Abstract
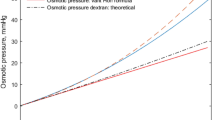
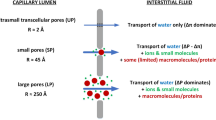
THE passive permeability of kidney slices may be expressed in terms of the equivalent pore radius. The present work is concerned with measurement of this parameter for kidney slices from the amphibian, Necturus maculosus, both under normal conditions, and as affected by the action of anti-diuretic hormone and calcium. Measurements have been made by the method of D. A. Goldstein and A. K. Solomon (private communication), which depends on the determination of the external concentration of permeant solute required to prevent water movement into or out of the cell at the instant of immersion in the medium. When the initial rate of change in volume of the cell is zero, the cell is in transient osmotic equilibrium with its environment. As Staverman1 has pointed out, the concentrations required to produce transient osmotic equilibrium are higher for permeant solutes than for impermeant ones. Goldstein and Solomon have shown how these zero -time isotonic concentrations may be related to the equivalent pore radius.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Staverman, A. J., Rec. Trav. Chim., 74, 344 (1951).
Paganelli, C. V., and Solomon, A. K., J. Gen. Physiol., 41, 259 (1957).
Ussing, H. H., “Colston Papers”, 7, 33 (Butterworths Scientific Publications, London, 1954).
Sawyer, W. H., Endocrinol., 66, 112 (1960).
Hays, R. M., Lamdin, E., Maffly, R. H., and Leaf, A., Fed. Proc., 18, 66 (1959).
Fukuda, T., J. Cell. and Comp. Physiol., 7, 301 (1936).
Bozler, E., Amer. J. Physiol., 197, 505 (1959).
Schultz, S. G., and Solomon, A. K., Fourth Ann. Meeting of the Biophysical Society, Abstract F4 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WHITTEMBURY, G., SUGINO, N. & SOLOMON, A. Effect of Anti-Diuretic Hormone and Calcium on the Equivalent Pore Radius of Kidney Slices from Necturus . Nature 187, 699–701 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1038/187699a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/187699a0
This article is cited by
-
An automatic monitoring system for epithelial cell height
Pflügers Archiv (1993)
-
Effect of hydrostatic pressure on ADH induced osmotic water flow in toad bladder
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1982)
-
Osmotic water flow in leaky epithelia
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1979)
-
Cellular aspects of renal sodium transport and cell volume regulation
Kidney International (1976)
-
Effects of magnesium, calcium and lanthanum ions on stomatal oscillations in Avena sativa L.
Planta (1975)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.