Abstract
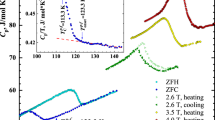
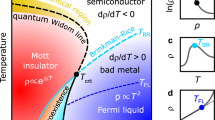
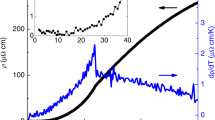
Colossal magnetoresistance1—an unusually large change of resistivity observed in certain materials following application of magnetic field—has been extensively researched in ferromagnetic perovskite manganites. But it remains unclear why the magnetoresistive response increases dramatically when the Curie temperature (T C) is reduced. In these materials, T C varies sensitively with changing chemical pressure; this can be achieved by introducing trivalent rare-earth ions of differing size into the perovskite structure2,3,4, without affecting the valency of the Mn ions. The chemical pressure modifies local structural parameters such as the Mn–O bond distance and Mn–O–Mn bond angle, which directly influence the case of electron hopping between Mn ions (that is, the electronic bandwidth). But these effects cannot satisfactorily explain the dependence of magnetoresistance on T C. Here we demonstrate, using electron microscopy data, that the prototypical (La,Pr,Ca)MnO3 system is electronically phase-separated into a sub-micrometre-scale mixture of insulating regions (with a particular type of charge-ordering) and metallic, ferromagnetic domains. We find that the colossal magnetoresistive effect in low-T C systems can be explained by percolative transport through the ferromagnetic domains; this depends sensitively on the relative spin orientation of adjacent ferromagnetic domains which can be controlled by applied magnetic fields.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin, S. et al. Thousandfold change in resistivity in magnetoresistive La-Ca-Mn-O films. Science 264, 413–415 (1994).
Hwang, H. Y. et al. Lattice effects on the magnetoresistance in doped LaMnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 914–917 (1995).
Coey, J. M. D. et al. Electronic localization in mixed-valence manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3910–3913 (1995).
Khazeni, K. et al. Effect of pressure on the magnetoresistance of single crystal Nd0.5Sr0.366Pb0.14MnO3−δ. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 295–298 (1996).
Zener, C. Interaction between the d-shells in the transition metals II. Ferromagnetic compounds of manganese with perovskite structure. Phys. Rev. 82, 403–405 (1951).
Radaelli, P. G. et al. Structural effects on the magnetic and transport properties of perovskite A1−xA′xMnO3. Phys. Rev. B 56, 8265–8276 (1997).
Cheong, S.-W. & Hwang, H. Y. in Colossal Magnetoresistance Oxides(ed. Tokura, Y.) Ch. 7 (Monogr. in Condensed Matter Sci, Gordon & Breach, London, (1999).
Laukhin, V. et al. Pressure effects on the metal-insulator transition in magnetoresistive manganese perovskites. Phys. Rev. B 56, R10009–R10012 (1997).
Hwang, H. Y. et al. Softening and broadening of the zone boundary magnons in Pr0.63Sr0.37MnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1316–1319 (1998).
Fernandez-Baca, J. A. et al. Evolution of the low-frequency spin dynamics in ferromagnetic manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4012–4015 (1998).
Millis, A. J., Littlewood, P. D. & Shraiman, B. I. Double exchange alone does not explain the resistivity of La1−xSrxMnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 5144–5147 (1995).
Millis, A. J., Shraiman, B. I. & Mueller, R. Dynamic Jahn-Teller effect and colossal magnetoresistance in La1−xSrxMnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 175–178 (1996).
Roder, H., Zang, J. & Bishop, A. R. Lattice effects in the colossal-magnetoresistance manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 1356–1559 (1996).
Zhou, J.-S. & Goodenough, J. B. Phonon-assisted double exchange in perovskite manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2665–2668 (1998).
Tomioka, Y. et al. Magnetic-field-induced metal-insulator phenomena in Pr1−xCaxMnO3with controlled charge-ordering instability. Phys. Rev. B 53, R1689–1692 (1996).
Chen, C. H. & Cheong, S.-W. Commensurate to incommensurate charge ordering and its real-space images in La0.5Ca0.5MnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 4042–4045 (1996).
Mori, S., Chen, C. H. & Cheong, S.-W. Paired and unpaired charge stripes in the ferromagnetic phase of La0.5Ca0.5MnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 3972–3975 (1998).
Chen, C. H., Cheong, S.-W. & Hwang, H. Y. Charge-ordered stripes in La1−xCaxMnO3with x > 0.5. J.Appl. Phys. 81, 4326–4330 (1997).
Hilliard, J. E. in Phase Transformations(ed. Cohen, M.) Ch. 12 (Am. Soc. for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, (1970).
Shklovskii, B. I. & Efros, A. L. Electronic Properties of Doped Semiconductors(Springer, New York, (1984).
Hwang, H. Y. & Cheong, S.-W. in Colossal Magnetoresistance Oxides(ed. Tokura, Y.) Ch. 9 (Monogr. in Condensed Matter Sci., Gordon & Breach, London, (1999).
Emery, V. J. & Kivelson, S. A. Frustrated phase separation and high-temperature superconductivity. Physica C 209, 597–621 (1993).
Nagaev, E. L. Phase separation in degenerate semiconductors and high-temperature superconductors. Phys. Status Solidi B 186, 9–42 (1994).
Goodenough, J. B. & Zhou, J.-S. New forms of phase segregation. Nature 386, 229–230 (1997).
De Teresa, J. M. et al. Evidence for magnetic polarons in the magnetoresistive perovskites. Nature 386, 256–259 (1997).
Yunoki, S. et al. Phase separation in electronic models for manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 845–848 (1998).
Allodi, G. et al. Electronic phase separation in lanthanum manganites: evidence from 55Mn NMR. Phys. Rev. B 56, 6036–6046 (1997).
Kiryukhin, V. et al. An X-ray induced insulator–metal transition in a magnetoresistive manganite. Nature 386, 813–815 (1997).
Asamitsu, A. et al. Current switching of resistive states in mangetoresistive manganites. Nature 388, 50–52 (1997).
Fiebig, M. et al. Visualization of the local insulator-metal transition in Pr0.7Ca0.3MnO3. Science 280, 1925–1928 (1998).
Rodriguez-Martinez, L. M. & Attfield, J. P. Cation disorder and size effects in magnetoresistive manganese oxide perovskites. Phys. Rev. B 54, R15622–R15625 (1996).
Zhao, G. et al. Giant oxygen isotope shift in the magnetoresistive perovskite La1−xCaxMnO3−y. Nature 381, 676–678 (1996).
Shannon, R. D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751–767 (1976).
Acknowledgements
We benefitted from the transport system set up by C. Hess, and we thank M.Gershenson, A. Ruckenstein, G. Kotliar, A. J. Millis and N. Furukawa for discussions. We also thank B. Batlogg for magnetic susceptibility measurements. M.U. and S-W.C. were supported by the NSF, and M.U. acknowledges support from the JPSJ Fellowships for Young Scientists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uehara, M., Mori, S., Chen, C. et al. Percolative phase separation underlies colossal magnetoresistance in mixed-valent manganites. Nature 399, 560–563 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/21142
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/21142
This article is cited by
-
Tailoring of magnetism & electron transport of manganate thin films by controlling the Mn–O–Mn bond angles via strain engineering
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Effect of heterointerfaces on the magnetic and electrical properties of (La0.7Sr0.3MnO3)0.5:NiO0.5 nanocomposite thin films
Applied Physics A (2023)
-
Temperature-dependent magnetic and electrical behavior in the La0.50Pr0.50Mn0.8Co0.2O3 perovskite
Emergent Materials (2023)
-
Non-volatile electric-field control of inversion symmetry
Nature Materials (2023)
-
Deciphering the phase transition-induced ultrahigh piezoresponse in (K,Na)NbO3-based piezoceramics
Nature Communications (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.