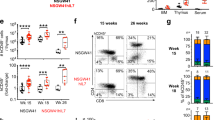
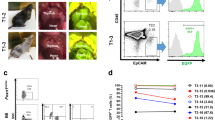
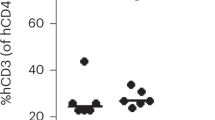
Abstract
THE congenitally athymic mouse which is homozygous for nude (nu/nu), compared with the phenotypically normal heterozygote (+/nu) or the normal mouse (+/+) is severely deficient in its plaque-forming cell (PFC) response to sheep erythrocytes (SE)1,2. The minimal response of the nude is generally attributed to a deficiency of thymus-derived helper cells which are essential for a full PFC response to thymus-dependent antigens such as SE1–3. The amount of helper activity (T cell or T-cell-like) that nude mice may receive from their mothers is of concern in several laboratories4–9, since most nude mice obtained routinely are born of phenotypically normal (+/nu) mothers that have T cells. There is debate about the relative importance of T-cell precursors observed in nude mice10, which may be stimulated to express T-cell antigens by soluble factors11, and the equally important possibilities that nudes may receive T cells and/or soluble factors in utero from their normal +/nu mothers or from their +/nu or +/+ littermates or from the colostrum of +/nu mothers12. The results of studies designed to resolve this issue remain equivocal14–13. There is a need12 for studies with nude mice born of homozygous nude parents (nu/nu ♀ × nu/nu ♂) and raised by nude mothers to minimise the possibilities of transfer of functionally mature T cells in utero or the transfer of T cells or T-cell-like factors by the colostrum. So far this criterion has been difficult to meet since nude mothers from most common mouse strains were poorly fertile or could not raise their young14.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pantelouris, E. M., Immunology, 20, 247–252 (1971).
Kendred, B., Eur. J. Immun., 1, 59–61 (1971).
Reed, N. D., and Jutila, J. W., Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med., 139, 1234–1237 (1971).
Raff, M. C., Nature, 246, 350–351 (1973).
Loor, F., and Roelants, G. E., Nature, 251, 229–230 (1974).
Roelants, G. E., et al., Eur. J. Immun., 5, 127–131 (1975).
Humber, D. P., Pinder, M., and Hetherington, C. M., Transplantation, 19, 91–93 (1975).
Loor, F., Hagg, L.-B., Mayor, K. S., and Roelants, G. E., Nature, 255, 657–658 (1975).
Holub, M., Rossman, P., Tlaskalova, H., and Vidmarova, H., Nature, 256, 491–493 (1975).
Wortis, H., Nehlsen, S., and Owen, J., J. exp. Med., 134, 681–692 (1971).
Komuro, K., and Boyse, E. A., Lancet, i, 740–741 (1973).
Raff, M., Nature, 251, 184–185 (1974).
Pantelouris, E. M., Nature, 254, 140–141 (1975).
Festing, M. F. W., and King, D., in Proc. Int. Workshop Nude Mice (edit. by Rygaard, J., and Povlsen, C. O.), 203–205 (Fisher, Stuttgart, 1974).
Uzunova, A. D., and Hanna, E. E., Cell Immun., 7, 507–511 (1973).
Hanna, E. E., and Hale, M., Infect. Immun., 11, 265–272 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HALE, M., HANNA, E. & HANSEN, C. Nude mice from homozygous nude parents show smaller PFC responses to sheep erythrocytes than nude mice from heterozygous mothers. Nature 260, 44–45 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/260044a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/260044a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.