Abstract
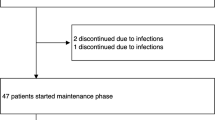
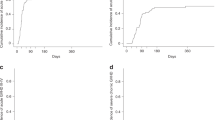
We have treated 20 patients, affected by acute myelogenous leukemia in advanced phase of the disease, with intravenous high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 (IL2) as induction treatment, achieving a complete remission (CR) in 11/20 of patients (55%). All CR patients were planned to receive a maintenance program with lower subcutaneous doses of IL2 until relapse. Currently, 5/11 patients are alive in continuous complete remission with a minimum follow-up of 9 years from IL2 induction. In the aim to investigate the treatment's side-effects during or after prolonged IL2 therapy, we decided to submit these patients to a clinical and immunological evaluation. Four patients have been evaluated as one, who independently stopped IL2 after 6 years, refused the check-up. No organ-specific treatment sequelae that may decrease the quality of life or may be life-threatening were found, concerning renal, liver and cardiovascular function. Endocrine abnormalities were detected in three patients, the most serious being a severe hypothyroidism, which prompted cessation of IL2 maintenance after 6 years and required thyroid supplementation treatment. Immunological studies were carried out prior to the last IL2 cycle and showed high levels of CD3-positive T cells expressing the IL2 receptor alpha chain (CD25), both in the peripheral blood and in the bone marrow. Our study shows that low-dose IL2 can be given for a prolonged period of time without serious organ-specific late sequelae and with a good quality of life.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ortaldo JR, Mason AT, Gerard JP, Henderson LE, Ferrar W, Hopkins RF III, Herberman BB, Rabin H . Effects of natural and recombinant IL-2 on regulation of IFN production and natural killer activity; lack of involvement of the Tac antigen for these immunoregulatory effects J Immunol 1984 133: 779–783
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, Leitman S, Chang AE, Ettinghausen SE, Maory YL, Skibber JM, Shiloni E, Vetto JT, Selpp CA, Simpson C, Reichert CM . Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukine-2 to patients with metastatic cancer N Engl J Med 1985 313: 1485–1492
Maraninchi D, Blaise D, Viens P, Brandely M, Olive D, Lopez M, Sainty D, Marit G, Stoppa AM, Reiffers J, Gratecos N, Bertau-Perez P, Mannoni P, Mawas C, Hercend T, Sebahoun G, Carcassonne Y . High-dose recombinant interleukin-2 and acute myeloid leukaemias in relapse Blood 1991 78: 2182–2187
Foa R, Meloni G, Tosti S, Novarino A, Fenu S, Gavosto F, Mandelli F . Treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia patients with recombinant interleukin-2: a pilot study Br J Haematol 1991 77: 491–496
Wiernik PH, Dutcher JP, Todd M, Caliendo G, Benson L . Polyethylene glycolated interleukin-2 as maintenance therapy for acute myelogenous leukemia in second remission Am J Hematol 1994 47: 41–44
Bergmann L, Heil G, Kolbe K, Lengfelder E, Puzicha E, Martin H, Lohmeyer J, Mitrou PS, Hoelzer D . Interleukin-2 bolus infusion as late consolidation therapy in 2nd remission of acute myeloblastic leukemia Leuk Lymphoma 1995 16: 271–279
Mier JW, Aroson FR, Numerof RP, Vachino G, Atkins MB . Toxicity of immunotherapy with interleukin-2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells Pathol Immunopathol Res 1988 7: 459–476
Thomson JA, Lee DJ, Lindgren CG, Benz LA, Collins C, Levitt D, Fefer A . Influence of dose and duration of infusion of Interleukin-2 on toxicity and immunomodulation J Clin Oncol 1988 6: 669–678
Raab C, Weidmann E, Schmidt A, Bergmann L, Badenhoop K, Usadel KH, Haak T . The effects of interleukin-2 treatment on endothelin and the activation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis Clin Endocrinol 1999 50: 37–44
Umeuchi M, Makino T, Arisawa M, Izumi S, Saito S, Nozawa S . The effect of interleukin-2 on the release of gonadotropin and prolactin in vivo and in vitro Endocr J 1994 41: 547–551
Klempner MS, Noring R, Mier JW, Atkins MB . An acquired chemotactic defect in neutrophils from patients receiving interleukin-2 immunotherapy N Engl J Med 1990 322: 959–965
Meloni G, Foa R, Vignetti M, Guarini A, Fenu S, Tosti S, Tos AG, Mandelli F . Interleukin-2 may induce prolonged remission in advanced acute myelogenous leukemia Blood 1994 84: 2158–2163
Meloni G, Vignetti M, Andrizzi C, Capria S, Foa R, Mandelli F . Interleukin-2 for the treatment of advanced acute myelogenous leukemia patients with limited disease: update experience with 20 cases Leuk Lymphoma 1996 21: 429–435
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by FIRC, MURST 40% and ROMAIL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meloni, G., Trisolini, S., Capria, S. et al. How long can we give interleukin-2? Clinical and immunological evaluation of AML patients after 10 or more years of IL2 administration. Leukemia 16, 2016–2018 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402566
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402566
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Optimal Therapy for Adult Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Complete Remission
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2014)
-
Fine-tuning anti-tumor immunotherapies via stochastic simulations
BMC Bioinformatics (2012)
-
Lytic activity against primary AML cells is stimulated in vitro by an autologous whole cell vaccine expressing IL-2 and CD80
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2010)
-
Cytotoxic chemotherapy administered to two patients with partially refractory leukaemia while receiving intensive care treatment
Supportive Care in Cancer (2004)
-
Pretransplant minimal residual disease level predicts clinical outcome in patients with acute myeloid leukemia receiving high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation
Leukemia (2003)