Abstract
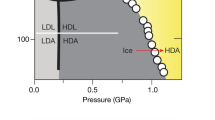
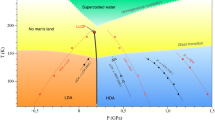
There has been considerable interest in the structure of liquid water at low temperatures and high pressure following the discovery of the high-density amorphous (HDA) phase of ice Ih (ref. 1). HDA ice forms at a pressure close to the extrapolated melting curve of ice, leading to the suggestion that it may have structure similar to that of dense water. On annealing, HDA ice transforms into a low-density amorphous (LDA) phase with a distinct phase boundary2,3. Extrapolation of thermodynamic data along the HDA–LDA coexistence line into the liquid region has led to the hypothesis that there might exist a second critical point for water and the speculation that liquid water is mixture of two distinct structures with different densities4,5. Here we critically examine this hypothesis. We use quasi-harmonic lattice-dynamics calculations to show that the amorphization mechanism in ice Ih changes from thermodynamic melting for T > 162 K to mechanical melting at lower temperatures. The vibrational spectra of ice Ih, LDA ice and quenched water also indicate a structure for LDA ice that differs from that of the liquid. These results call into question the validity of there being a thermodynamic connection between the amorphous and liquid phases of water.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mishima, O., Calvert, L. D. & Whalley, E. ‘Melting’ ice I at 77 K and 10 kbar: a new method of making amorphous solids. Nature 310, 393–395 (1984).
Mishima, O., Calvert, L. D. & Whalley, E. An apparently first-order transition between two amorphous phases of ice induced by pressure. Nature 314, 76–78 (1985).
Mishima, O. Reversible first-order transition between the two H2O amorphs at 0.2 GPa and 135 K. J. Chem. Phys. 100, 5910–5912 (1994).
Mishima, O. & Stanley, E. H. Decompression-induced melting of ice IV and the liquid–liquid transition in water. Nature 392, 164–168 (1998).
Mishima, O. & Stanley, H. E. The relationship between liquid, supercooled and glassy water. Nature 396, 329–335 (1992).
Shpakov, V. P., Tse, J. S., Belosludov, V. R. & Beloslodov, R. V. Elastic moduli & instability in molecular crystals. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 9, 5853–5865 (1997).
Born, M. & Huang, K. Dynamical Theory of Crystal Lattices (Oxford Univ. Press, London, 1954).
Bruesch, P. Phonons: Theory and Experiments I (Springer, New York, 1982).
Belosludov, R. V., Grochev, E. V., Dyanin, Yu. A. & Belosludov, V. R. in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Natural Gas Hydrate 303–309 (PROGEP, Toulouse, 1996).
Tse, J. S., Shpakov, V. P. & Belosludov, V. R. High-pressure elastic constants of solid krypton from quasi-harmonic lattice-dynamics calculations. Phys. Rev. B 58, 2365–2368 (1998).
Mishima, O. Relationship between melting and amorphization of ice. Nature 384, 546–549 (1996).
Handa, Y. P., Tse, J. S., Klug, D. D. & Whalley, E. Pressure-induced phase transitions in clathrate hydrates. J. Chem. Phys. 94, 623–627 (1991).
Tse, J. S., Klug, D. D., Ripmeester, J. A., Desgreniers, S. & Lagarec, K. The role of non-deformable units in pressure-induced reversible amorphization of clathrasils. Nature 369, 724–727 (1994).
Whalley, E., Klug, D. D. & Handa, Y. P. Entropy of amorphous ice. Nature 342, 782–783 (1989).
Tse, J. S. Mechanical instability in ice Ih: A mechanism for pressure-induced amorphization. J. Chem. Phys. 96, 5482–5487 (1992).
Bellissent-Funel, M. C. Is there a liquid-liquid phase transition in supercooled water? Europhys. Lett. 42, 161–166 (1998).
Floriano, M. A., Whalley, E., Svensson, E. C. & Sears, V. F. Structure of high-density amorphous ice by neutron diffraction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 57, 3062–3064 (1986).
Bosio, L., Johari, G. P. & Teixeira, J. X-ray study of high-density amorphous water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 460–463 (1986).
Bizid, A., Bosio, L., Defrain, A. & Oumezzine, M. Structure of a high-density amorphous water. I. X-ray diffraction. J. Chem. Phys. 87, 2225–2230 (1987).
Bellissent-Funel, M. C., Bosio, L., Hallbrucker, A., Mayer, E. & Sridi-Dorbez, R. X-ray and neutron scattering studies of the structure of hyperquenched glassy water. J. Chem. Phys. 97, 1282–1286 (1992).
Okhulkov, A. V., Demianets, Y. N. & Gorbaty, Y. E. X-ray scattering in liquid water at pressures of up to 7.7 kbar: Test of a fluctuation model. J. Chem. Phys. 100, 1578–1588 (1994).
Tulk, C. A., Klug, D. D., Branderhorst, R., Sharpe, P. & Ripmeester, J. A. Hydrogen bonding in glassy liquid water from Raman spectroscopic studies. J. Chem. Phys. 109, 8478–8484 (1998).
Jorgensen, W. L., Chandrasakhar, J., Madura, R. W., Impey, R. W. & Klein, M. L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 79, 926–936 (1983).
Sprik, M., Impey, R. I. & Klein, M. L. Second order elastic constants for Lennard-Jones solid. Phys. Rev. B 29, 4368–4674 (1984).
Acknowledgements
Inelastic scattering data were acquired at Argonne National Laboratory: these measurements were supported by the US DOE-BES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tse, J., Klug, D., Tulk, C. et al. The mechanisms for pressure-induced amorphization of ice Ih. Nature 400, 647–649 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/23216
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/23216
This article is cited by
-
Absence of amorphous forms when ice is compressed at low temperature
Nature (2019)
-
A twist in the tale of the structure of ice
Nature (2019)
-
Reversible switching between pressure-induced amorphization and thermal-driven recrystallization in VO2(B) nanosheets
Nature Communications (2016)
-
Universal elastic-hardening-driven mechanical instability in α-quartz and quartz homeotypes under pressure
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Vertical and radial profiles in tracheid characteristics along the trunk of Douglas-fir trees with implications for water transport
Trees (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.