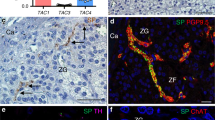
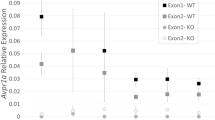
Abstract
Arginine-vasopressin (AVP) is a neurohypophysial nonapeptide with antidiuretic activity involved in the control of blood volume and plasma osmolality1. Recently, by immunological methods, the presence of AVP has been demonstrated in extrahypothalamic areas of the brain, in the spinal cord2 and in the ovary3, testis4 and adrenal gland5. The Brattleboro rat is regarded as having an autosomal recessively inherited lack of neurohypophysial vasopressin6 and its associated neurophysin7. Since its discovery over 20 years ago8 this animal has been widely used in studies on the physiological role of vasopressin. We have recently investigated the presence of immunoreactive vasopressin and the related nonapeptide oxytocin in the adrenal glands of the human, rat and cow, and report here the isolation from the Brattleboro rat adrenal of material with similar immunological, physical and biological properties to synthetic vasopressin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moses, A. M. & Miller, M. Handbook of Physiology, Section 7 Vol. 4, Pt 1, 225–242 (American Physiological Society, 1974).
Jenkins, J. S., Ang, V. T. Y., Hawthorn, J., Rosser, M. N. & Iversen, L. L. Brain Res. 291, 111–117 (1984).
Wathes, D. C., Swann, R. W., Birkett, S. D., Porter, D. G. & Pickering, B. T. Endocrinology 113, 693–698 (1983).
Nicholson, H. D. et al. Acta endocr. 103 (Suppl. 256), 243 (1983).
Ang, V. T. Y. & Jenkins, J. S. J. clin. Endocr. 58, 688–691 (1984).
Valtin, H. & Schroeder, H. A. Am. J. Physiol. 206, 425–430 (1964).
Burford, G. D., Jones, C. W. & Pickering, B. T. Biochem. J. 124, 809–813 (1971).
Valtin, H., Schroeder, H. A., Benirschke, K. & Sokol, H. W. Nature 196, 1109–1110 (1962).
Bisset, G. W. & Chowdrey, H. S. J. Physiol., Lond. (in the press).
Sawyer, W. H. et al. Science 212, 49–51 (1981).
Schmale, H. & Richter, D. Nature 308, 705–709 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nussey, S., Ang, V., Jenkins, J. et al. Brattleboro rat adrenal contains vasopressin. Nature 310, 64–66 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/310064a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/310064a0
This article is cited by
-
Vasopressin signaling at brain level controls stress hormone release: the vasopressin-deficient Brattleboro rat as a model
Amino Acids (2015)
-
Oxytocin-producing and vasopressin-producing eosinophils in the mouse spleen: immunohistochemical, immuno-electron-microscopic and in situ hybridization studies
Cell and Tissue Research (1995)
-
Processing endopeptidase deficiency in neurohypohysial secretory granules of the diabetes insipidus (Brattleboro) rat
Bioscience Reports (1992)
-
GFR and the concentration of urine in the absence of vasopressin. Berliner-Davidson re-explored
Kidney International (1987)
-
Immunohistochemical localization of oxytocin and vasopressin in the adrenal glands of rat, cow, hamster and guinea pig
Cell and Tissue Research (1987)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.