Abstract
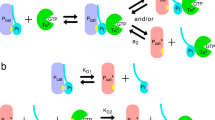
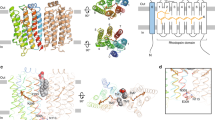
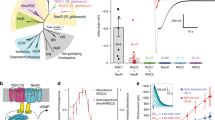
A multitude of heptahelical receptors use heterotrimeric G proteins to transduce signals to specific effector target molecules. The G protein transducin, Gt, couples photon-activated rhodopsin with the effector cyclic GMP phosophodiesterase (PDE) in the vertebrate phototransduction cascade. The interactions of the Gt α-subunit (αt) with the inhibitory PDE γ-subunit (PDEγ) are central to effector activation, and also enhance visual recovery in cooperation with the GTPase-activating protein regulator of G-protein signalling (RGS)-9 (refs 1,2,3). Here we describe the crystal structure at 2.0 Å of rod transducin Å·GDP·AlF-4 in complex with the effector molecule PDEγ and the GTPase-activating protein RGS9. In addition, we present the independently solved crystal structures of the RGS9 RGS domain both alone and in complex with αt/i1·GDP·AlF-4. These structures reveal insights into effector activation, synergistic GTPase acceleration, RGS9 specificity and RGS activity. Effector binding to a nucleotide-dependent site on αt sequesters PDEγ residues implicated in PDE inhibition, and potentiates recruitment of RGS9 for hydrolytic transition state stabilization and concomitant signal termination.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angleson, J. K. & Wensel, T. G. A GTPase-accelerating factor for transducin, distinct from its effector cGMP phosphodiesterase, in rod outer segment membranes. Neuron 11, 939–949 (1993).
He, W., Cowan, C. W. & Wensel, T. G. RGS9, a GTPase accelerator for phototransduction. Neuron 20, 95–102 (1998).
Chen, C.-K. et al. Slowed recovery of rod photoresponse in mice lacking the GTPase accelerating protein RGS9-1. Nature 403, 557–560 (2000).
Skiba, N. P., Bae, H. & Hamm, H. E. Mapping of effector binding sites of transducin α-subunit using Gαi/Gαi1 chimeras. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 413–424 (1996).
Skiba, N. P., Yang, C.-S., Huang, T., Bae, H. & Hamm, H. E. The α-helical domain of Gαt determines specific interaction with regulator of G protein signaling 9. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 8770–8778 (1999).
Noel, J. P., Hamm, H. E. & Sigler, P. B. The 2.2 Å crystal structure of transducin-α complexed with GTPγS. Nature 366, 654–663 (1993).
Lambright, D. G., Noel, J. P., Hamm, H. E. & Sigler, P. B. Structural determinants for activation of the α-subunit of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature 369, 621–628 (1994).
Sondek, J., Lambright, D. G., Noel, J. P., Hamm, H. E. & Sigler, P. B. GTPase mechanism of G proteins from the 1.7-Å crystal structure of transducin α·GDP·AlF-4. Nature 372, 276–279 (1994).
Tesmer, J. J. G., Berman, D. M., Gilman, A. G. & Sprang, S. R. Structure of RGS4 bound to AlF-4-activated Giα1: Stabilization of the transition state for GTP hydrolysis. Cell 89, 251–261 (1997).
Spink, K. E., Polakis, P. & Weis, W. I. Structural basis of the Axin–adenomatous polyposis coli interaction. EMBO J. 19, 2270–2279 (2000).
De Alba, E., De Vries, L., Farquhar, M. G. & Tjandra, N. Solution structure of human GAIP (Gα interacting protein): a regulator of G protein signaling. J. Mol. Biol. 291, 927–939 (1999).
Tsang, S. H. et al. Role for the target enzyme in deactivation of photoreceptor G protein in vivo. Science 282, 117–121 (1998).
Slepak, V. Z. et al. An effector site that stimulates G-protein GTPase in photoreceptors. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 14319–14324 (1995).
Faurobert, E., Otto-Bruc, A., Chardin, P. & Chabre, M. Tryptophan W207 in transducin Tα is the fluorescence sensor of the G protein activation switch and is involved in the effector binding. EMBO J. 12, 4191–4198 (1993).
Natochin, M., Granovsky, A. E. & Artemyev, N. O. Identification of effector residues on photoreceptor G protein, transducin. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 21808–21815 (1998).
Muradov, K. G. & Artemyev, N. O. Loss of the effector function in a transducin-α mutant associated with Nougaret night blindness. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 6969–6974 (2000).
Liu, Y., Arshavsky, V. Y. & Ruoho, A. E. Interaction sites of the COOH-terminal region of the γ subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase with the GTP-bound α subunit of transducin. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 26900–26907 (1996).
Artemyev, N. O., Rarick, H. M., Mills, J. S., Skiba, N. P. & Hamm, H. E. Sites of interaction between rod G-protein α-subunit and cGMP-phosphodiesterase γ-subunit: Implications for the phosphodiesterase activation mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 25067–25072 (1992).
Tesmer, J. J. G., Sunahara, R. K., Gilman, A. G. & Sprang, S. R. Crystal structure of the catalytic domains of adenylyl cyclase in a complex with Gsα·GTPγS. Science 278, 1907–1916 (1997).
Yan, S.-Z., Huang, Z.-H., Rao, V. D., Hurley, J. H. & Tang, W.-J. Three discrete regions of mammalian adenylyl cyclase form a site for Gsα activation. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18849–18854 (1997).
Lipkin, V. M., Dumler, I. L., Muradov, K. G., Artemyev, N. O. & Etingof, R. N. Active sites of the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase γ-subunit of retinal rod outer segments. FEBS Lett. 234, 287–290 (1988).
Brown, R. L. Functional regions of the inhibitory subunit of retinal rod cGMP phosphodiesterase identified by site-specific mutagenesis and fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry 31, 5918–5925 (1992).
Lambright, D. G. et al. The 2.0 Å crystal structure of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature 379, 311–319 (1996).
Natochin, M. & Artemyev, N. O. Substitution of transducin Ser202 by Asp abolishes G-protein/RGS interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 4300–4303 (1998).
Nekrasova, E. R. et al. Activation of transducin guanosine triphosphatase by two proteins of the RGS family. Biochemistry 36, 7638–7643 (1997).
McEntaffer, R. L., Natochin, M. & Artemyev, N. O. Modulation of transducin GTPase activity by chimeric RGS16 and RGS9 regulators of G protein signaling and the effector molecule. Biochemistry 38, 4931–4937 (1999).
Sowa, M. E., He, W., Wensel, T. G. & Lichtarge, O. A regulator of G protein signaling interaction surface linked to effector specificity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 1483–1488 (2000).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Brunger, A. T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
Jones, T. A., Zou, J. Y., Cowan, S. W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron-density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Berlot, Y. Korkhin, D. Lambright, L. Rice and J. Steitz for useful discussions; A. Brunger, P. Adams, R. Grosse-Kunstleve for help with CNS; and W. Minor and Z. Otwinowski for pre-release of HKL2000. We also thank staff of the SBC beamline 19-ID: R. Alkire, N. E.C. Duke, S. L. Ginell, K. Lazarski, S. Korolev, F. J. Rotella, R. Sanishvili, J. Lazarz, and A. Joachimiak. Use of the ANL SBC beamline at the APS was supported by the US Department of Energy, Office of Biological and Environmental Research. This work is supported in part by a NIH grant to P.B.S. M.A.K. is a HHMI Fellow of the LSRF. C.W.C. was supported by an NIH grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slep, K., Kercher, M., He, W. et al. Structural determinants for regulation of phosphodiesterase by a G protein at 2.0 Å. Nature 409, 1071–1077 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35059138
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35059138
This article is cited by
-
Splicing-accessible coding 3′UTRs control protein stability and interaction networks
Genome Biology (2020)
-
Transducin activates cGMP phosphodiesterase by trapping inhibitory γ subunit freed reversibly from the catalytic subunit in solution
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Therapeutic targeting of 3′,5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: inhibition and beyond
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2019)
-
Molecular mechanism of Gαi activation by non-GPCR proteins with a Gα-Binding and Activating motif
Nature Communications (2017)
-
The structural basis of the dominant negative phenotype of the Gαi1β1γ2 G203A/A326S heterotrimer
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.