Abstract
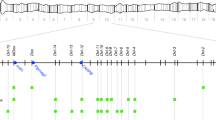
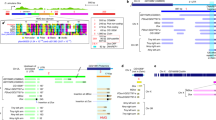
A high degree of polymorphism for the length and copy number of rDNA spacers, in both the X and Y chromosome clusters, has been found in a wild population of Drosophila melanogaster. The genetic behaviour of rDNA structural variants in separate and mixed populations derived from isofemale lines suggests that they are not subject to strong selection and are stable for over 1,000 generations. The high structural variability suggests an evolutionary rapid process of turnover in the family which could partly explain widespread sequence homogeneity (concerted evolution) of rDNA within a species.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dover, G. A. et al. in Genome Evolution (eds Dover, G. A. & Flavell, R. B.) 343–374 (Academic, London, 1982).
Jeffreys, A. in Genome Evolution (eds Dover, G. A. & Flavell, R. B.) 157–176 (Academic, London, 1982).
Dover, G. A. & Coen, E. S. Nature 290, 731–732 (1981).
Smith, G. P. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 38, 507–513 (1974).
Otha, T. Evolution and Variation of Multigene Families (Springer, New York, 1980).
Klein, H. L. & Petes, T. D. Nature 289, 144–148 (1981).
Scherer, S. & Davis, R. W. Science 209, 1380–1384 (1980).
Brown, S. D. M. & Dover, G. A. J. molec. Biol. 150 441–466 (1981).
Petes, T. D. Cell 19, 765–774 (1980).
Szostak, J. W. & Wu, R. Nature 284, 426–430 (1980).
Tartof, K. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 38, 491–500 (1974).
Coen, E. S. Strachan, T. & Dover, G. A. J. molec. Biol. (in the press).
Schalet, A. Genetics 63, 133–153 (1969).
Ritossa, F. in The Genetics and Biology of Drosophila Vol. 1b (eds Ashburner, M. & Novitski, E.) 801–846 (Academic, New York, 1976).
Federoff, N. Cell 16, 697–710 (1979).
Long, E. O. & Dawid, I. B. A. Rev. Biochem. 49, 727–764 (1980).
Woodruff, R. C. & Thompson, J. N. Jr Heredity 38, 291–307 (1977).
Endow, S. A. & Glover, D. M. Cell 17, 597–605 (1979).
Endow, S. A. Cell 22, 149–155 (1980).
Ritossa, F., Malva, C., Boncinelli, E., Graziani, F. & Polito, L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 68, 1580–1584 (1971).
Tartof, K. D. & Dawid, I. P. Nature 263, 27–30 (1976).
Yagura, T., Yagura, M. & Muramatsu, M. J. molec. Biol. 133, 533–547 (1979).
Milkman, R. & Zeitler, R. R. Genetics 78, 1191–1193 (1974).
Renkawitz-Pohl, R., Glatzer, K. H. & Kuntz, W. Nucleic Acids Res. 8, 4593–4611 (1981).
Rae, P. M. M., Barnett, T. & Murtif, V. L. Chromosoma (Berl.) 82, 637–655 (1981).
Schafer, M., Wyman, A. R. & White, R. J. molec. Biol. 146, 179–200 (1981).
Downes, S. P. thesis, Univ. Cambridge (1981).
Gerasimova, T. I. & Ananjev, E. V. Drosoph. Inf. Serv. 48, 93 (1972).
Frankham, R., Briscoe, D. A. & Nurthen, R. K. Genetics 95, 727–742 (1980).
Strachan, T., Coen, E. S., Webb, D. A. & Dover, G. A. J. molec. Biol. (in the press).
Arnheim, N. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 7323–7327 (1980).
Roiha, H., Miller, R. M., Woods, L. C. & Glover, D. M. Nature 290, 749–753 (1981).
Roiha, H. & Glover, D. M. J. molec. Biol. 140, 341–355 (1980).
Glover, D. M. & Hogness, D. S. Cell 10, 167–176 (1977).
Wahl, G. M., Stern, M. & Stark, G. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 3683–3687 (1979).
Rigby, P. W. J., Dieckmann, M., Rhodes, C. & Berg, P. J. molec. Biol. 113, 237–251 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coen, E., Thoday, J. & Dover, G. Rate of turnover of structural variants in the rDNA gene family of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 295, 564–568 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/295564a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/295564a0
This article is cited by
-
Evolutional dynamics of 45S and 5S ribosomal DNA in ancient allohexaploid Atropa belladonna
BMC Plant Biology (2017)
-
Molecular evidence for the presence of malaria vector species a of the Anopheles annularis complex in Sri Lanka
Parasites & Vectors (2011)
-
The Rate of Unequal Crossing Over in the dumpy Gene from Drosophila melanogaster
Journal of Molecular Evolution (2010)
-
Nuclear background affects frequency dynamics of mitochondrial DNA variants in Drosophila simulans
Heredity (1994)
-
Aspects of nonrandom turnover involved in the concerted evolution of intergenic spacers within the ribosomal DNA of Drosophila melanogaster
Journal of Molecular Evolution (1994)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.