Abstract
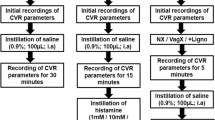
THE recent observation that certain histamine responses which were resistant to antihistaminic blockade may now be abolished by the newly synthesised compounds burimamide (N-methyl-N1 [4-(4/5)-imidasolyl) butyl] thiourea) and metiamide (N-methyl-N1 [2/(5 methylimidazol-4-yl) methylthio/ethyl] thiourea) (both compounds, Smith, Kline and French) has culminated in the interpretation of histamine action in terms of both H1-and H2-receptors1. Until now the attention of workers in this field has centred upon gastric acid secretion. Our own studies, however, have been directed at the receptor control of the microcirculation and we have previously reported failure of conventional antihistaminics to block histamine responses in our experimental model2. Here we report results obtained in the canine diarthrodial joint which demonstrate the abolition of histamine responses by H2 and not by H1-bloeking compounds and thus supporting the conclusion that H2-receptors are involved in the control of peripheral blood vessels.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black, T. W., Duncan, A. M., Durant, C. T., Ganellia, C. R.', and Parsons, E. M., Nature, 236, 385–390 (1972).
St Onge, R. A., and Dick, W. C., Modern Trends in Rheumatology, 2 (edit. by Hill, A. G. S.) 5, (Butterworths, London, 1970).
Dick, W. C., et al. Ann rheum. Dis., 29, 131 (1970).
Dick, W. C., Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 1, 301 (1972).
Powell, J. R., and Brody, M. J., Int. Symp. on H2 Receptor Antagonists, London, (edit. by Wood, C.) 137, (1973).
Glover, W. E., Carroll, P. R., and Latt, N., Int. Symp. H2-Receptor Antagonists, London, (edit. by Wood, C.) 169 (1973).
Reed, J. D., Smy, J. R., Venables, C. W., and Harris, D. W., Int. Symp. on H2-Receptor Antagonists. London, (edit. by Wood, C.) 231 (1973).
Douglas, W. W., in The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (edit. by Goodman, L. S., and Gilman, A.) 615–627 (McMillan, New York, 1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GRENNAN, D., ROONEY, P., GILBERTSON, E. et al. H2-receptors in peripheral blood vessels. Nature 249, 368–370 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/249368a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/249368a0
This article is cited by
-
Classification and biological distribution of histamine receptor sub-types
Agents and Actions (1994)
-
Classification and biological distribution of histamine receptor sub-types
Agents and Actions (1975)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.