Abstract
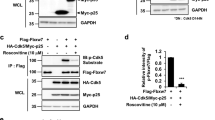
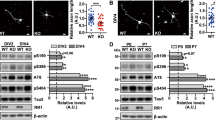
The normal development of the mammalian central nervous system requires a protein kinase known as Cdk5, the activity of which depends on its interaction with a regulatory subunit, p35. An abnormal truncated form of p35 (p25) produced by the action of proteases1,2 can also activate Cdk5, but causes apoptotic cell death in cultured primary neurons3. Patrick et al. have reported that p25 accumulates 20–40-fold in brain lysates from patients with Alzheimer's disease, and infer that p25 may contribute to the pathogenesis of neurodegeneration3. Here we show that the amount of p25 in the frontal cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease or Down's syndrome is actually lower than in controls. Although there is evidence for a role for p25 in neurodegeneration from cells in culture2,3 and in rats4 and mice5, our contradictory finding casts doubt on the involvement of p25 in neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, M. et al. Nature 405, 360–364 (2000).
Nath, R. et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 274, 16–21 (2000).
Patrick, G. N. et al. Nature 402, 615–622 (1999).
Kusakawa, G. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 17166–17172 (2000).
Ahlijanian, M. K. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2910–2915 (2000).
Tierney, M. C. et al. Neurology 38, 359–364 (1988).
Mirra, S. S. et al. Neurology 41, 479–486 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, B., Lubec, G. p25 protein in neurodegeneration. Nature 411, 763–764 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35081146
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35081146
This article is cited by
-
A Cdk5 inhibitory peptide reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and apoptosis in neurons
The EMBO Journal (2005)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.