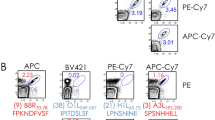
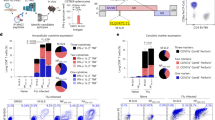
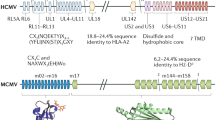
Abstract
MICE generate cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) which are able to lyse virus infected target cells in vitro after infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) and pox-viruses1–3. CTL kill syngeneic and semiallogenic infected cells but not allogenic infected targets. Target cell lysis in these systems seems to be restricted by H-2 antigens, especially by the K or D end of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). In experiments where virus specific sensitised lymphocytes kill virus infected allogenic target cells4 the effector lymphocytes have not been characterised exactly. Recent investigations suggest that the active cell in this assay, at least in the measles infection, is a non-thymus derived cell (H. Kreth, personal communication). An H-2 restriction of cell mediated cytolysis (CMC) to trinitrophenol (TNP)-modified lymphocytes has also been described5. Zinkernagel and Doherty6 postulated that the CTL is directed against syngeneic H-2 antigens and viral antigens and they suggested an alteration of H-2 induced by the LCMV infection. Earlier7 we found a close topological relationship between H-2 antigens and the target antigen(s) responsible for CMC in the vaccinia system. Here we report experiments which were carried out to prove alteration of H-2 after infection of L-929 fibroblasts with vaccinia virus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doherty, P. C., Zinkernagel, R. M., and Ramshaw, I. H., J. Immun., 112, 1548–1552 (1974).
Gardner, I. D., Bowern, N. A., and Blanden, R. V., Eur. J. Immun., 4, 68–72 (1974).
Koszinowski, U., and Thomssen, R., Eur. J. Immun., 5, 246–251 (1975).
Kreth, W. H., Kackell, M. Y., and Ter Meulen, V., J. Immun., 114, 1042–1046 (1975).
Shearer, G. M., Eur. J. Immun., 4, 527–533 (1974).
Zinkernagel, R. M., and Doherty, P. C., Nature, 511, 547–548 (1974).
Koszinowski, U., and Ertl, H., Nature, 255, 254–256 (1975).
Snell, G. D., Catalogue of Mouse Antisera, Transplantation Immunology Branch Publication Supplement (NIAID, NIH, Bethesda, Maryland, 1968, 1974).
Ting, C. C., and Herberman, R. B., Nature new Biol., 232, 118–120 (1971).
Alter, B. J., and Bach, F. H., J. exp. Med., 140, 1410–1415 (1974).
Lilly, F., in RNA viruses and Host Genome in Oncogenesis (edit. by Emmelot, P., and Bentvelzen, P.), 220–238 (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1972).
Tsakralides, E., Smith, C., Kersey, J. H., and Good, R. A., J. natn. Cancer Inst., 45, 979–988 (1970).
Cikes, M., J. natn. Cancer Inst., 45, 979–988 (1970).
Boyse, E. A., in Immune Surveillance (edit. by Smith, R. T., and Landy, M.), 5–30 (Academic, New York and London, 1970).
Wekerle, H., Kölsch, E., and Feldman, M., Eur. J. Immun., 4, 246–250 (1974).
Lesley, J., Hyman, R., and Dennert, G., J. natn. Cancer Inst., 53, 1759–1765 (1974).
Berke, G., and Amos, D. B., Nature new Biol., 242, 237–238 (1973).
Widmer, M. B., Alter, B. J., Bach, F. H., Bach, M. L., and Bailey, D. W., Nature new Biol., 242, 239–241 (1973).
Klein, J., Hauptfeld, M., and Hauptfeld, V., J. exp. Med., 140, 1127–1132 (1974).
Gardner, I. D., Bowern, N. A., and Blanden, R. V., Eur. J. Immun., 5, 122–127 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KOSZINOWSKI, U., ERTL, H. Altered serological and cellular reactivity to H-2 antigens after target cell infection with vaccinia virus. Nature 257, 596–597 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/257596a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/257596a0
This article is cited by
-
Changes in epidermal Langerhans cells, γδ T cells and CD4 T cells after intradermal infection with recombinant vaccinia virus expressing cytokine genes
Immunology & Cell Biology (1994)
-
MURINE CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS: DISEASE PATTERNS IN INTACT AND NUDE MICE OF VARIOUS GENOTYPES AND EXAMINATION OF SOME DIFFERENCES BETWEEN NORMAL AND INFECTED MACROPHAGES
Australian Journal of Experimental Biology and Medical Science (1979)
-
Effect of anH-2 mutation on cytotoxic T cell recognition. Specific antigen can determine the pattern ofH-2 restriction
Immunogenetics (1979)
-
The question of derepression ofH-2 specificities in virus-infected cells: Failure to detect specific alloreactive T cells after systemic virus infection or alloantigens detectable by alloreactive T cells on virus-infected target cells
Immunogenetics (1977)
-
H–2 region product as determinant in immune cytolysis of syngeneic tumour cells by anti-MSV T lymphocytes
Nature (1976)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.