Abstract
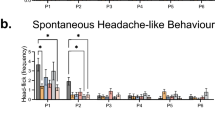
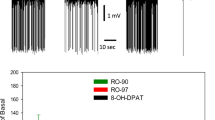
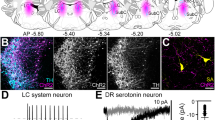
When rats are given a series of electroconvulsive shocks (ECSs) over several days, they display enhanced behavioural responses to both serotonin- and dopamine-receptor agonists 1–3. Because these changes are seen when the ECS is given in ways closely mimicking the clinical administration of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), it has been suggested that the changes in post-synaptic monoamine function may be involved in the antide-pressant mechanisms of ECT4,5. Ligand-binding studies have excluded the possibility that ECS alters the characteristics of either the serotonin or dopamine receptor6–8; ECS may therefore be acting on neuronal systems which modulate monoamine neurotransmission. As repeated ECS has recently been reported to decrease both noradrenaline (NA)-sensitive adenylate cyclase9 and β-adrenoreceptor binding8,10,11, we have examined here whether changes in NA function are related to the effects of ECS on the serotonin- and dopamine-mediated behaviours. We demonstrate that although selective depletion of NA does not alter the drug-induced serotonin- and dopamine-mediated responses, it abolishes the ECS-induced enhancement of these behaviours.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Modigh, K. J. neural Transmission 36, 19–32 (1975).
Evans, J. P. M., Grahame-Smith, D. G., Green, A. R. & Tordoff, A. F. C. Br. J. Pharmac. 56, 193–199 (1976).
Green, A. R., Heal, D. J. & Grahame-Smith, D. G. Psychopharmacology 52, 195–200 (1977).
Costain, D. W., Green, A. R. & Grahame-Smith, D. G. Psychoparmacology 61, 167–170 (1979).
Grahame-Smith, D. G., Green, A. R. & Costain, D. W. Lancet i, 254–257 (1978).
Cross, A. J. et al. Br. J. pharmac. 66, 111P (1979).
Atterwill, C. K. & Prince, A. K. 11th int. Meet. int. Soc. Neurochem., Jerusalem (1979).
Bergstrom, D. A. & Kellar, K. J. Nature 278, 464–466 (1979).
Vetulani, J., Schwartz, R. J., Dingell, J. V. & Sulser, F. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 293, 109–114 (1976).
Pandey, G. N., Heinze, W. J., Brown, B. D. & Davis, J. M. Nature 280, 234–235 (1979).
Deakin, J. F. W., Owen, F. & Poulter, M. Neurosci. Lett. (in the press).
Curzon, G. & Green, A. R. Br. J. Pharmac. 39, 653–655 (1970).
Chang, C. C. Int. J. Neuropharmac. 3, 645–649 (1964).
Green, A. R., Youdim, M. B. H. & Grahame-Smith, D. G. Neuropharmacology 15, 173–179 (1976).
Green, A. R. & Grahame-Smith, D. G. Neuropharmacology 13, 949–959 (1974).
Mussachio, J. M., Julou, L., Kety, S. S. & Glowinski, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 63, 1117–1119 (1969).
Modigh, K. Psychopharmacology 49, 179–185 (1976).
Kety, S. S., Javoy, F., Therry, A. M., Julou, L. & Glowinski, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 58, 1249–1254 (1967).
Modigh, K. in Neuropsychopharmacology (eds Saletu, B. & Hollister, L.) (Pergamon, Oxford, in the press).
Hendley, E. D. Psychopharmac. Commun. 2, 17–25 (1976).
van Praag, H. M. Depression and Schizophrenia (Spectrum, Flushing, 1976).
Green, A. R., Costain, D. W. & Deakin, J. F. W. Neuropharmacology (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Green, A., Deakin, J. Brain noradrenaline depletion prevents ECS-induced enhancement of serotonin-and dopamine-mediated behaviour. Nature 285, 232–233 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/285232a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/285232a0
This article is cited by
-
Electroconvulsive shock does not modify striatal contents of dopamine in MPTP-treated mice
Neurochemical Research (1993)
-
Regional neurotransmitter responses after acute and chronic electroconvulsive shock
Psychopharmacology (1990)
-
Effects of long-term administration of antidepressants and neuroleptics on receptors in the central nervous system
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (1989)
-
The influence of central noradrenergic function on 5-HT2-mediated head-twitch responses in mice: Possible implications for the actions of antidepressant drugs
Psychopharmacology (1986)
-
Antidepressants and serotonergic neurotransmission: An integrative review
Psychopharmacology (1985)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.