Abstract
Objective:
A single value of plasma creatinine cannot be used to define renal dysfunction in premature babies, as levels are influenced by gestation and postnatal age. The aim of this study was to create reference ranges for plasma creatinine in cohort of extremely premature infants.
Study Design:
Retrospective analysis of plasma creatinine levels in the first 8 weeks of life from 161 consecutively admitted premature infants 28 weeks gestation.
Result:
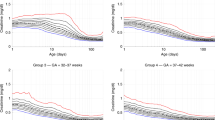
Babies were divided into three groups according to gestation. Peak (10th, 90th percentiles) creatinine levels were 132 (106,162) in 22 to 24 weeks gestational infants, 127 (89,151) in those from 25 to 26 weeks and 110 (87,134) in those from 27 to 28 weeks (P<0.001). Creatinine at birth was similar across the groups with levels increasing during the first few days. It decreases thereafter before reaching stable levels by 5 weeks of age.
Conclusion:
Gestation- and age-based reference charts should be used for interpretation of creatinine values in extremely premature babies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haycock GB . Management of acute and chronic renal failure in the newborn. Semin Neonatol 2003; 8 (4): 325–334.
Bueva A, Guignard JP . Renal function in preterm neonates. Pediatr Res 1994; 36 (5): 572–577.
Gallini F, Maggio L, Romagnoli C, Marrocco G, Tortorolo G . Progression of renal function in preterm neonates with gestational age < or=32 weeks. Pediatr Nephrol 2000; 15 (1–2): 119–124.
Atiyeh BA, Dabbagh SS, Gruskin AB . Evaluation of renal function during childhood. Pediatr Rev 1996; 17 (5): 175–180.
Wilkins BH . Renal function in sick very low birthweight infants: 2. Urea and creatinine excretion. Arch Dis Child 1992; 67 (10 Spec No): 1146–1153.
van den Anker JN, de GR, Broerse HM, Sauer PJ, van der Heijden BJ, Hop WC et al. Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in preterm infants by serum creatinine: comparison with inulin clearance. Pediatrics 1995; 96 (6): 1156–1158.
Trompeter RS, Al-Dahhan J, Haycock GB, Chik G, Chantler C . Normal values for plasma creatinine concentration related to maturity in normal term and preterm infants. Int J Pediatr Nephrol 1983; 4 (3): 145–148.
Auron A, Mhanna MJ . Serum creatinine in very low birth weight infants during their first days of life. J Perinatol 2006; 26 (12): 755–760.
Miall LS, Henderson MJ, Turner AJ, Brownlee KG, Brocklebank JT, Newell SJ et al. Plasma creatinine rises dramatically in the first 48 h of life in preterm infants. Pediatrics 1999; 104 (6): e76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thayyil, S., Sheik, S., Kempley, S. et al. A gestation- and postnatal age-based reference chart for assessing renal function in extremely premature infants. J Perinatol 28, 226–229 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211905
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211905
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association between postmenstrual age and furosemide dosing practices in very preterm infants
Journal of Perinatology (2022)
-
Gestational age, sex, and time affect urine biomarker concentrations in extremely low gestational age neonates
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Creatinine filtration kinetics in critically Ill neonates
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Prevalence of acute kidney injury (AKI) in extremely low gestational age neonates (ELGAN)
Pediatric Nephrology (2020)
-
Risk of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated renal dysfunction among neonates diagnosed with patent ductus arteriosus and treated with gentamicin
Journal of Perinatology (2017)