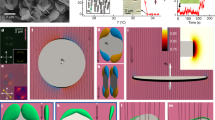
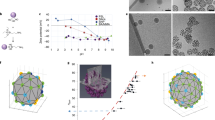
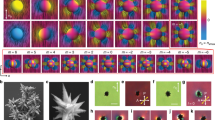
Abstract
Some binary mixtures exist as a single phase at high temperatures and as two phases at lower temperatures; rapid cooling therefore induces phase separation that proceeds through the initial formation of small particles and subsequent growth and coarsening1. In solid and liquid media, this process leads to growing particles with a range of sizes, which eventually separate to form a macroscopically distinct phase. Such behaviour is of particular interest in systems composed of an isotropic fluid and a liquid crystal2, where the random distribution of liquid-crystal droplets in an isotropic polymer matrix may give rise to interesting electro-optical properties. Here we report that a binary mixture consisting of an isotropic fluid and a liquid crystal forming the continuous phase does not fully separate into two phases, but self-organizes into highly ordered arrays of monodisperse colloidal droplet chains. We find that the size and spatial organization of the droplets are controlled by the orientational elasticity of the liquid-crystal phase and the defects caused by droplets exceeding a critical size. We expect that our approach to forming monodisperse, spatially ordered droplets in liquid crystals will allow the controlled design of ordered composites that may have useful rheological and optical properties.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gunton, J. M., San Miguel, M. & Sahni, P. S. in Phase Transition and Critical Phenomena Vol. 8 (ed. Lebowitz, J. L.) 267 (Academic, London, 1983).
Drzaic, P. Liquid Crystal Dispersions (Series on Liquid Crystals Vol. 1, World Scientific, Singapore, 1995).
Benmouna, F., Bedjaoui, L., Maschke, U., Coqueret, X. & Benmouna, M. On the phase behavior of blends of polymers and nematic liquid crystals. Macromol. Theory Simul. 7, 599–611 ( 1998).
Shen, C. & Kyu, T. Spinodals in a polymer dispersed liquid crystal. J. Chem. Phys. 102, 556– 562 (1995).
Yurke, B., Pargellis, A. N., Chuang, I. & Turok, N. Coarsening dynamics in nematic liquid crystals. Physica B 178, 56–72 (1992).
De Gennes, P. G. & Prost, J. The Physics of Liquid Crystals 2nd edn (Clarendon, Oxford, 1993).
Poulin, P., Stark, H., Lubensky, T. C. & Weitz, D. A. Novel colloidal interactions in anisotropic fluids. Science 275, 1770–1173 (1997).
Mondain-Monval, O., Frances, N. & Poulin, P. Weak surface energy in nematic dispersions: Saturn ring defects and quadrupolar interactions. Eur. Phys. J. B 12, 167–170 (1999).
Ruhwandl, R. W. & Terentjev, E. M. Monte Carlo simulation of topological defects in the nematic liquid crystal matrix around a spherical colloid particle. Phys. Rev. E 56, 5561–5565 (1997).
Stark, H. Director field configurations around a spherical particle in a nematic liquid crystal. Eur. Phys. J. B 10, 311– 321 (1999).
Lubensky, T. C., Pettey, D. & Currier, N. Topological defects and interactions in nematic emulsions. Phys. Rev. E 57, 610–625 (1998).
Poulin, P. & Weitz, D. A. Inverted and multiple nematic emulsions. Phys. Rev. E 57, 626–637 (1998).
Poulin, P., Cabuil, V. & Weitz, D. A. Direct measurement of colloidal forces in an anisotropic solvent. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 4862– 4865 (1997).
Lavrentovich, O. D., Nazarenko, V. G., Sergan, V. V. & Durand, G. Dielectric quenching of the electric polar surface instability in a nematic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. A 45, R6969– R6972 (1992).
Halsey, T. C. & Toor, W. Structure of electrorheological fluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 2820– 2823 (1990).
Miyazima, S., Meakin, P. & Family, F. Aggregation of oriented anisotropic particles. Phys. Rev. A 36, 1421–1427 (1987).
See, H. & Doi, M. Aggregation kinetics in electrorheological fluids. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 60, 2778– 2782 (1991).
Carmen Miguel, M. & Pastor-Satorras, R. Kinetic growth of field-oriented chains in dipolar colloidal solutions. Phys. Rev. E 59, 826–834 (1999).
Halsey, T. C. & Toor, W. Fluctuation-induced couplings between defect lines or particle chains. J. Statist. Phys. 61, 1257–1281 (1990).
Meeker, S. P., Poon, W. C. K., Crain, J. & Terentjev, E. M. Colloid liquid crystal composites: An unusual soft solid. Phys. Rev. E 61, R6083–R6086 ( 2000).
Calderon, F. L., Stora, T., Monval, O. M., Poulin, P. & Bibette, J. Direct measurement of colloidal forces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 2959–2962 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loudet, JC., Barois, P. & Poulin, P. Colloidal ordering from phase separation in a liquid- crystalline continuous phase. Nature 407, 611–613 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35036539
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35036539
This article is cited by
-
Optical and Spectral Properties of Dispersed ZnO p-n-Octyloxy Benzoic Acid Liquid Crystalline Compounds
Journal of Applied Spectroscopy (2023)
-
Total synthesis of colloidal matter
Nature Reviews Materials (2021)
-
Degenerate conic anchoring and colloidal elastic dipole-hexadecapole transformations
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Optical properties of metamaterial split ring nematic colloids
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Fumed alumina-in-nematic liquid crystal suspensions under shear and electric field
Rheologica Acta (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.