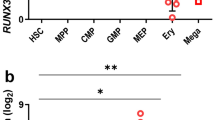
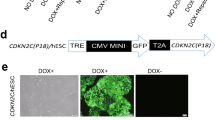
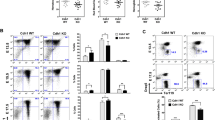
Abstract
The biological activity of p53 in IW32 erythroleukemia cells was investigated. IW32 cells had no detectable levels of p53 mRNA and protein expression. By transfecting a temperature- sensitive mutant p53 cDNA, tsp53val135, into the cells, we have established several clones stably expressing the mutant p53 allele. At permissive temperature, these p53 transfectants were arrested in G1 phase and underwent apoptosis. Moreover, differentiation along the erythroid pathway was observed as evidenced by increased benzidine staining and mRNA expression of β-globin and the erythroid-specific δ-aminolevulinic acid synthase (ALAS-E). Treatment of cells with protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor vanadate blocked the p53-induced differentiation, but not that of cell death or growth arrest. Increased protein tyrosine phosphatase activity as well as mRNA levels of PTPβ2 and PTPε could be observed by wild-type p53 overexpression. These results indicate that p53 induced multiple phenotypic consequences through separate signal pathways in IW32 erythroleukemia cells, and protein tyrosine phosphatase is required for the induced differentiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pfeifer GP, Holmquist GP . Mutagenesis in the p53 gene Biochim Biophys Acta 1997 1333: M1–M8
Lane DP . p53, guardian of the genome Nature 1992 358: 15–16
Levine AJ . p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division Cell 1997 88: 323–331
Maltzman W, Czyzyk L . UV irradiation stimulates levels of p53 cellular tumor antigen in nontransformed mouse cells Mol Cell Biol 1984 4: 1689–1694
Kuerbitz SJ, Plunkett BS, Walsh WV, Kastan MB . Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 7491–7495
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Craig RW . Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage Cancer Res 1991 51: 6304–6311
Woo RA, McLure KG, Lees-Miller SP, Rancourt DE, Lee PW . DNA-dependent protein kinase acts upstream of p53 in response to DNA damage Nature 1998 394: 700–704
Nakagawa K, Taya Y, Tamai K, Yamaizumi M . Requirement of ATM in phosphorylation of the human p53 protein at serine 15 following DNA double-strand breaks Mol Cell Biol 1999 19: 2828–2834
Linke SP, Clarkin KC, Leonardo AD, Tsou A, Wahl GM . A reversible, p53-dependent G0/G1 cell cycle arrest induced by ribonucleotide depletion in the absence of detectable DNA damage Genes Dev 1996 10: 934–947
Cross SM, Sanchez CA, Morgan CA, Schimke MK, Ramel S, Idzerda RL, Raskind WH, Reid BJ . A p53-dependent mouse spindle checkpoint Science 1995 267: 1353–1356
Almog N, Rotter V . Involvement of p53 in cell differentiation and development Biochim Biophys Acta 1997 1333: F1–F27
Kastan MB, Radin AI, Kuerbitz SJ, Onyekwere O, Wolkow CA, Civin CI, Stone KD, Woo T, Ravindranath Y, Craig RW . Levels of p53 protein increase with maturation in human hematopoietic cells Cancer Res 1991 51: 4279–4286
Feinstein E, Gale RP, Reed J, Canaani E . Expression of the normal p53 gene induces differentiation of K562 cells Oncogene 1992 7: 1853–1857
Soddu S, Blandino G, Citro G, Scardigli R, Piaggio G, Ferber A, Calabretta B, Sacchi A . Wild-type p53 gene expression induces granulocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells Blood 1994 83: 2230–2237
Johnson P, Chung S, Benchimol S . Growth suppression of Friend virus-transformed erythroleukemia cells by p53 protein is accompanied by hemoglobin production and is sensitive to erythropoietin Mol Cell Biol 1993 13: 1456–1463
Poluha W, Schonhoff CM, Harrington KS, Lachyankar MB, Crosbie NE, Bulseco DA, Ross AH . A novel, nerve growth factor-activated pathway involving nitric oxide, p53 and p21WAF1 regulates neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells J Biol Chem 1997 272: 24002–24007
Lang D, Miknyoczki SJ, Huang L, Ruggeri BA . Stable reintroduction of wild-type p53 (MTmp53ts) causes the induction of apoptosis and neuroendocrine-like differentiation in human ductal pancreatic carcinoma cells Oncogene 1998 16: 1593–1602
Eizenberg O, Faber-Elman A, Gottlieb E, Oren M, Rotter V, Schwartz M . p53 plays a regulatory role in differentiation and apoptosis of central nervous system-associated cells Mol Cell Biol 1996 16: 5178–5185
Soddu S, Blandino G, Scardigli R, Coen S, Marchetti A, Rizzo MG, Bossi G, Cimino L, Crescenzi M, Sacchi A . Interference with p53 protein inhibits hematopoietic and muscle differentiation J Cell Biol 1996 134: 193–204
Tamir Y, Bengal E . p53 protein is activated during muscle differentiation and participates with MyoD in the transcription of muscle creatine kinase gene Oncogene 1998 17: 347–356
Donehower LA, Harvey M, Slagle BL, McArthur MJ, Montgomery CA Jr, Butel JS, Bradley A . Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours Nature 1992 356: 215–221
Cho J, Donehowe LA . p53 in embryonic development: maintaining a fine balance Cell Mol Life Sci 1999 55: 38–47
Pan H, Griep AE . Altered cell cycle regulation in the lens of HPV-16 E6 or E7 transgenic mice: implications for tumor suppressor gene function in development Genes Dev 1994 8: 1285–1299
Pan H, Griep AE . Temporally distinct patterns of p53-dependent and p53-independent apoptosis during mouse lens development Genes Dev 1995 9: 2157–2169
Gottlieb E, Oren M . p53 facilitates pRb cleavage in IL-3-deprived cells: novel pro-apoptotic activity of p53 EMBO J 1998 17: 3587–3596
Yonish-Rouach E, Resnitzky D, Lotem J, Sachs L, Kimchi A, Oren M . Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6 Nature 1991 352: 345–347
Helps NR, Barker HM, Elledge SJ, Cohen PTW . Protein phosphatase 1 interacts with p53BP2, a protein which binds to the tumour suppressor p53 FEBS Lett 1995 377: 295–300
Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, Sakaguchi K, Shen S, Mercer WE, Vande Woude G F, O'Connor PM, Appella E . Wip1, a novel human protein phosphatase that is induced in response to ionizing radiation in a p53-dependent manner Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 6048–6053
Okamoto K, Kamibayashi C, Serrano M, Prives C, Mumby MC, Beach D . p53-dependent association between cyclin G and the B subunit of protein phosphatase 2A Mol Cell Biol 1996 16: 6593–6602
Kume T, Tsuneizumi K, Watanabe T, Thomas ML, Oishi M . Induction of specific protein tyrosine phosphatase transcripts during differentiation of mouse erythroleukemia cells J Biol Chem 1996 269: 4709–4712
Kume T, Watanabe T, Sanokawo R, Chida D, Nakamura T, Oishi M . Expression of the protein tyrosine phosphatase β2 gene in mouse erythroleukemia cells induces terminal erythroid differentiation J Biol Chem 1996 271: 30916–30921
LaMontagne KR Jr, Hannon G, Tonks NK . Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B suppresses p210 bcr-abl-induced transformation of rat-1 fibroblasts and promotes differentiation of K562 cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 14094–14099
Aoki N, Yamaguchi-Aoki Y, Ullrich A . The novel protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTP20 is a positive regulator of PC12 cell neuronal differentiation J Biol Chem 1996 271: 29422–29426
Wang MC, Liu JH, Wang FF . Protein tyrosine phosphatase-dependent activation of β-globin and δ-aminolevulinic acid synthase genes in the camptothecin-induced IW32 erythroleukemia cell differentiation Mol Pharmacol 1997 51: 558–566
Michalovitz D, Halevy O, Oren M . Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53 Cell 1990 62: 671–680
Choppin J, Lacombe C, Casadevall N, Muller O, Tambourin P, Varet B . Characterization of erythropoietin produced by IW32 murine erythroleukemia cells Blood 1984 64: 341–347
Orkin SH, Harosi FI, Leder P . Differentiation in erythroleukemic cells and their somatic hybrids Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1975 72: 98–102
El-Deiry WS, Tokono T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression Cell 1993 75: 817–825
Miyashita T, Reed JC . Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activartor of the human bax gene Cell 1995 80: 293–299
Ronen D, Schwartz D, Teitz Y, Goldfinger N, Rotter V . Induction of HL-60 cells to undergo apoptosis is determined by high levels of wild-type p53 protein whereas differentiation of the cells is mediated by lower p53 levels Cell Growth Differ 1996 7: 21–30
Ehinger M, Bergh G, Johnsson E, Gullberg U, Olsson I . The tumor suppressor gene p53 can mediate transforming the growth factor β1-induced differentiation of leukemic cells independently of activation of the retinoblastoma protein Cell Growth Differ 1997 8: 1127–1137
Ehinger M, Bergh G, Johnsson E, Baldetorp B, Olsson I, Gullberg U . p53-dependent and -independent differentiation of leukemic U-937 cells: relationship to cell cycle control Exp Hematol 1998 26: 1043–1052
Friedman SL, Shaulian E, Littlewood T, Resnitzky D, Oren M . Resistance to p53-mediated growth arrest and apoptosis in Hep 3B hepatoma cells Oncogene 1997 15: 63–70
Giaccia AJ, Kastan MB . The complexity of p53 modulation: emerging patterns from divergent signals Genes Dev 1998 12: 2973–2983
Tanuma N, Nakamura K, Kikuchi K . Distinct promoters control transmembrane and cytosolic protein tyrosine phosphatase ε expression during macrophage differentiation Eur J Biochem 1999 259: 46–54
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr M Oren (Weizmann Institute, Israel) for kindly providing us with the tsp53val135 cDNA. This work was supported by Grants NSC 88-2316-B010-022-M46 and NSC 89–2316-B010-017-M16 from National Science Council, Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, PP., Wang, FF. Induction of IW32 erythroleukemia cell differentiation by p53 is dependent on protein tyrosine phosphatase. Leukemia 14, 1292–1300 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401823
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401823
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Correlation analysis of two-dimensional gel electrophoretic protein patterns and biological variables
BMC Bioinformatics (2006)
-
Mouse DDA3 gene is a direct transcriptional target of p53 and p73
Oncogene (2002)
-
Germ-line deletion of p53 reveals a multistage tumor progression in spi-1/PU.1 transgenic proerythroblasts
Oncogene (2001)