Abstract
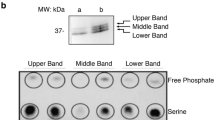
In human T lymphocytes the antigen receptor (Ti) is associated non-covalently on the cell surface with the invariant T3 antigen which comprises 3 chains: two glycosylated polypeptides of relative molecular mass 26,000 (Mr26K) and 21K (γ and δ) and one non-N-glycosylated polypeptide of Mr 19K (ε)1–7. The proposed function of T3 is to transduce the activation signals delivered via the antigen receptor8–13. Recently we have shown that phorbol esters, which stimulate protein kinase C, can induce phosphorylation of the γ subunit of the T3 antigen14,15. But the critical question is whether T3 phosphorylation occurs as a normal consequence of immune activation of T lymphocytes. In this respect, it has been shown that immune stimulation of murine T cells results in phosphorylation of Ti-associated polypeptides that may be the functional analogues of the human T3 antigen16,17. We have therefore monitored T3 phosphorylation after exposure of human T cells to antigen or phytohaemagglutinin (PHA). The data show that both stimuli initiate phosphorylation of the γ subunit of the T3 antigen which indicates that T3 phosphorylation is a physiological response to immune activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meuer, S. C. et al. J. exp. Med. 157, 705–719 (1983).
Acuto, O. et al. Cell 34, 717 (1983).
Meuer, S. C. et al. Science 222, 1239–1241 (1983).
Meuer, S. C. et al. Nature 303, 808–810 (1983).
Brenner, M. B., Trowbridge, J. S. & Strominger, J. L. Cell 40, 183–190 (1985).
Kanellopoulus, J. M., Wigglesworth, N. M., Owen, M. J. & Crumpton, M. J. EMBO J. 2, 1807–1814 (1983).
Borst, J., Alexander, S., Elder, J. & Terhorst, C. J. biol. Chem. 258, 5135–5141 (1983).
Van Wauve, J. P., De Mey, J. R. & Goosens, J. G. J. Immun. 125, 2708–2712 (1980).
Chang, T. W., Kung, P. C., Gingrus, S. P. & Goldstein, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 1805–1808 (1981).
Burns, G. R., Boyd, A. W. & Beverley, P. C. L. J. Immun. 129, 1451–1457 (1982).
Reinherz, E. L. et al. Cell 30, 735–743 (1982).
Oettgen, H. C., Terhost, C., Cantley, L. C. & Roscoff, P. M. Cell 40, 583–590 (1985).
Roscoff, P. M. & Cantley, L. W. J. biol. Chem. 260, 14053–14059 (1985).
Cantrell, D. A., Davies, A. A. & Crumpton, M. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 8158–8162 (1985).
Davies, A. A., Cantrell, D. A. & Crumpton, M. J. Biosciences 5, 867–876 (1985).
Samelson, L. E., Harford, J. B., Schwartz, N. H. & Klausner, R. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 1969–1973 (1985).
Samelson, L. E., Harford, J. B. & Klausner, R. D. Cell 43, 223–231 (1985).
Beverley, P. C. L. & Callard, R. E. Eur. J. Immun. 11, 329–334 (1981).
Walsh, F. S. & Crumpton, M. J. Nature 269, 307–311 (1977).
Barnstable, C. J. et al. Cell 14, 9–20 (1978).
Chilson, O. P., Boylston, A. W. & Crumpton, M. J. EMBO J. 3239–3245 (1984).
O'Flynn, K., Krensky, A. M., Beverley, P. C. L., Burakoff, S. J. & Lynch, D. C. Nature 313, 686–687 (1985).
Ohashi, P. S. et al. Nature 316, 606–609 (1985).
Lamb, J. R., Eckels, D. D., Lack, P., Woody, J. U. & Green, N. Nature 300, 66–69 (1982).
Farrar, W. L. & Ruscetti, F. W. J. Immun. 136, 1266–1273 (1985).
Imboden, J. B. & Stobo, J. O. J. exp. Med. 161, 446–456 (1985).
Oettgen, H. C., Pettey, C. L., Maloy, L. & Terhorst, C. Nature 320, 272–275 (1986).
Reinherz, E. L. et al. Cell 30, 735–743 (1982).
Zanders, E., Lamb, J., Feldman, M., Green, N. & Beverley, P. Nature 313, 318–320 (1983).
Delia, D. et al. Int. J. Cancer 29, 23–31 (1982).
Ando, I., Hariri, G., Wallace, D. & Beverley, P. Euro. J. Immun. 15, 196–199 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cantrell, D., Davies, A., Londei, M. et al. Association of phosphorylation of the T3 antigen with immune activation of T lymphocytes. Nature 325, 540–542 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/325540a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/325540a0
This article is cited by
-
Modulation of cellular processes by H7, a non-selective inhibitor of protein kinases
Agents and Actions (1991)
-
T cell targeting in cancer therapy
Cancer Immunology Immunotherapy (1991)
-
Phosphorylation and down-regulation of CD4 and CD8 in human CTLs and mouse L cells
Immunogenetics (1989)
-
Chromosomal locations of the gene coding for the CD3 (T3) ? subunit of the human and mouse CD3/T-cell antigen receptor complexes
Immunogenetics (1987)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.