Abstract
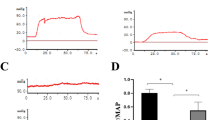
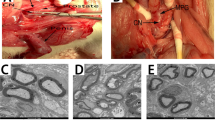
The purpose of this work was to study the effect of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and its binding protein (IGFBP-3) on the recovery of erectile function in a rat model for neurogenic impotence. In all, 28 male Spraque–Dawley rats were divided into four groups: seven underwent a sham operation; seven underwent bilateral cavernous nerve freezing (control group); seven underwent bilateral cavernous nerve freezing followed by intraperitoneal injection of IGF-1; and seven underwent bilateral cavernous nerve freezing followed by intraperitoneal injection of IGFBP-3. Erectile response was assessed by cavernous nerve electrostimulation at 3 months, and samples of penile tissue were evaluated histochemically for nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-containing fibers. In the sham and IGF-1 group, there were significantly higher maximal intracavernous pressures compared to the IGFBP-3 complex and the control group. Correspondingly in the cavernosum, there were significantly more NOS-containing nerve fibers in the sham and IGF-1 groups. In conclusion, administration of IGF-1 can facilitate the regeneration of NOS-containing nerve fibers in penile tissue and enhance the recovery of erectile function after bilateral cavernous nerve cryoablation. The reverse effect was noted with the IGFBP-3 complex injection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnett AL et al. Nitric oxide: a physiologic mediator of penile erection. Science 1992; 257: 401.
Kim N et al. A nitric oxide-like factor mediates nonadrenergic–noncholinergic neurogenic relaxation of penile corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. J Clin Invest 1991; 88: 112.
Sullivan ME et al. Nitric oxide and penile erection: is erectile dysfunction another manifestation of vascular disease? Cardiovasc Res 1999; 43: 658–665.
Burnett AL et al. Immunohistochemical localization of nitric oxide synthase in autonomic innervation of the human penis. J Urol 1993; 150: 73–76.
El-Sakka A et al. Possible molecular mechanisms of cyoablation-induced impotence in a rat model. Urology 1998; 52: 1144–1150.
El-Sakka A et al. Effect of cavernous nerve freezing on protein and gene expression of nitric oxide synthase in the rat penis and pelvic ganglia. J Urol 1998; 160: 2245–2252.
Carrier S et al. Regeneration of nitric oxide synthase-containing nerves after cavernous nerve neurotomy in the rat. J Urol 1995; 153: 1722–1727.
Jung CW, Spencer M, Lue TF . Growth hormone enhances regeneration of nitric oxide synthase-containing penile nerves after cavernous nerve neurotomy in rats. J Urol 1997; 157(Suppl): 413.
Hammarberg H et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factors and corresponding binding proteins (IGFBP 1–6) in rat spinal cord and peripheral nerve after axonal injuries. J Comp Neurol 1998; 400: 57–72.
Heidenreich KA . Insulin and IGF-1 receptor signaling in cultured neurons. Ann NY Acad Sci 1993; 692: 72–88.
Mclnnes C, Sykes BD . Growth factor receptors: structure, mechanism, and drug discovery. Biopolymers 1997; 43: 339–366.
Ishii DN, Glazner GW, Pu SF . Role of insulin-like growth factors in peripheral nerve regeneration. Pharmacol Ther 1994; 62: 125–144.
Sjoberg J, Kanje M . Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) as a stimulator of regeneration in the freeze-injured rat sciatic nerve. Brain Res 1989; 485: 102–108.
Kanje M et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) stimulates regeneration of the rat sciatic nerve. Brain Res 1989; 486: 396–398.
Liu XW et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 promotes proliferation and migration of cavernous smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 280: 1307–1315.
Quinlan DM et al. The rat as a model for the study of penile erection. J Urol 1989; 141: 656.
Alm P et al. Immunohistochemical localization of peripheral nitric oxide synthase-containing nerves using antibodies raised against synthesized C- and N-terminal fragments of a cloned enzyme from rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand 1993; 148: 421.
Bakircioglu ME et al. The effect of adeno-associated virus mediated brain derived neurotrophic factor in an animal model of neurogenic impotence. J Urol 2001; 165: 2103–2109.
Caroni P, Grandes P . Nerve sprouting in innervated adult skeletal muscle induced by exposure to elevated levels of insulin-like growth factors. J Cell Biol 1990; 110: 1307–1317.
Kubler B et al. Isolation and characterization of circulating fragments of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3. FEBS Lett 2002; 518: 124–128.
Dore S et al. Rediscovering good old friend IGF-1 in the new millennium: possible usefulness in Alzheimer's disease and stroke. Pharmacol Acta Helv 2000; 74: 273–280.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially from the ISSIR (Pfizer) research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bochinski, D., Hsieh, PS., Nunes, L. et al. Effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 complex in cavernous nerve cryoablation. Int J Impot Res 16, 418–423 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901190
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901190
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pioglitazone’s beneficial effects on erectile function preservation after cavernosal nerve injury in the rat are negated by inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor: a preclinical study
International Journal of Impotence Research (2019)
-
Low serum insulin-like growth factor-1 in patients with erectile dysfunction
Basic and Clinical Andrology (2016)
-
Emerging tools for erectile dysfunction: a role for regenerative medicine
Nature Reviews Urology (2012)
-
Increased expression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 is implicated in erectile dysfunction in two-kidney one-clip hypertensive rats after propranolol treatment
Asian Journal of Andrology (2011)
-
Emerging gene and stem cell therapies for the treatment of erectile dysfunction
Nature Reviews Urology (2010)