Abstract
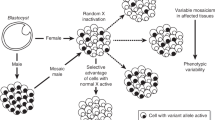
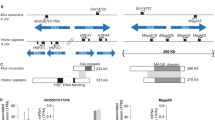
In the human there is an X-linked gene affecting steroid sulphatase (STS) activity which, when deficient, is associated with X-linked congenital ichthyosis1,2. The gene (STS) is located on the distal tip of the short arm3–6 and is only partially inactivated when it is on the inactive X-chromosome7–10. In the mouse, the genetics of STS are not clear; the results of one study using XX:X0 oocyte comparisons indicated X-linkage11, but three other studies using STS variants have produced segregation data compatible with autosomal linkage of murine STS12–14. Here we present the results of STS assays of crosses of deficient C3H/An male mice12 to normal X0 animals which demonstrate X-linkage of STS in the mouse and indirectly indicate the existence of a functional STS allele on the Y-chromosome which undergoes obligatory recombination during meiosis with the X-linked allele.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jobsis, A. G. et al. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneesk. 120, 1980 (1976).
Shapiro, L. J., Weiss, R., Webster, D. & France, J. T. Lancet i, 70–72 (1978).
Tiepolo, L. et al. Hum. Genet. 54, 205–206 (1980).
Muller, C. R. Westerveld, A., Migl, B., Franke, W. & Ropers, H. H. Hum. Genet. 54, 201–204 (1980).
Mohandas, T., Shapiro, L. J., Sparkes, R. S. & Sparkes, M. C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 5779–5783 (1979).
Mohandas, T., Sparkes, R. S., Hellkuhl, B., Grzeschik, K. H. & Shapiro, L. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 6759–6763 (1980).
Muller, C. R., Migl, B., Traupe, H. & Ropers, H. H. Hum. Genet. 54, 197–199 (1980).
Chance, P. F. & Gartler, S. M. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 35, 234–240 (1983).
Ropers, H. H. et al. Hum. Genet. 57, 354–356 (1981).
Migeon, B. R. et al. Nature 299, 838–840 (1982).
Gartler, S. M. & Rivest, M. Genetics 103, 137–141 (1983).
Balazs, I., Purrello, M., Rocchi, M. & Siniscalco, M. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 32, 251 (1982).
Erickson, R. P., Harper, K. & Kramer, J. M. Genetics 105, 181–189 (1983).
Keinanen, B. M., Nelson, K., Daniel, W. L. & Roque, J. M. Genetics 105, 191–206 (1983).
Solari, A. J. Int. Rev. Cytol. 38, 273–317 (1974).
Ferguson-Smith, M. A. Lancet ii, 475–476 (1966).
Burgoyne, P. S. Hum. Genet. 61, 85–90 (1982).
Polani, P. E. Hum. Genet. 60, 207–211 (1982).
Cattanach, B. M., Pollard, C. E. & Hawkes, S. G. Cytogenetics 10, 318–337 (1971).
Singh, L. & Jones, K. W. Cell 28, 205–216 (1982).
Evans, E. P., Burtenshaw, M. D. & Cattanach, B. Nature 300, 443–445 (1983).
Ashley, T. Hum. Genet. 67, 372–377 (1984).
Goodfellow, P. et al. Nature 302, 346–349 (1983).
Goodfellow, P. N. & Tippett, P. Nature 289, 404–405 (1981).
de la Chapelle, A. Hum. Genet. 58, 105–116 (1981).
Evans, H. J., Buckton, K. E., Spowart, G. & Carothers, A. D. Hum. Genet. 49, 11–31 (1979).
Pierella, P., Craig, I., Bobrow, M. & de la Chapelle, A. Hum. Genet. 59, 87–88 (1981).
Wieacker, P., Voiculescu, J., Muller, C. R. & Ropers, H. H. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 35, 72–74 (1983).
de la Chapelle, A. Tippett, P. A., Wetterstrand, G. & Page, D. Nature 307, 170–171 (1984).
Guellaen, G. et al. Nature 307, 172–173 (1984).
Crocker, M. & Craig, I. Nature 303, 721–722 (1983).
Shapiro, L. J., Cousins, L., Fluharty, A. L., Stevens, R. L. & Kihara, H. Pediat. Res. 11, 894–897 (1977).
McNaught, R. W. & France, J. T. J. Steroid Biochem. 13, 363–373 (1980).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Lewis Farr, A. & Randall, R. J. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keitges, E., Rivest, M., Siniscalco, M. et al. X-linkage of steroid sulphatase in the mouse is evidence for a functional Y-linked allele. Nature 315, 226–227 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/315226a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/315226a0
This article is cited by
-
A primer on the use of mouse models for identifying direct sex chromosome effects that cause sex differences in non-gonadal tissues
Biology of Sex Differences (2016)
-
A pronounced evolutionary shift of the pseudoautosomal region boundary in house mice
Mammalian Genome (2012)
-
Escape from X inactivation in mice and humans
Genome Biology (2010)
-
Brain Pathways Mediating the Pro-Aggressive Effect of the Steroid Sulfatase (Sts) Gene
Behavior Genetics (2010)
-
CSF2RA, ANT3, and STS are autosomal in marsupials: implications for the origin of the pseudoautosomal region of mammalian sex chromosomes
Mammalian Genome (1998)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.