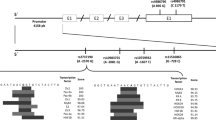
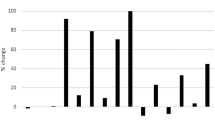
Abstract
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) is required for detection of Gram negative bacterial infections by binding lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and for the initiation of inflammatory signaling. Recent studies have demonstrated that a nonsynonymous single-nucleotide polymorphism (Asp299Gly, A+896G) is associated with decreased endotoxin responsiveness and poor outcomes from sepsis. We show that human carriers of this polymorphism show no deficit in LPS induced peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity, no reduction in sensitivity to endotoxin, and variable differences in whole-blood inflammatory cytokine production. These results indicate that this mutation is not a primary determinant of human endotoxin sensitivity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sorensen TI, Nielsen GG, Andersen PK et al. Genetic and environmental influences on premature death in adult adoptees. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 727–732.
Westendorp RG, Langermans JA, Huizinga TW et al. Genetic influence on cytokine production and fatal meningococcal disease. Lancet 1997; 349: 170–173.
Mira JP, Cariou A, Grall F et al. Association of TNF2, a TNF-alpha promoter polymorphism, with septic shock susceptibility and mortality: a multicenter study. JAMA 1999; 282: 561–568.
Munford RS, Pugin J . Normal responses to injury prevent systemic inflammation and can be immunosuppressive. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 163: 316–321.
Waterer GW, Quasney MW, Cantor RM et al. Septic shock and respiratory failure in community-acquired pneumonia have different TNF polymorphism associations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 163: 1599–1604.
Barber RC, O'Keefe GE . Characterization of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the lipopolysaccharide binding protein and its association with sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 167: 1316–1320.
Arbabi S, Maier RV . Mitogen-activated protein kinases. Crit Care Med 2002; 30 (Suppl): S74–S79.
Poltorak A, Smirnova I, Clisch R et al. Limits of a deletion spanning Tlr4 in C57BL/10ScCr mice. J Endotoxin Res 2000; 6: 51–56.
Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kawai T et al. Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J Immunol 1999; 162: 3749–3752.
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998; 282: 2085–2088.
Du X, Poltorak A, Silva M et al .Analysis of Tlr4-mediated LPS signal transduction in macrophages by mutational modification of the receptor. Blood Cells Mol Dis 1999; 25: 328–338.
Lorenz E, Frees KL, Schwartz DA . Determination of the TLR4 genotype using allele-specific PCR. Biotechniques 2001; 31: 22–24.
Arbour NC, Lorenz E, Schutte BC et al. TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat Genet 2000; 25: 187–191.
Werner M, Topp R, Wimmer K et al TLR4 gene variants modify endotoxin effects on asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 112: 323–330.
Michel O, LeVan TD, Stern D et al. Systemic responsiveness to lipopolysaccharide and polymorphisms in the toll-like receptor 4 gene in human beings. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 112: 923–929.
Schwartz DA . The genetics of innate immunity. Chest 2002; 121 (Suppl): 62S–68S.
Agnese DM, Calvano JE, Hahm SJ et al. Human toll-like receptor 4 mutations but not CD14 polymorphisms are associated with an increased risk of Gram-negative infections. J Infect Dis 2002; 186: 1522–1525.
Lorenz E, Mira JP, Frees KL et al. Relevance of mutations in the TLR4 receptor in patients with Gram-negative septic shock. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162: 1028–1032.
Child NJ, Yang IA, Pulletz MC et al. Polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor 4 and the systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Biochem Soc Trans 2003; 31 (Part 3): 652–653.
Erridge C, Stewart J, Poxton IR . Monocytes heterozygous for the Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile mutations in the Toll-like receptor 4 gene show no deficit in lipopolysaccharide signaling. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 1787–1791.
Read RC, Pullin J, Gregory S et al. A functional polymorphism of toll-like receptor 4 is not associated with likelihood or severity of meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis 2001; 184: 640–642.
Heesen M, Bloemeke B, Kunz D . The cytokine synthesis by heterozygous carriers of the Toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly polymorphism does not differ from that of wild type homozygotes. Eur Cytokine Network 2003; 14: 234–237.
Yang IA, Barton SJ, Rorke S et al. Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphism and severity of atopy in asthmatics. Genes Immun 2004; 5: 41–45.
Schippers EF, van 't Veer C, van Voorden S et al. TNF-alpha promoter, Nod2 and toll-like receptor-4 polymorphisms and the in vivo and ex vivo response to endotoxin. Cytokine 2004; 26: 16–24.
von Aulock S, Schroder NW, Gueinzius K et al. Heterozygous toll-like receptor 4 polymorphism does not influence lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine release in human whole blood. J Infect Dis 2003; 188: 938–943.
Beutler B, Hoebe K, Du X et al. How we detect microbes and respond to them: the Toll-like receptors and their transducers. J Leukocyte Biol 2003; 74: 479–485.
Beutler B, Poltorak A . Positional cloning of Lps, and the general role of toll-like receptors in the innate immune response. Eur Cytokine Network 2000; 11: 143–152.
Beutler B . TLR4 as the mammalian endotoxin sensor. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2002; 270: 109–120.
Schmitt C, Humeny A, Becker CM et al. Polymorphisms of TLR4: rapid genotyping and reduced response to lipopolysaccharide of TLR4 mutant alleles. Clin Chem 2002; 48: 1661–1667.
Smirnova I, Mann N, Dols A et al. Assay of locus-specific genetic load implicates rare Toll-like receptor 4 mutations in meningococcal susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 6075–6080.
van der Linden MW, Huizinga TW, Stoeken DJ et al. Determination of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10 production in a whole blood stimulation system: assessment of laboratory error and individual variation. J Immunol Methods 1998; 218: 63–71.
Rivera-Chavez FA, Peters-Hybki DL, Barber RC et al. Interleukin-6 promoter haplotypes and interleukin-6 cytokine responses. Shock 2003; 20: 218–223.
Hubacek JA, Stuber F, Frohlich D et al. Gene variants of the bactericidal/permeability increasing protein and lipopolysaccharide binding protein in sepsis patients: gender-specific genetic predisposition to sepsis. Crit Care Med 2001; 29: 557–561.
Gibot S, Cariou A, Drouet L et al. Association between a genomic polymorphism within the CD14 locus and septic shock susceptibility and mortality rate. Crit Care Med 2002; 30: 969–973.
Kabesch M, Hasemann K, Schickinger V et al. A promoter polymorphism in the CD14 gene is associated with elevated levels of soluble CD14 but not with IgE or atopic diseases. Allergy 2004; 59: 520–525.
Baldini M, Lohman IC, Halonen M et al. A polymorphism* in the 5' flanking region of the CD14 gene is associated with circulating soluble CD14 levels and with total serum immunoglobulin E. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1999; 20: 976–983.
Hamann L, Kumpf O, Muller M et al. A coding mutation within the first exon of the human MD-2 gene results in decreased lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling. Genes Immun 2004; 5: 283–288.
Weighardt H, Kaiser-Moore S, Vabulas RM et al. Cutting edge: myeloid differentiation factor 88 deficiency improves resistance against sepsis caused by polymicrobial infection. J Immunol 2002; 169: 2823–2827.
Kawai T, Adachi O, Ogawa T et al. Unresponsiveness of MyD88-deficient mice to endotoxin. Immunity 1999; 11: 115–122.
Swantek JL, Tsen MF, Cobb MH et al. IL-1 receptor-associated kinase modulates host responsiveness to endotoxin. J Immunol 2000; 164: 4301–4306.
Medvedev AE, Lentschat A, Kuhns DB et al. Distinct mutations in IRAK-4 confer hyporesponsiveness to lipopolysaccharide and interleukin-1 in a patient with recurrent bacterial infections. J Exp Med 2003; 198: 521–531.
Cardon LR, Bell JI . Association study designs for complex diseases. Nat Rev Genet 2001; 2: 91–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Grant support: T32 GM 07037.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imahara, S., Jelacic, S., Junker, C. et al. The TLR4 +896 polymorphism is not associated with lipopolysaccharide hypo-responsiveness in leukocytes. Genes Immun 6, 37–43 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364147
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genetic Susceptibility to Fungal Infections: What is in the Genes?
Current Clinical Microbiology Reports (2016)
-
Polymorphisms in Toll-like receptors-2 and -4 are not associated with disease manifestations in acute Q fever
Genes & Immunity (2007)
-
Gingival epithelial cells heterozygous for Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile are hypo-responsive to Porphyromonas gingivalis
Genes & Immunity (2006)