, Diez D, Miranda-Saavedra D . The IL-10/STAT3-mediated anti-inflammatory response: recent developments and future challenges. Brief Funct Genomics 2013; in press.
Wang S, Le TQ, Kurihara N, Chida J, Cisse Y, Yano M et al. Influenza virus-cytokine-protease cycle in the pathogenesis of vascular hyperpermeability in severe influenza. J Infect Dis 2010; 202: 991–1001.
Sun Y, Jin C, Zhan F, Wang X, Liang M, Zhang Q et al. Host cytokine storm is associated with disease severity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J Infect Dis 2012; 206: 1085–1094.
Ioannidis I, McNally B, Willette M, Peeples ME, Chaussabel D, Durbin JE et al. Plasticity and virus specificity of the airway epithelial cell immune response during respiratory virus infection. J Virol 2012; 86: 5422–5436.
Arcaroli JJ, Liu N, Yi N, Abraham E . Association between IL-32 genotypes and outcome in infection-associated acute lung injury. Crit Care 2011; 15: R138.
Choi JD, Bae SY, Hong JW, Azam T, Dinarello CA, Her E et al. Identification of the most active interleukin-32 isoform. Immunology 2009; 126: 535–542.
Bae S, Kang D, Hong J, Chung B, Choi J, Jhun H et al. Characterizing antiviral mechanism of interleukin-32 and a circulating soluble isoform in viral infection. Cytokine 2012; 58: 79–86.
Alten R . Tocilizumab: a novel humanized anti-interleukin 6 receptor antibody for the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 2011; 3: 133–149.
Rose-John S, Scheller J, Elson G, Jones SA . Interleukin-6 biology is coordinated by membrane-bound and soluble receptors: role in inflammation and cancer. J Leuk Biol 2006; 80: 227–236.
Sumida K, Wakita D, Narita Y, Masuko K, Terada S, Watanabe K et al. Anti-IL-6 receptor mAb eliminates myeloid-derived suppressor cells and inhibits tumor growth by enhancing T-cell responses. Eur J Immunol 2012; 42: 2060–2072.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research grants from the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (no. 2013CB911102), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81271821 and 81461130019) and the National Mega Project on Major Infectious Diseases Prevention (no. 2012ZX10004503-004). The funding agencies had no role in the study design, data collection or analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, Q., Han, T. et al. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor is elevated during influenza A virus infection and mediates the IL-6 and IL-32 inflammatory cytokine burst. Cell Mol Immunol 12, 633–644 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.80
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.80
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
IL-32-driven neutrophil activation in preeclampsia
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2023)
-
Immune system-related soluble mediators and COVID-19: basic mechanisms and clinical perspectives
Cell Communication and Signaling (2022)
-
Comorbidities and inflammation associated with ovarian cancer and its influence on SARS-CoV-2 infection
Journal of Ovarian Research (2021)
-
Placenta-derived IL-32β activates neutrophils to promote preeclampsia development
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2021)
-
Inducible Rubicon facilitates viral replication by antagonizing interferon production
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2017)