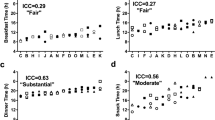
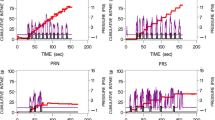
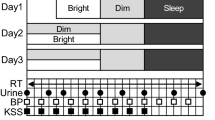
Abstract
RATS allowed food and water ad lib. show a circadian rhythm of drinking and a close association of water intake with eating. One estimate of the proportion of total water taken at night is 78%1. Meals apparently influence the timing and the amount of water drunk. About 57% of the total drinking occurs within 20 min of meals2. A meal introduces solutes into the blood and shifts water from the body fluids into the gut. To compensate for this, between 1 and 1.5 ml. of water would need to be drunk for each gram of food eaten3. Water requirements over a longer term are also determined by the diet4, because of obligatory renal water losses occasioned by solutes from the food.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stellar, E., and Hill, J. H., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 45, 96 (1952).
Kissileff, H. R., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 67, 284 (1969).
Oatley, K., and Toates, F. M., Psychon. Sci., 16, 225 (1969).
Radford, E. P., Amer. J. Physiol., 196, 1098 (1959).
Oatley, K., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 64, 183 (1967).
Oatley, K., Psychon. Sci., 9, 439 (1967).
Fitzsimons, J. T., thesis, Univ. Cambridge (1960).
Fitzsimons, J. T., and Le Magnen, J., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 67, 284 (1969).
Kissileff, H. R., Physiol. Behav., 5, 163 (1970).
Kavanau, J. L., and Rischer, C. E., Science, 161, 1256 (1968).
Morrison, S. D., Physiol. Behav., 3, 75 (1968).
Oatley, K., and Tonge, D. A., Quart. J. Exp. Psychol., 21, 162 (1969).
Minorsky, N., Nonlinear Oscillations (Van Nostrand, Princeton, 1962).
Kakolewski, J. W., and Deaux, E., Amer. J. Physiol., 218, 590 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
OATLEY, K. Dissociation of the Circadian Drinking Pattern from Eating. Nature 229, 494–496 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/229494a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/229494a0
This article is cited by
-
Feeding patterns of endurance athletes
European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology (1981)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.